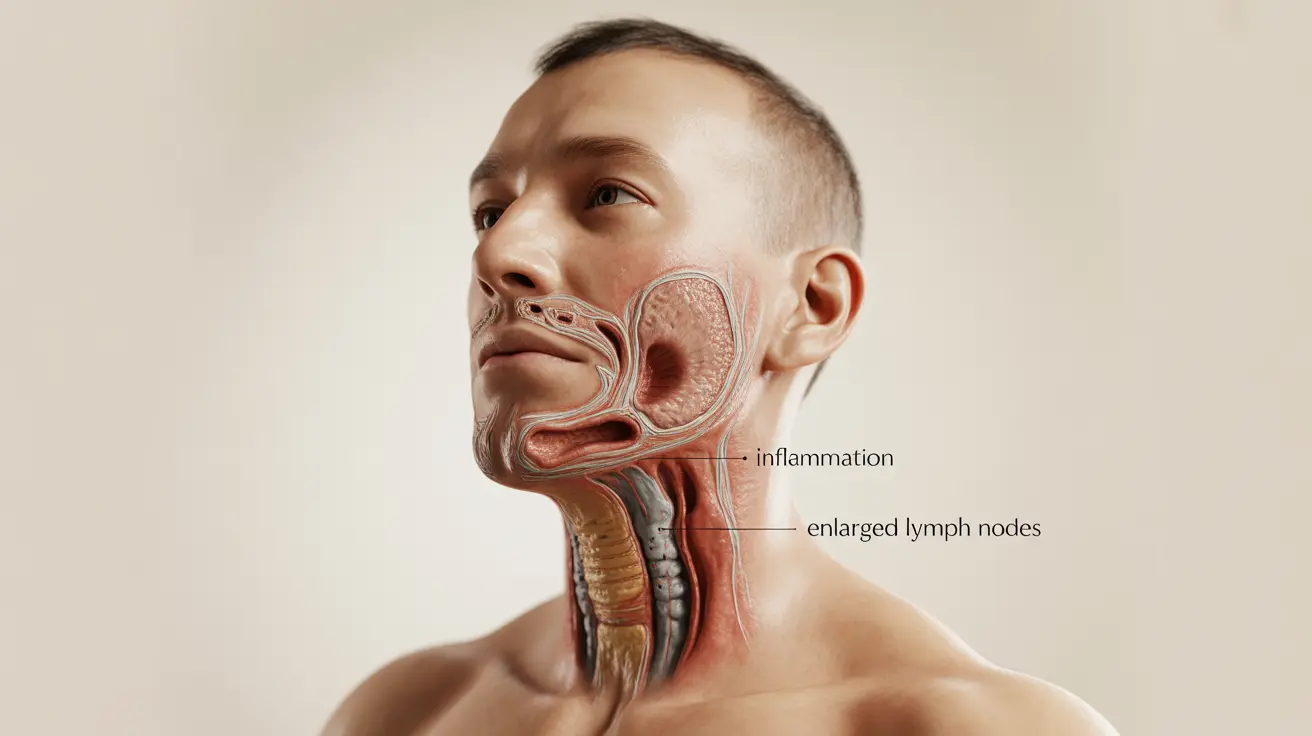
Tuberculosis (TB) affecting the throat, also known as laryngeal tuberculosis, is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. While less common than pulmonary TB, throat tuberculosis can significantly impact a person's quality of life and requires specific treatment approaches. Understanding the symptoms and seeking early medical care is crucial for successful treatment.
This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of throat tuberculosis, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, helping you better understand this condition and when to seek medical help.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Throat Tuberculosis
Throat tuberculosis presents with several distinctive symptoms that may develop gradually over time:
- Persistent hoarseness or voice changes
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic sore throat
- Pain while speaking
- Persistent cough
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
These symptoms may vary in severity and can sometimes be mistaken for other throat conditions, making proper medical evaluation essential.
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding who is at higher risk for developing throat tuberculosis is crucial for early detection and prevention:
- People with weakened immune systems
- HIV-positive individuals
- Those with direct exposure to active TB patients
- Healthcare workers
- People living in crowded conditions
- Individuals from regions with high TB prevalence
The primary cause is the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria spreading from the lungs to the throat area, though direct infection of the throat can also occur in some cases.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing throat tuberculosis requires a comprehensive medical evaluation:
Physical Examination
Doctors will conduct a thorough examination of the throat and neck area, looking for visible signs of infection or inflammation.
Diagnostic Tests
- Laryngoscopy
- Throat swab cultures
- Sputum analysis
- Chest X-rays
- Blood tests
- Tuberculin skin test
- Biopsy of affected tissue (when necessary)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for throat tuberculosis typically involves:
Medication Protocol
A combination of anti-tuberculosis medications is prescribed, usually including:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Ethambutol
- Pyrazinamide
Treatment duration typically lasts 6-12 months, depending on the severity of the infection and response to medication.
Supportive Care
Additional measures may include:
- Voice rest
- Throat lozenges for comfort
- Adequate hydration
- Nutritional support
- Regular medical monitoring
Prevention and Management
Preventing the spread of throat tuberculosis involves several key measures:
- Regular screening for those at high risk
- Proper ventilation in living and working spaces
- Using protective masks when necessary
- Completing the full course of prescribed medications
- Following infection control guidelines
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of tuberculosis in the throat or laryngeal tuberculosis?
Common symptoms include persistent hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, chronic sore throat, voice changes, and pain while speaking. Patients may also experience coughing, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss.
How is tuberculosis in the throat diagnosed and distinguished from other throat infections?
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, laryngoscopy, throat cultures, sputum analysis, chest X-rays, and sometimes tissue biopsy. Blood tests and tuberculin skin tests may also be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What causes tuberculosis to affect the throat, and who is at higher risk?
Throat tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. Those at higher risk include people with weakened immune systems, HIV-positive individuals, healthcare workers, and people living in areas with high TB prevalence.
How is throat tuberculosis treated and how long does the treatment usually last?
Treatment involves a combination of anti-tuberculosis medications taken for 6-12 months. The standard regimen includes isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide, along with supportive care measures.
Can tuberculosis in the throat cause hoarseness and difficulty swallowing?
Yes, hoarseness and difficulty swallowing are common symptoms of throat tuberculosis. These symptoms occur due to inflammation and infection of the laryngeal tissues, affecting normal throat function.