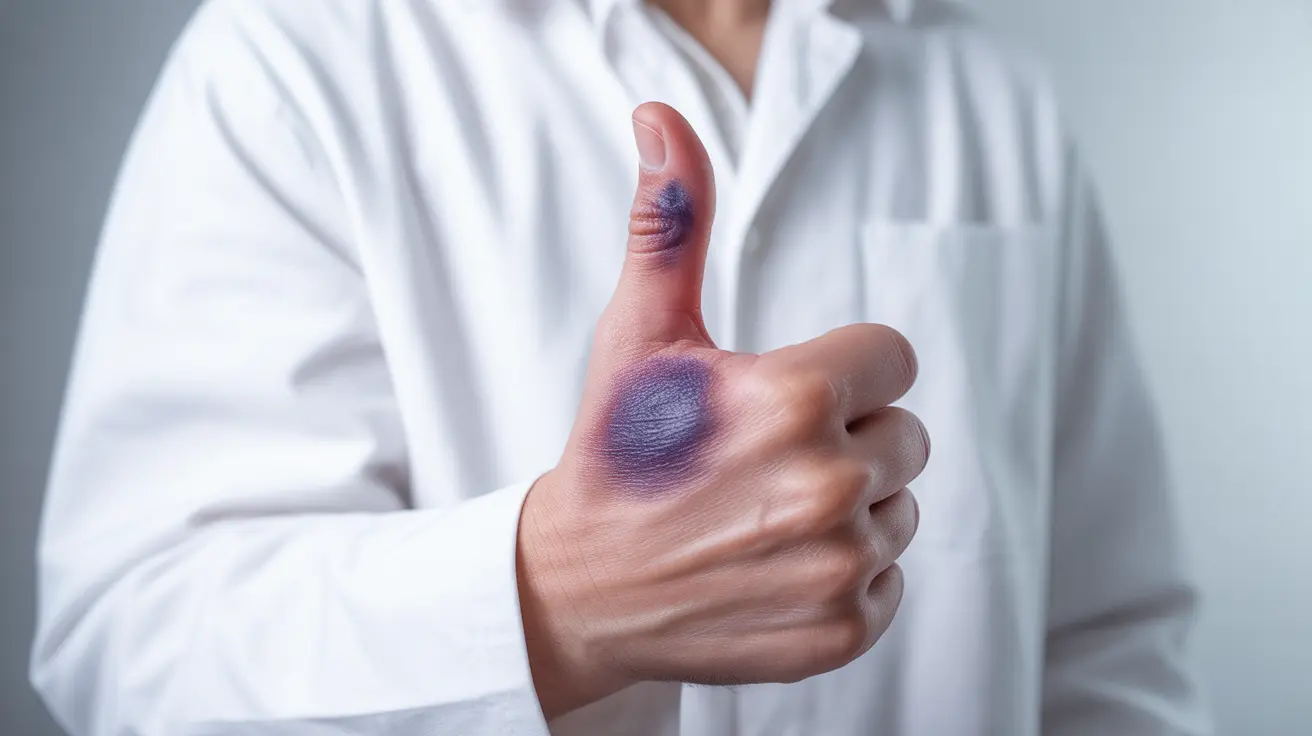
A swollen thumb can significantly impact your daily activities, from gripping objects to typing on a keyboard. Whether the swelling developed suddenly after an injury or gradually over time, understanding the underlying causes and appropriate treatment options is essential for proper management and recovery.
Thumb swelling can result from various conditions ranging from minor injuries to chronic inflammatory diseases. While some cases resolve with simple home remedies, others may require professional medical attention to prevent complications and restore full function to this crucial digit.
Common Causes of Thumb Swelling
Understanding what causes a swollen thumb is the first step toward effective treatment. The underlying cause often determines both the severity of symptoms and the most appropriate therapeutic approach.
Acute Injuries and Trauma
Sudden thumb swelling frequently results from direct trauma or injury. Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can cause sprains, strains, or fractures that lead to immediate inflammation. A sprained thumb typically involves damage to the ligaments connecting the thumb bones, while fractures may affect any of the thumb's three bones.
Signs of acute injury include sudden onset of pain, visible deformity, inability to move the thumb normally, and rapid swelling development. The skin may also appear bruised or discolored around the affected area.
Arthritis and Joint Disorders
Various forms of arthritis commonly affect the thumb joints, particularly the carpometacarpal joint at the base of the thumb. Osteoarthritis develops from wear and tear over time, while rheumatoid arthritis involves autoimmune inflammation that can affect multiple joints simultaneously.
Arthritis-related thumb swelling typically develops gradually and may be accompanied by stiffness, especially in the morning, reduced range of motion, and a grinding sensation during movement.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Bacterial infections can cause significant thumb swelling, particularly around the nail bed or following cuts or puncture wounds. These infections may spread rapidly and cause severe pain, warmth, and redness in addition to swelling.
Other inflammatory conditions, such as tendonitis or trigger thumb, can also result in swelling along with pain during specific movements or when gripping objects.
