While antibiotics are crucial medications that help fight bacterial infections, taking them too frequently or inappropriately can lead to serious health consequences. Understanding the signs of antibiotic overuse is essential for maintaining your health and ensuring these medications remain effective when you truly need them.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key warning signs that may indicate you're taking too many antibiotics, along with the potential health impacts and prevention strategies you need to know.
Common Warning Signs of Antibiotic Overuse
Recognizing the symptoms of excessive antibiotic use is crucial for preventing long-term health complications. Here are the primary warning signs to watch for:
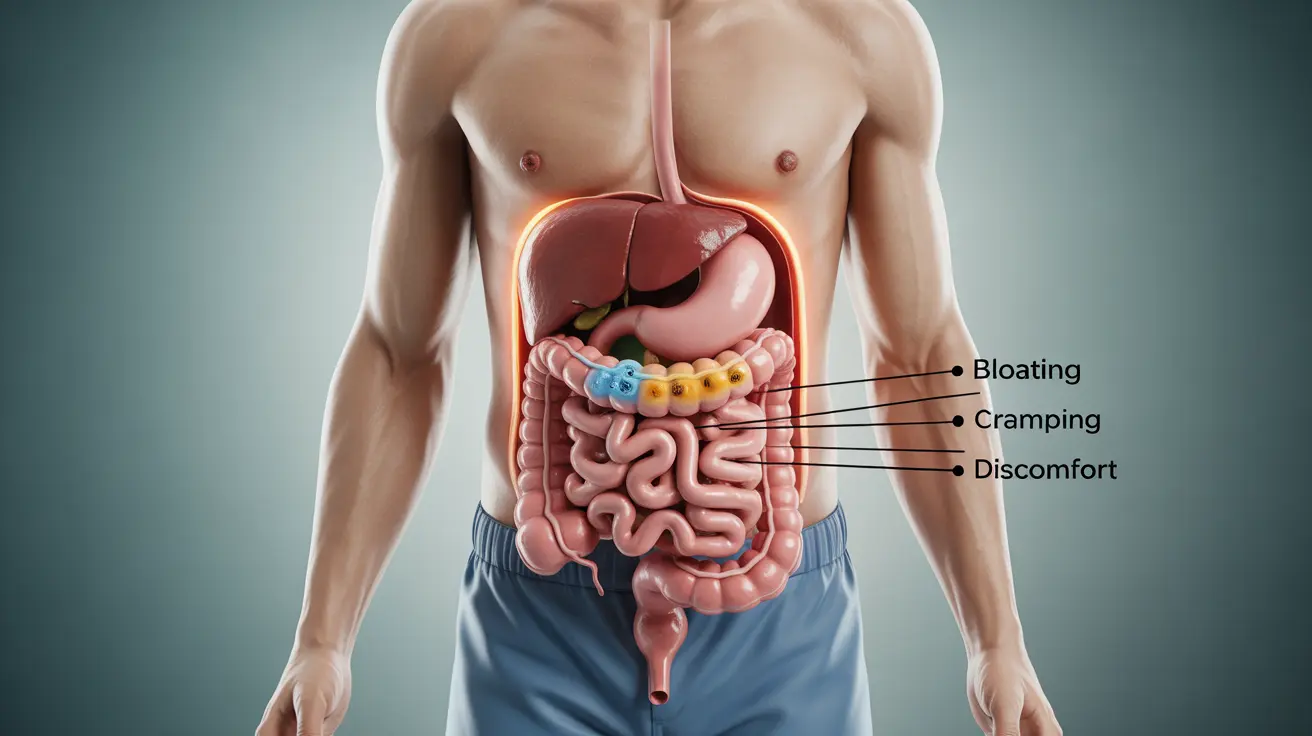
Digestive System Disturbances
The most immediate signs often appear in your digestive system:
- Severe diarrhea
- Stomach pain and cramping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating and gas
Oral and Skin Changes
Antibiotic overuse can manifest through various external symptoms:
- White patches in the mouth (oral thrush)
- Unusual rashes or hives
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight
- Dry, itchy skin
- Fungal infections
Impact on Gut Health and Microbiome
Antibiotics can significantly disrupt your digestive system's delicate balance. These medications don't discriminate between harmful and beneficial bacteria, leading to:
- Reduced diversity of gut bacteria
- Weakened immune system function
- Increased risk of gastrointestinal infections
- Potential nutrient absorption issues
- Long-term digestive sensitivity
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance
One of the most serious consequences of antibiotic overuse is the development of antibiotic resistance. This occurs when bacteria evolve to survive the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Signs of Developing Resistance
Watch for these indicators that might suggest developing antibiotic resistance:
- Recurring infections
- Infections that don't respond to standard treatments
- Longer recovery times from bacterial infections
- Need for stronger or multiple antibiotics to treat infections
Prevention and Protection Strategies
To minimize the risks associated with antibiotic overuse, consider these important steps:
- Only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Complete the full prescribed course of antibiotics
- Never use leftover antibiotics from previous prescriptions
- Consider probiotic supplementation during and after antibiotic treatment
- Maintain good hygiene practices to prevent infections
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms that indicate I am taking too many antibiotics?
Common symptoms include severe diarrhea, stomach pain, recurring yeast infections, oral thrush, skin rashes, and increased susceptibility to infections. If you experience these symptoms, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
How does overusing antibiotics affect my digestive system and gut health?
Antibiotic overuse can severely disrupt your gut microbiome, leading to digestive issues, nutrient absorption problems, and a weakened immune system. This disruption can cause chronic diarrhea, bloating, and increased susceptibility to gut infections.
Can taking too many antibiotics cause antibiotic resistance and how does that impact future infections?
Yes, frequent antibiotic use can lead to bacterial resistance, making future infections harder to treat. This means you might need stronger antibiotics or longer treatment periods, and some infections may become resistant to multiple antibiotics.
What side effects and allergic reactions should I watch for when using antibiotics?
Watch for severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing, severe rashes, or swelling. Other concerning side effects include severe diarrhea, intense stomach pain, fever, and signs of liver problems like yellowing skin or eyes.
How can I prevent complications and secondary infections caused by excessive antibiotic use?
Take probiotics during and after antibiotic treatment, only use antibiotics when prescribed, complete the full course as directed, maintain good hygiene, and focus on supporting your immune system through proper diet and lifestyle habits.