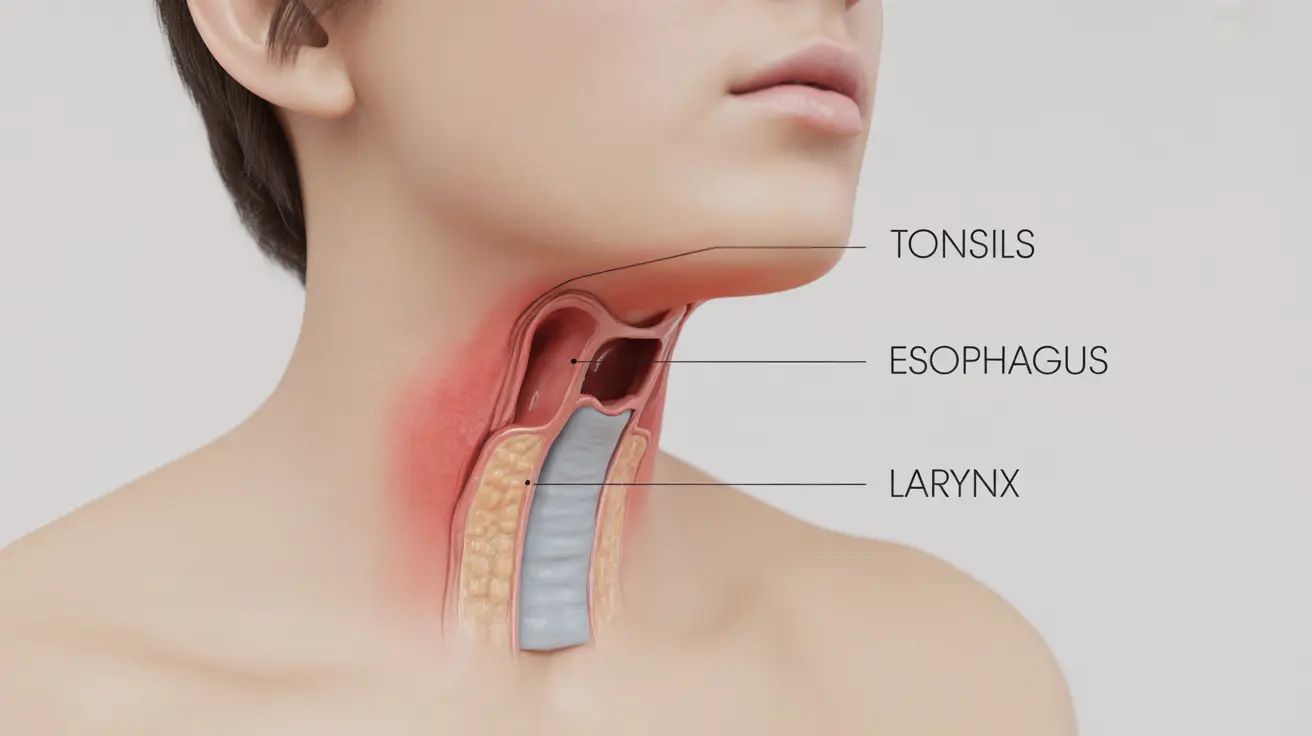
Discovering blood in your throat can be an alarming experience that requires careful attention and often medical evaluation. Throat bleeding can occur for various reasons, ranging from minor irritations to more serious underlying conditions. Understanding the causes, recognizing warning signs, and knowing when to seek medical help is crucial for proper management of this condition.
This comprehensive guide will explore the common causes of throat bleeding, help you identify warning signs, and provide information about diagnosis and treatment options. We'll also discuss important factors that might increase your risk and when immediate medical attention is necessary.
Common Causes of Throat Bleeding
Throat bleeding can stem from several different sources, each requiring specific attention and treatment approaches:
Trauma and Injury
Physical injuries to the throat area can cause bleeding, including:
- Accidental scratches from sharp food
- Hot liquid burns
- External trauma to the neck
- Persistent coughing or throat clearing
Infections and Inflammation
Various infections can lead to throat bleeding:
- Severe strep throat
- Tonsillitis
- Viral infections
- Bacterial infections causing tissue damage
Medical Conditions
Several underlying health conditions may contribute to throat bleeding:
- Esophageal varices
- Throat or esophageal cancer
- Peptic ulcers
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Warning Signs and Emergency Situations
Certain symptoms accompanying throat bleeding warrant immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty breathing
- Large amounts of blood
- Severe chest or throat pain
- Difficulty swallowing
- High fever
- Dizziness or fainting
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers may use various methods to identify the source of throat bleeding:
Physical Examination
The initial assessment typically includes:
- Visual inspection of the throat
- Assessment of vital signs
- Review of medical history
- Discussion of symptoms and their onset
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Further testing may involve:
- Endoscopy
- Imaging studies (CT scan or X-ray)
- Blood tests
- Throat culture if infection is suspected
Treatment Approaches
Treatment varies based on the underlying cause and severity of the bleeding:
Conservative Management
Minor cases might be treated with:
- Rest and voice conservation
- Avoiding irritants
- Gargling with salt water
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
Medical Interventions
More serious cases may require:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Acid-reducing medications
- Blood-clotting medications
- Surgical intervention when necessary
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of throat bleeding and how can I identify them?
The most common causes include trauma from sharp foods, severe infections, chronic coughing, and underlying medical conditions like GERD. You can identify the cause by noting associated symptoms, the amount of bleeding, and when the bleeding occurs.
When should I seek emergency medical care for bleeding in my throat?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, large amounts of blood, severe pain, trouble swallowing, high fever, or feel dizzy or faint. These symptoms may indicate a serious condition requiring urgent care.
How do doctors diagnose the source of blood when I notice bleeding in my throat?
Doctors typically start with a physical examination and medical history review. They may then proceed with diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, imaging studies, blood tests, or throat cultures depending on suspected causes.
What treatments are available for throat bleeding caused by infections or injuries?
Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest and salt water gargles to medical interventions including antibiotics, acid-reducing medications, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause and severity.
Can medications like blood thinners increase the risk of throat bleeding and what should I do about it?
Yes, blood thinners can increase the risk of bleeding, including in the throat. If you're on blood thinners and experience throat bleeding, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Don't stop taking blood thinners without medical consultation, as this could lead to serious complications.