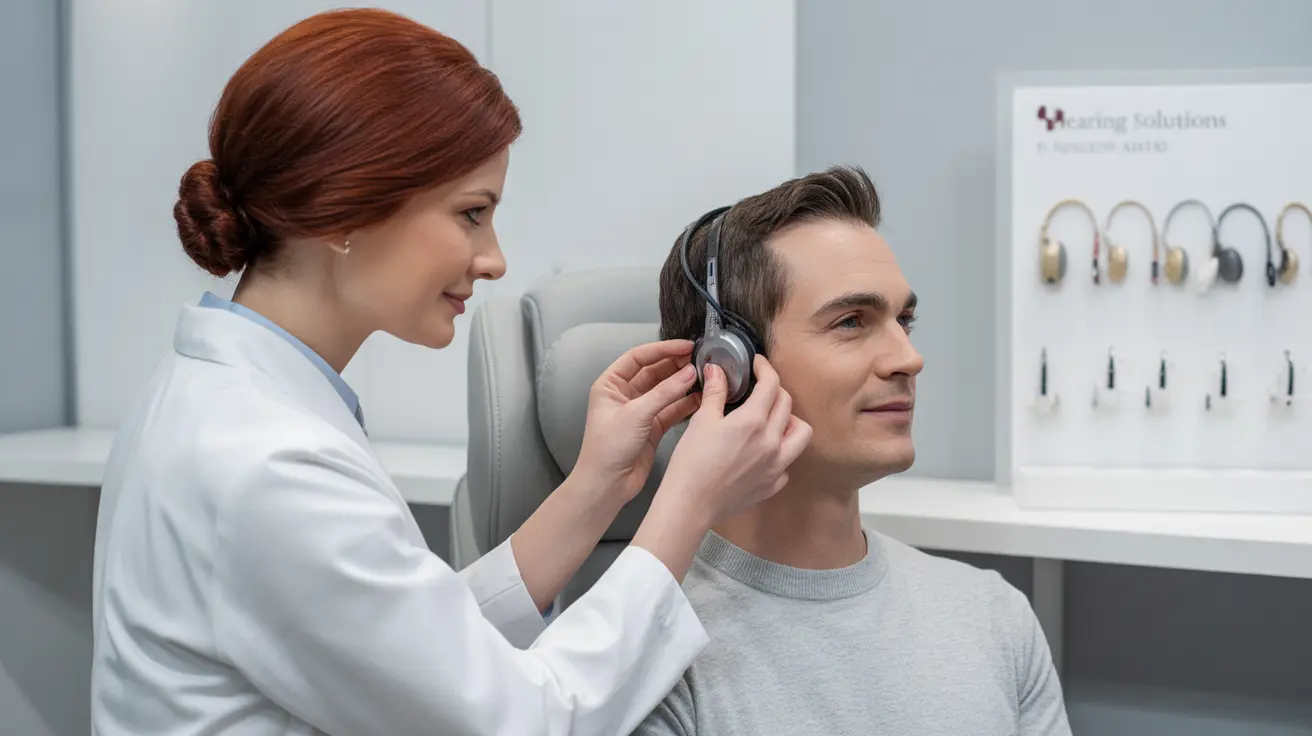
If you're experiencing ringing, buzzing, or other phantom sounds in your ears, you may need a tinnitus test to determine the underlying cause and severity of your condition. Understanding the various diagnostic procedures available can help you better prepare for your evaluation and take the first step toward managing your symptoms.
This comprehensive guide explores the different types of tinnitus tests, what to expect during evaluation, and how medical professionals use these assessments to develop an effective treatment plan.
Professional Tinnitus Evaluation Methods
Healthcare providers use several specialized tests to diagnose tinnitus and identify its potential causes. These evaluations typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination of your ears.
Audiological Examination
The cornerstone of tinnitus diagnosis is a complete hearing evaluation. This includes:
- Pure-tone audiometry
- Speech recognition testing
- Loudness discomfort levels assessment
- Tinnitus pitch and loudness matching
- Sound sensitivity measurements
Tympanometry Testing
This test measures how well your eardrum moves and helps identify any middle ear problems that might be contributing to your tinnitus. The procedure is quick, painless, and provides valuable information about your ear's physical function.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
Acoustic Reflex Testing
This examination evaluates how certain muscles in your middle ear respond to loud sounds, helping doctors determine if there are any neurological issues contributing to your tinnitus.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
OAE testing checks the function of your inner ear's hair cells, which play a crucial role in hearing and can influence tinnitus symptoms when damaged.
Imaging Studies and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, additional testing may be necessary to rule out underlying medical conditions:
- MRI scans to check for tumors or structural abnormalities
- CT scans to examine bone structures
- Blood tests to check for underlying health conditions
- Neurological examinations when necessary
Preparing for Your Tinnitus Evaluation
To get the most accurate results from your tinnitus test, consider these preparation steps:
- Avoid loud noise exposure for 24 hours before testing
- Bring a list of current medications
- Document your tinnitus symptoms and patterns
- Note any relevant medical history
- Prepare questions for your healthcare provider
Frequently Asked Questions
What tests are used by doctors to diagnose tinnitus and how do they work?
Doctors primarily use audiological tests, including pure-tone audiometry, speech recognition testing, and tinnitus matching procedures. These tests help determine the pitch and loudness of your tinnitus, measure your hearing ability, and identify potential causes of your symptoms.
How can hearing tests like audiograms and tympanometry help identify the cause of tinnitus?
Audiograms reveal patterns of hearing loss that may be related to tinnitus, while tympanometry measures eardrum movement and middle ear function. Together, these tests can identify specific types of hearing problems or physical conditions causing tinnitus.
Are imaging tests like MRI or CT scans necessary for tinnitus diagnosis?
Imaging tests aren't always necessary but may be recommended if your healthcare provider suspects structural abnormalities, tumors, or vascular issues as the cause of your tinnitus. These tests are typically reserved for cases where standard hearing tests don't provide sufficient information.
Is there a safe and effective home test available for tinnitus detection?
While there are some smartphone apps and online hearing tests available, these should not replace professional evaluation. Home screening tools can be useful for initial assessment, but accurate diagnosis requires comprehensive testing by qualified healthcare professionals.
How should I prepare for a tinnitus evaluation with an audiologist?
Before your evaluation, avoid loud noise exposure for 24 hours, list your symptoms and their patterns, bring a complete medical history including current medications, and prepare questions about your condition. It's also helpful to track when your tinnitus is most noticeable and what factors seem to affect it.