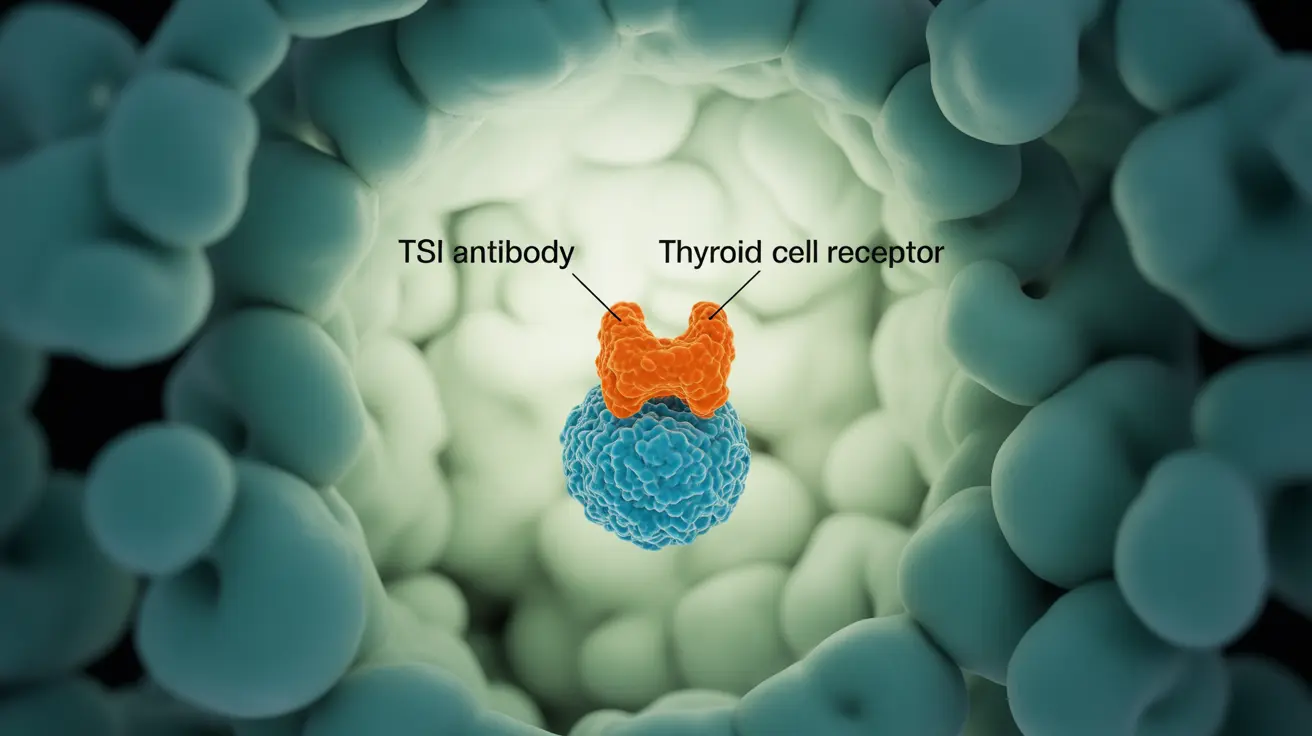
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) plays a crucial role in thyroid function and autoimmune disorders. This specialized antibody can significantly impact thyroid health and is particularly important in diagnosing and monitoring Graves' disease, a common autoimmune thyroid condition.
Understanding TSI's role in thyroid function is essential for both healthcare providers and patients, as it helps guide diagnosis and treatment decisions for thyroid disorders. This comprehensive guide explores what TSI is, how it affects the body, and its significance in thyroid health management.
What Is Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin?
Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin is an antibody produced by the immune system that mimics thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Unlike normal thyroid regulation, TSI can cause the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism. These antibodies bind to thyroid cell receptors, triggering continuous hormone production without normal regulatory controls.
The Role of TSI in Graves' Disease
Graves' disease is the most common condition associated with elevated TSI levels. In this autoimmune disorder, the body produces TSI antibodies that overstimulate the thyroid gland, leading to excessive hormone production. This overproduction can affect multiple body systems and requires careful medical management.
Common Symptoms of High TSI Levels
When TSI levels are elevated, patients may experience various symptoms, including:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Anxiety and nervousness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Heat sensitivity and excessive sweating
- Tremors in hands and fingers
- Sleep difficulties
- Eye problems (Graves' ophthalmopathy)
TSI Testing and Diagnosis
The TSI blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool for identifying Graves' disease and other thyroid disorders. Healthcare providers typically order this test when patients show symptoms of hyperthyroidism or have abnormal results on other thyroid function tests.
Understanding TSI Test Results
TSI test results are typically reported as a percentage of activity compared to normal values. A positive result usually indicates Graves' disease, though the severity of symptoms doesn't always correlate directly with TSI levels. Regular monitoring may be necessary to track disease progression and treatment effectiveness.
Distinguishing TSI from Other Thyroid Antibodies
While TSI is specific to Graves' disease, other thyroid antibodies serve different functions and indicate different conditions. Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and thyroglobulin antibodies are more commonly associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition causing hypothyroidism. Understanding these distinctions helps healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses and choose appropriate treatments.
Treatment Approaches for High TSI Levels
Treatment options for elevated TSI levels and Graves' disease include:
- Antithyroid medications to reduce hormone production
- Radioactive iodine therapy to decrease thyroid function
- Thyroid surgery (thyroidectomy) in severe cases
- Beta-blockers to manage symptoms
- Regular monitoring of thyroid function and TSI levels
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) and how does it affect thyroid function? TSI is an antibody that mimics thyroid-stimulating hormone, binding to thyroid receptors and causing excessive hormone production. This can lead to hyperthyroidism and associated symptoms.
How is the TSI blood test used to diagnose Graves' disease? The TSI blood test measures antibody levels to help confirm a Graves' disease diagnosis. Elevated TSI levels, combined with clinical symptoms and other thyroid function tests, indicate the presence of this autoimmune condition.
What symptoms might indicate high TSI levels or Graves' disease? Common symptoms include rapid heartbeat, anxiety, unexplained weight loss, heat sensitivity, tremors, and eye problems. These symptoms occur due to excessive thyroid hormone production stimulated by TSI.
How does TSI differ from other thyroid antibodies like thyroid peroxidase or thyroglobulin antibodies? TSI specifically stimulates thyroid hormone production and is associated with Graves' disease, while TPO and thyroglobulin antibodies are linked to Hashimoto's thyroiditis and typically indicate thyroid destruction leading to hypothyroidism.
What treatment options are available for Graves' disease linked to elevated TSI levels? Treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, thyroid surgery, and symptom management with beta-blockers. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors and severity of the condition.