When unusual patches appear on your skin, determining whether you're dealing with tinea versicolor or psoriasis can be challenging. These two distinct skin conditions may share some similar appearances, but they have different causes, treatments, and long-term management approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for getting the right diagnosis and appropriate care.
Let's explore the key distinctions between tinea versicolor and psoriasis, helping you better understand their unique characteristics and treatment options.
Understanding the Root Causes
Tinea versicolor and psoriasis emerge from fundamentally different origins. Tinea versicolor is caused by an overgrowth of naturally occurring yeast on the skin, specifically Malassezia furfur. This typically occurs in warm, humid conditions or when someone has oily skin. In contrast, psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system triggers rapid skin cell production, causing cells to build up on the skin's surface.
Distinctive Visual Characteristics
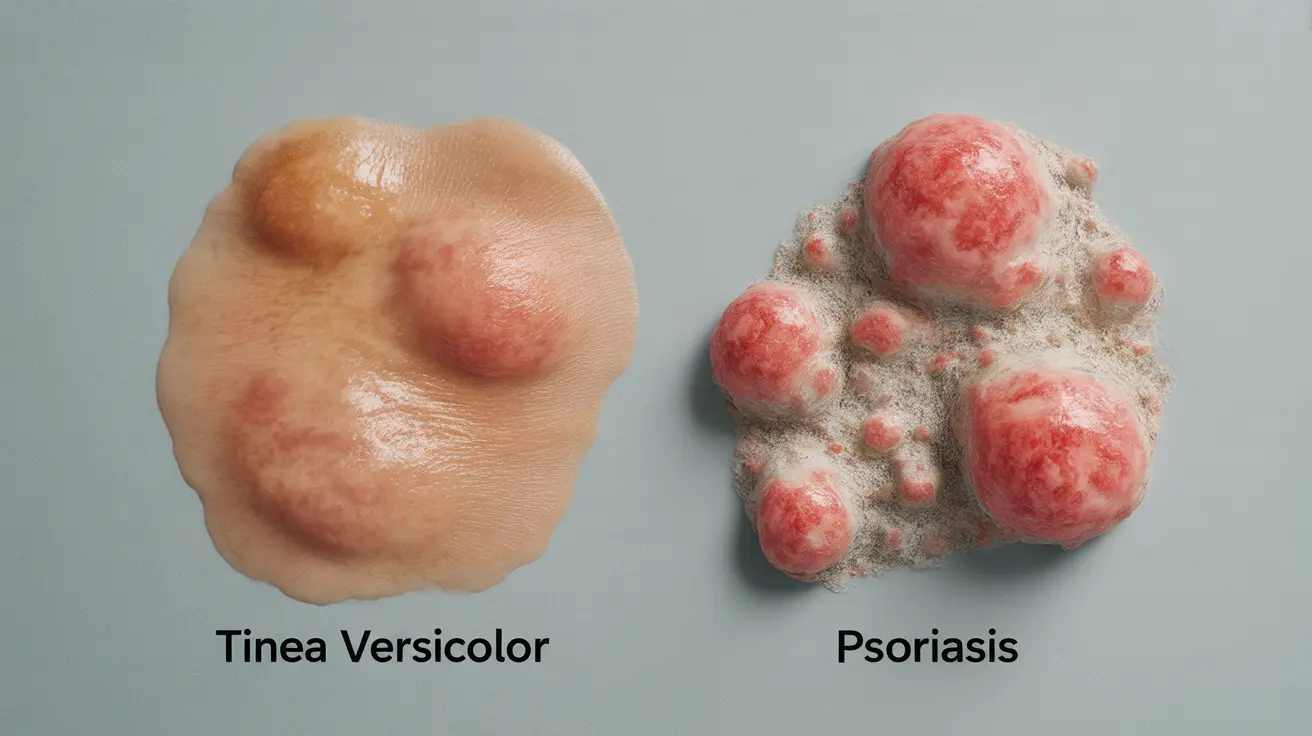
Tinea Versicolor Appearance
Tinea versicolor typically presents as light or dark patches that may be pink, tan, or brown. These patches often have a fine, scaly texture and can be slightly itchy. The condition commonly appears on the chest, back, and shoulders, especially in warm weather.
Psoriasis Appearance
Psoriasis manifests as thick, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. These patches, known as plaques, are often raised and can be quite painful or intensely itchy. Common locations include elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, though they can appear anywhere on the body.
Treatment Approaches
Managing Tinea Versicolor
Treating tinea versicolor typically involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally. Common treatments include:
- Selenium sulfide shampoos
- Over-the-counter antifungal creams
- Prescription-strength antifungal medications
- Oral antifungal pills for severe cases
Addressing Psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment is generally more complex and may include:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogues
- Phototherapy (light treatment)
- Systemic medications
- Biologic drugs for severe cases
Prevention and Long-term Management
Both conditions require different approaches to prevention and management. For tinea versicolor, keeping skin dry, wearing breathable fabrics, and using medicated cleansers can help prevent recurrence. Psoriasis management often involves identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a consistent treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences in causes and symptoms between tinea versicolor and psoriasis?
Tinea versicolor is caused by yeast overgrowth, resulting in discolored patches that can be light or dark. Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition causing thick, red plaques with silvery scales. Tinea versicolor tends to be mildly itchy, while psoriasis can be both itchy and painful.
How can I tell if my red, scaly skin patches are tinea versicolor or psoriasis?
Tinea versicolor patches are usually lighter or darker than surrounding skin, with fine scaling and mild itching, typically on the trunk. Psoriasis patches are raised, red, and covered with thick silvery scales, often appearing on elbows, knees, and scalp.
What treatments work best for tinea versicolor compared to psoriasis?
Tinea versicolor responds well to antifungal treatments, while psoriasis requires anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids or biologics. Tinea versicolor usually clears with simple interventions, whereas psoriasis often needs ongoing management with multiple treatment approaches.
Can tinea versicolor or psoriasis cause changes in skin color, and how long do these changes last after treatment?
Both conditions can cause skin discoloration. Tinea versicolor patches may take several weeks to months to return to normal color after treatment. Psoriasis often leaves temporary discoloration that typically fades once plaques heal, though this can take several months.
How can I prevent tinea versicolor from recurring, and does this apply to psoriasis as well?
Tinea versicolor recurrence can be prevented by maintaining dry skin, using antifungal products periodically, and avoiding excessive heat and humidity. Psoriasis cannot be prevented, but flares can be reduced by identifying and avoiding triggers, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.