Home Treatment and Pain Management Strategies
Many cases of thumb swelling respond well to conservative home treatment, particularly when the underlying cause is mild trauma or overuse. However, proper technique and timing are crucial for optimal results.
Immediate Care with RICE Protocol
The RICE method remains a cornerstone of acute injury management. Rest involves avoiding activities that worsen pain or swelling, while ice application for 15-20 minutes several times daily can reduce inflammation and numb pain.
Compression using an elastic bandage or thumb splint provides support and limits swelling, but should not be so tight as to restrict blood circulation. Elevation of the affected hand above heart level when possible can also help reduce fluid accumulation.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can effectively reduce both pain and swelling. These medications work best when taken consistently as directed rather than only when pain becomes severe.
Topical anti-inflammatory creams may provide localized relief with fewer systemic side effects, making them suitable for people who cannot tolerate oral medications.
Gentle Movement and Stretching
Once acute pain subsides, gentle range-of-motion exercises can prevent stiffness and maintain thumb function. Simple movements like touching the thumb to each fingertip or making circular motions can promote healing and prevent joint adhesions.
Professional Treatment for Chronic Conditions
When thumb swelling results from arthritis or autoimmune conditions, professional medical management becomes essential for long-term joint health and function preservation.
Arthritis Management Approaches
Treatment for arthritis-related thumb swelling typically involves a multi-modal approach. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis to slow joint damage progression, while corticosteroid injections can provide targeted relief for severe inflammation.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining joint mobility and strength while teaching protective techniques to minimize stress on affected joints during daily activities.
Advanced Interventional Options
Severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatment may require more advanced interventions. Joint replacement surgery or fusion procedures can restore function when arthritis has caused significant joint destruction.
Newer treatment options include platelet-rich plasma injections and stem cell therapies, though these remain investigational for many thumb conditions.
Recognizing Emergency Situations
Certain symptoms accompanying thumb swelling warrant immediate medical attention to prevent serious complications or permanent damage.
Signs of Serious Infection
Red streaks extending from the thumb up the arm, fever, or pus discharge indicate a spreading infection that requires urgent antibiotic treatment. Delayed treatment of serious infections can lead to systemic illness or permanent joint damage.
Sudden, severe swelling accompanied by intense pain and inability to move the thumb may suggest a fracture or severe soft tissue injury requiring immediate evaluation and treatment.
Circulation and Nerve Concerns
Numbness, tingling, or color changes in the thumb or fingers may indicate compromised blood flow or nerve compression. These symptoms require prompt evaluation to prevent permanent damage to tissues or nerves.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Preventing thumb swelling often involves addressing modifiable risk factors and adopting protective strategies during daily activities.
Ergonomic Considerations
Proper hand positioning during repetitive activities, such as typing or using tools, can reduce stress on thumb joints. Ergonomic keyboards, tool grips, and frequent breaks from repetitive motions help prevent overuse injuries.
Maintaining good overall health through regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management supports the body's natural anti-inflammatory processes and may reduce the risk of developing inflammatory conditions.
Nutritional Support
Anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and phytonutrients may help reduce systemic inflammation. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels and consuming sufficient calcium supports bone health and may slow arthritis progression.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of a swollen thumb and how can I identify them?
The most common causes include acute injuries like sprains or fractures, arthritis (particularly osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis), infections around the nail bed or following cuts, and overuse conditions like tendonitis. Acute injuries typically cause sudden onset of pain and swelling, while arthritis develops gradually with morning stiffness. Infections present with warmth, redness, and possible pus, while overuse conditions cause pain during specific movements.
How can I reduce swelling and pain in my thumb at home before seeing a doctor?
Apply the RICE protocol: rest the thumb by avoiding aggravating activities, apply ice for 15-20 minutes several times daily, use compression with an elastic bandage or splint without restricting circulation, and elevate your hand above heart level when possible. Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can reduce both pain and inflammation. Gentle range-of-motion exercises may help once acute pain subsides.
What treatment options are available for thumb swelling caused by arthritis or autoimmune diseases?
Treatment includes disease-modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis, corticosteroid injections for severe inflammation, physical therapy to maintain joint function, and protective techniques to reduce joint stress. Advanced options may include joint replacement surgery, fusion procedures, or newer treatments like platelet-rich plasma injections. A rheumatologist can develop a comprehensive treatment plan based on the specific type and severity of arthritis.
When should I seek medical attention for a swollen thumb that might be infected or fractured?
Seek immediate medical care if you notice red streaks extending up your arm, fever, pus discharge, or sudden severe swelling with intense pain and inability to move the thumb. Additionally, numbness, tingling, color changes, or visible deformity require prompt evaluation. Any swelling that worsens despite home treatment or persists beyond a few days should be professionally assessed.
Can changes in diet or lifestyle help prevent or reduce swelling in my thumb?
Yes, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce systemic inflammation. Maintaining adequate vitamin D and calcium intake supports bone health. Lifestyle modifications include using ergonomic tools, taking frequent breaks during repetitive activities, maintaining proper hand positioning, and engaging in regular exercise to support overall joint health and circulation.