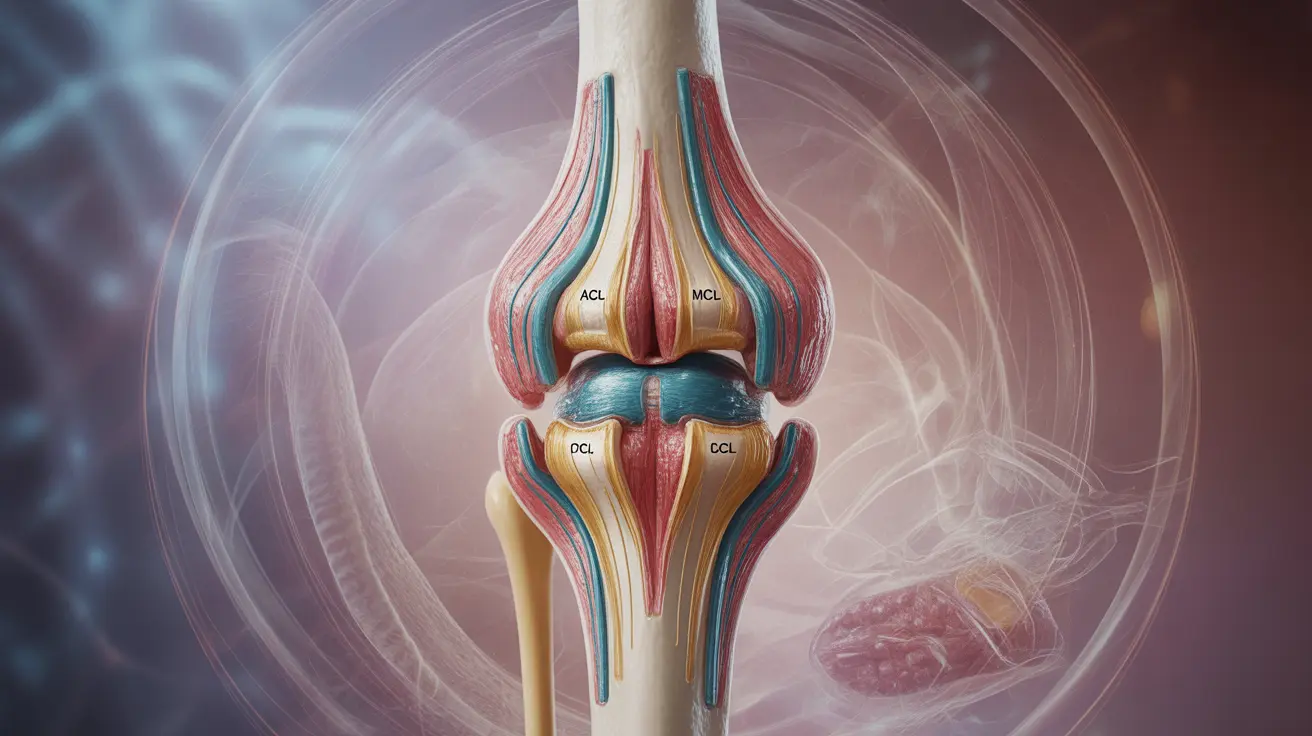
Living with loose ligaments, also known as ligament laxity, can present unique challenges for daily activities and physical movement. This condition occurs when the connective tissues that hold your joints together become more flexible than normal, potentially leading to instability and discomfort. Understanding how to manage and strengthen loose ligaments is crucial for maintaining joint health and preventing potential complications.
Whether you're experiencing symptoms of loose ligaments or have recently been diagnosed with ligament laxity, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the condition and explore effective management strategies, including exercises, treatments, and when to seek professional help.
Understanding Ligament Laxity
Ligament laxity refers to a condition where ligaments, the tough bands of tissue that connect bones and provide joint stability, become looser than normal. This can occur in specific joints or throughout the body, affecting mobility and potentially increasing the risk of joint injuries.
Common Symptoms and Signs
Identifying ligament laxity early can help prevent complications and guide appropriate treatment. Common signs include:
- Frequent joint dislocations or subluxations
- Increased joint flexibility beyond normal range
- Joint pain or discomfort
- Unstable feeling in affected joints
- Clicking or popping sounds during movement
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the underlying causes of ligament laxity is essential for proper management. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
Genetic Factors
Some people are born with naturally looser ligaments due to genetic conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome. These inherited conditions affect collagen production and connective tissue strength.
Physical Factors
Other causes may include:
- Previous injuries or trauma
- Hormonal changes
- Repetitive strain
- Age-related changes
- Pregnancy-related hormonal shifts
Strengthening and Support Strategies
Exercise Recommendations
Proper exercise is crucial for managing ligament laxity. Focus on:
- Low-impact strength training
- Controlled resistance exercises
- Balance and proprioception training
- Core strengthening activities
- Joint stabilization exercises
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help protect your joints:
- Using proper body mechanics
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Wearing supportive footwear
- Using appropriate bracing when needed
- Avoiding activities that cause pain or instability
Treatment Options
Several treatment approaches may help manage ligament laxity:
Conservative Treatments
Initial treatment typically involves non-invasive methods such as physical therapy, targeted exercises, and proper joint protection techniques. These approaches focus on building strength and stability around affected joints.
Medical Interventions
For more severe cases, medical treatments may include:
- Prolotherapy injections
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy
- Bracing or taping
- Pain management techniques
- Surgical intervention in severe cases
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I strengthen muscles to improve stability if I have loose ligaments?
Focus on controlled resistance exercises, emphasizing proper form and gradually increasing intensity. Work with a physical therapist to develop a safe, effective routine that targets the muscles surrounding affected joints. Include exercises that improve proprioception and balance.
What types of exercises are best for tightening or supporting loose ligaments?
The best exercises include isometric strengthening, closed-chain exercises, and stability training. Examples include wall sits, planks, bridge exercises, and controlled resistance training. Always start gradually and avoid exercises that cause pain or joint instability.
Can ligament laxity be caused by genetic conditions, and what symptoms should I watch for?
Yes, genetic conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can cause ligament laxity. Watch for symptoms such as frequent joint dislocations, easy bruising, unusually flexible joints, chronic joint pain, and skin that stretches more than normal. If you notice these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
Is prolotherapy an effective treatment to help tighten or heal loose ligaments?
Prolotherapy can be effective for some individuals with ligament laxity. This treatment involves injecting an irritant solution into affected areas to stimulate the body's natural healing response. Success rates vary, and multiple treatments may be necessary. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine if it's appropriate for your condition.
When should I see a doctor for pain or frequent dislocations caused by ligamentous laxity?
Seek medical attention if you experience frequent joint dislocations, persistent pain, difficulty performing daily activities, or if joint instability significantly impacts your quality of life. Early intervention can help prevent complications and guide appropriate treatment strategies.