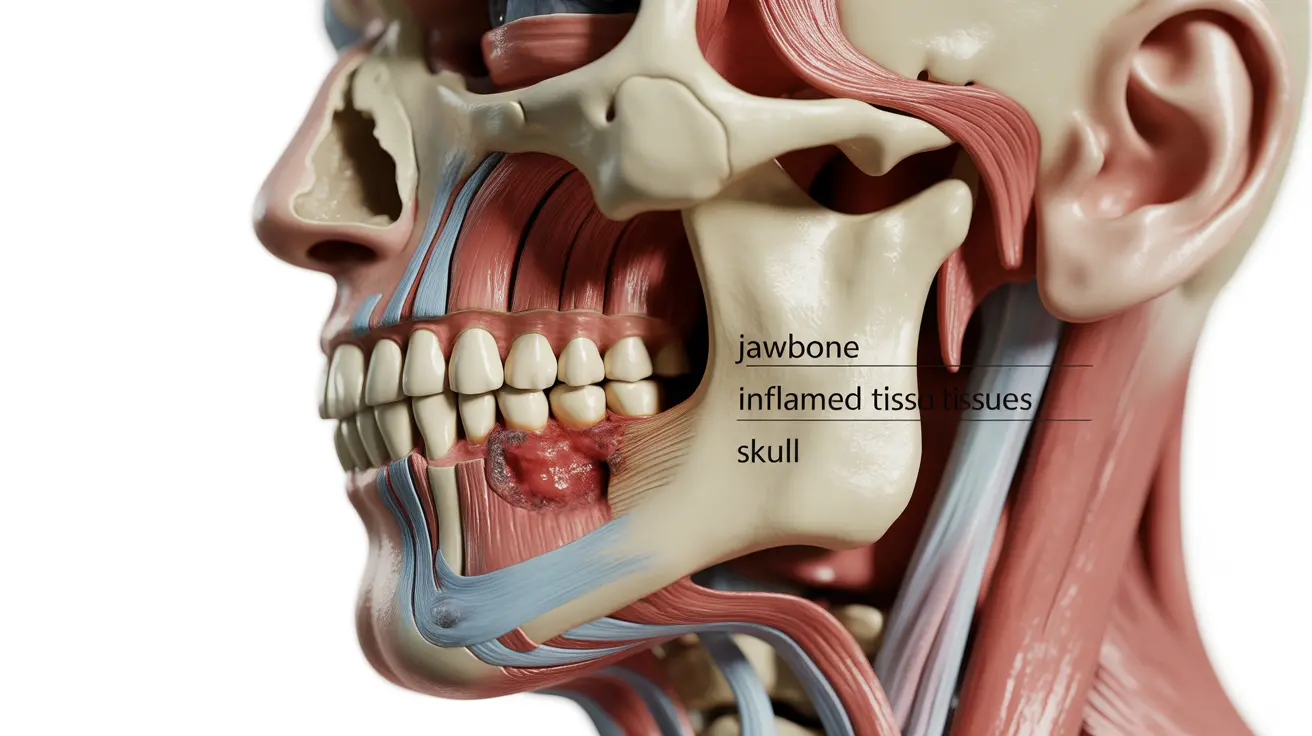
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can cause significant discomfort, with jaw swelling being one of the most noticeable symptoms. This condition affects the complex joint system connecting your jawbone to your skull, leading to various uncomfortable symptoms that can impact daily activities like eating and speaking.
When TMJ problems cause swelling, it's essential to understand the underlying causes and available treatment options to manage the condition effectively. Let's explore the key aspects of TMJ-related jaw swelling and learn how to identify and address this common issue.
Understanding TMJ Swelling and Its Causes
TMJ swelling typically occurs when the temporomandibular joint becomes inflamed or irritated. Several factors can contribute to this condition:
- Teeth grinding (bruxism)
- Joint overuse from excessive chewing
- Jaw injury or trauma
- Arthritis affecting the joint
- Stress-related muscle tension
- Misaligned bite or dental problems
The inflammation can affect both the joint itself and the surrounding muscles and tissues, leading to visible swelling and discomfort in the jaw area.
Identifying TMJ-Related Swelling
Distinguishing TMJ swelling from other facial swelling causes is crucial for proper treatment. Common characteristics of TMJ-related swelling include:
- Swelling localized near the ear and jaw joint
- Tenderness when touching the affected area
- Pain that worsens with jaw movement
- Swelling that may be more pronounced in the morning
- Possible clicking or popping sounds when moving the jaw
Common Symptoms Beyond Swelling
TMJ disorders often present with multiple symptoms beyond a swollen jaw:
- Facial pain or tenderness
- Difficulty opening or closing the mouth
- Headaches, particularly around the temples
- Ear pain or ringing
- Neck and shoulder discomfort
- Jaw locking or catching when moving
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild TMJ symptoms might resolve on their own, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation:
- Severe or persistent swelling
- Inability to open or close your mouth properly
- Intense pain that interferes with daily activities
- Swelling accompanied by fever
- Symptoms that last longer than a few weeks
Treatment Options for TMJ Swelling
Conservative Treatments
Initial treatment typically focuses on non-invasive approaches:
- Cold or heat therapy
- Gentle jaw exercises
- Stress management techniques
- Soft food diet
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications
Professional Interventions
More severe cases may require professional treatment options:
- Custom-fitted mouth guards or splints
- Physical therapy
- Prescription medications
- Dental work to correct bite issues
- In rare cases, surgical intervention
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes swelling in the jaw related to TMJ disorders? TMJ swelling is typically caused by inflammation of the joint due to factors like teeth grinding, jaw overuse, injury, arthritis, or stress-related muscle tension.
How can I tell if facial swelling is due to TMJ problems or another condition? TMJ-related swelling is usually localized near the jaw joint, accompanied by pain when moving the jaw, and may include clicking or popping sounds. The swelling typically affects one or both sides of the face near the ears.
What are the common symptoms of TMJ disorder besides a swollen jaw? Common additional symptoms include facial pain, difficulty opening or closing the mouth, headaches, ear pain, neck discomfort, and jaw clicking or locking.
When should I see a doctor for jaw swelling or pain linked to TMJ? Seek medical attention if you experience severe or persistent swelling, inability to open or close your mouth, intense pain, swelling with fever, or symptoms lasting more than a few weeks.
What treatment options are available for TMJ swelling and inflammation? Treatment options range from conservative approaches like cold/heat therapy, jaw exercises, and over-the-counter medications to professional interventions such as mouth guards, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.