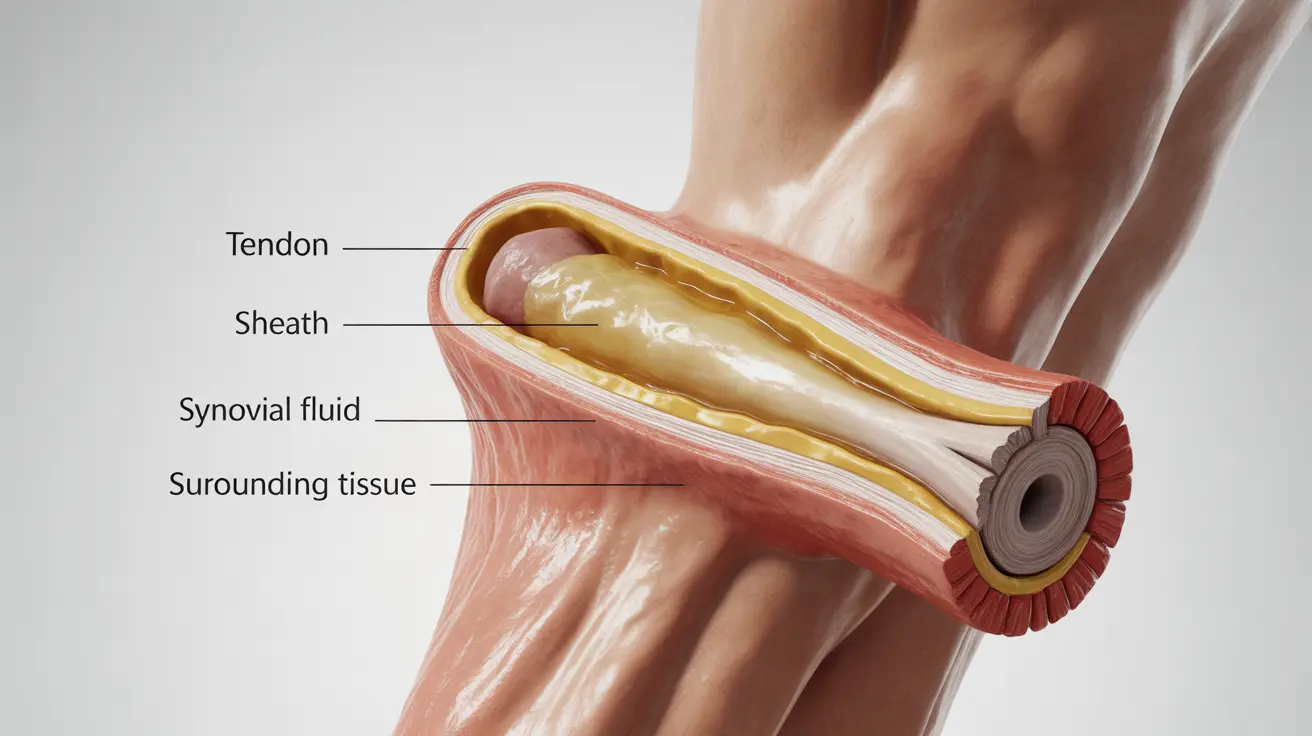
Tendon sheath inflammation, medically known as tenosynovitis, is a painful condition that occurs when the protective covering surrounding your tendons becomes irritated and swollen. This condition commonly affects the wrists, hands, and feet, potentially limiting movement and causing significant discomfort in daily activities. Understanding this condition is crucial for early recognition and proper treatment.
While anyone can develop tendon sheath inflammation, certain factors and activities can increase your risk. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding the Tendon Sheath and Its Function
The tendon sheath is a protective covering filled with synovial fluid that surrounds certain tendons throughout your body. This structure allows tendons to glide smoothly during movement while providing necessary lubrication and protection. When this sheath becomes inflamed, it can lead to pain, restricted movement, and other uncomfortable symptoms.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of tendon sheath inflammation early can help ensure prompt treatment and better outcomes. Common indicators include:
- Pain and tenderness along the affected tendon
- Swelling around the joint or tendon
- Difficulty moving the affected joint
- A crackling sensation when moving the tendon
- Stiffness, particularly in the morning
- Weakness in the affected area
Risk Factors and Common Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of tendon sheath inflammation:
Repetitive Movements
Activities requiring repeated motions, especially in the workplace or during sports, can strain the tendon sheath and lead to inflammation.
Medical Conditions
Certain underlying conditions can increase your risk, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Diabetes
- Infections
- Gout
Injury and Trauma
Direct injury or sudden strain to a tendon can trigger inflammation of the surrounding sheath.
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose tendon sheath inflammation accurately:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI)
- Movement assessments
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options typically progress from conservative measures to more intensive interventions if needed:
Conservative Treatment
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice or heat therapy
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Splinting or bracing
Medical Interventions
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, medical professionals may recommend:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Physical therapy
- Prescription medications
- Surgery (in severe cases)
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps can help reduce your risk of developing tendon sheath inflammation:
- Proper ergonomic setup at work
- Regular breaks during repetitive activities
- Stretching and strengthening exercises
- Maintaining good posture
- Using proper technique during activities
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms of tendon sheath inflammation (tenosynovitis)?
Common symptoms include pain and tenderness along the affected tendon, swelling around joints, difficulty moving the affected area, and a crackling sensation during movement. You may also experience stiffness, particularly in the morning, and weakness in the affected area.
- What causes tenosynovitis and which activities increase the risk?
Tenosynovitis is primarily caused by repetitive movements, overuse, or direct injury. Activities that increase risk include typing, assembly line work, playing musical instruments, and certain sports. Medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes can also contribute to its development.
- How is tenosynovitis diagnosed and what imaging tests are used to examine the tendon sheath?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. Ultrasound is often used as it can show inflammation in real-time, while MRI scans provide detailed images of the tendon and surrounding tissues. Your healthcare provider may also perform movement tests to assess pain and range of motion.
- What treatments are available for inflammation of the tendon sheath and when is surgery needed?
Treatment options range from conservative approaches like rest, ice/heat therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications to medical interventions such as corticosteroid injections and physical therapy. Surgery is typically only considered when conservative treatments fail or in cases of severe, persistent symptoms that significantly impact daily life.
- How can I prevent tenosynovitis, especially if I do repetitive hand or wrist movements?
Prevention strategies include taking regular breaks during repetitive activities, maintaining proper ergonomics, performing stretching exercises, and using correct posture and technique. It's also important to gradually build up intensity in activities and listen to your body's signals to avoid overuse.