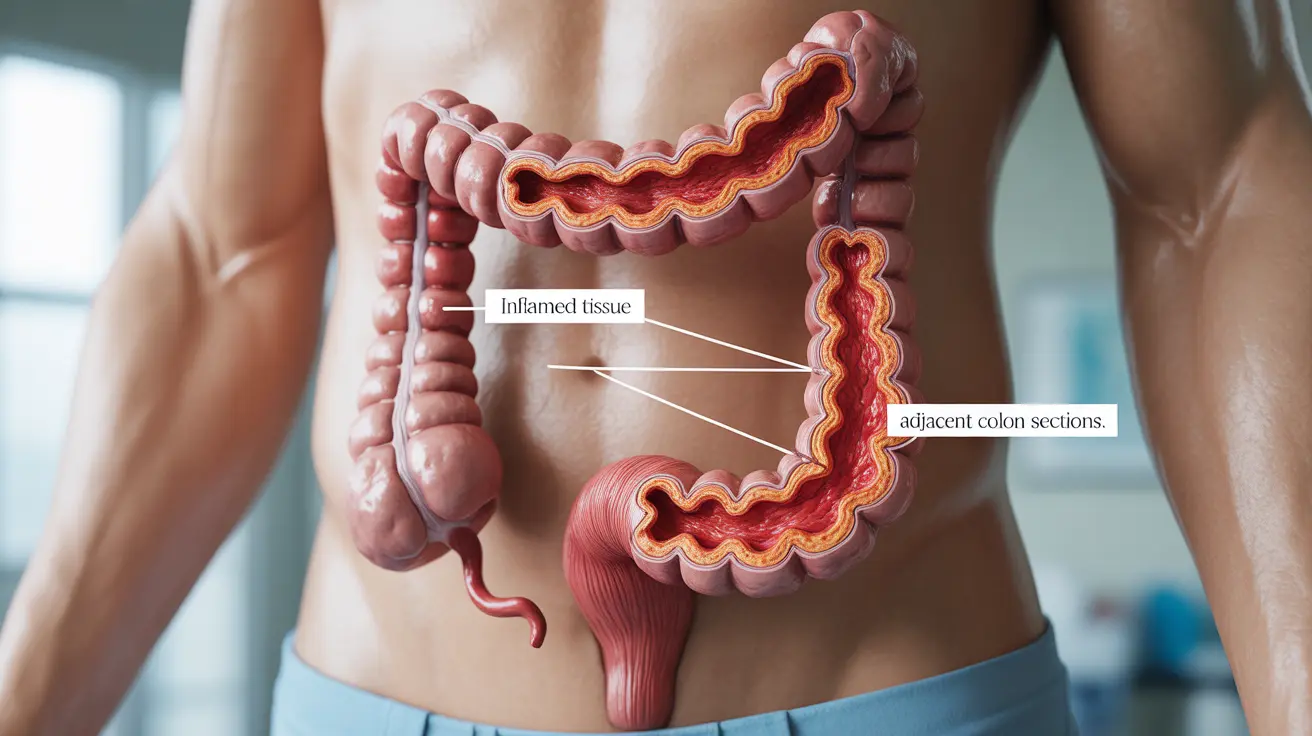
A swollen colon, also known as colitis or colon inflammation, is a concerning condition that can significantly impact your digestive health and overall well-being. Understanding the signs, causes, and available treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively and knowing when to seek medical attention.
While a swollen colon can range from mild to severe, early recognition of symptoms and proper medical intervention can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about managing and treating colon inflammation.
Key Symptoms of a Swollen Colon
Recognizing the symptoms of a swollen colon is crucial for early intervention. Common signs include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea or loose stools
- Blood in stool
- Frequent bowel movements
- Urgency to defecate
- Bloating and gas
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may come and go depending on the underlying cause and severity of the inflammation.
Common Causes of Colon Inflammation
Several factors can contribute to developing a swollen colon:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
This includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can lead to temporary colon inflammation, often resulting in infectious colitis.
Autoimmune Responses
Sometimes the immune system mistakenly attacks the colon's tissue, leading to inflammation and damage.
Other Contributing Factors
- Food allergies or sensitivities
- Certain medications
- Poor dietary habits
- Stress
- Environmental factors
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose a swollen colon:
- Physical examination and medical history review
- Blood tests to check for inflammation markers
- Stool samples to identify infections
- Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy
- Imaging tests (CT scan, MRI)
- Tissue biopsy if necessary
Treatment Approaches and Management
Treatment for a swollen colon typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Medical Treatments
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Antibiotics (if infection is present)
- Immune system suppressants
- Probiotics
- Pain management medications
Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
- Following a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Staying hydrated
- Managing stress levels
- Regular moderate exercise
- Getting adequate rest
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- Severe abdominal pain
- High fever
- Excessive bleeding
- Severe dehydration
- Persistent vomiting
- Signs of bowel obstruction
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of a swollen colon or colitis? The most common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stools, frequent bowel movements, and urgency to defecate. Other symptoms may include fatigue, weight loss, and bloating.
What causes the colon to become swollen or inflamed? A swollen colon can be caused by inflammatory bowel disease, infections, autoimmune responses, food allergies, certain medications, and poor dietary habits. Stress and environmental factors may also contribute to inflammation.
How is a swollen colon diagnosed by doctors? Doctors use various diagnostic tools including physical examinations, blood tests, stool samples, colonoscopy, imaging tests like CT scans or MRI, and sometimes tissue biopsies to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause.
What treatments and lifestyle changes can help reduce colon inflammation? Treatment typically includes medical interventions like anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, or immune suppressants, combined with lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications, stress management, and regular exercise.
When should someone with colon inflammation seek emergency medical care? Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, excessive bleeding, severe dehydration, persistent vomiting, or signs of bowel obstruction.