Experiencing trapped gas pain can be both uncomfortable and concerning, especially when it occurs in different areas of your abdomen. Understanding where gas pain typically occurs and how to distinguish it from other conditions is crucial for proper self-care and knowing when to seek medical attention.
This comprehensive guide will help you identify common locations of trapped gas pain, understand why it occurs in specific areas, and learn how to differentiate it from more serious conditions like appendicitis.
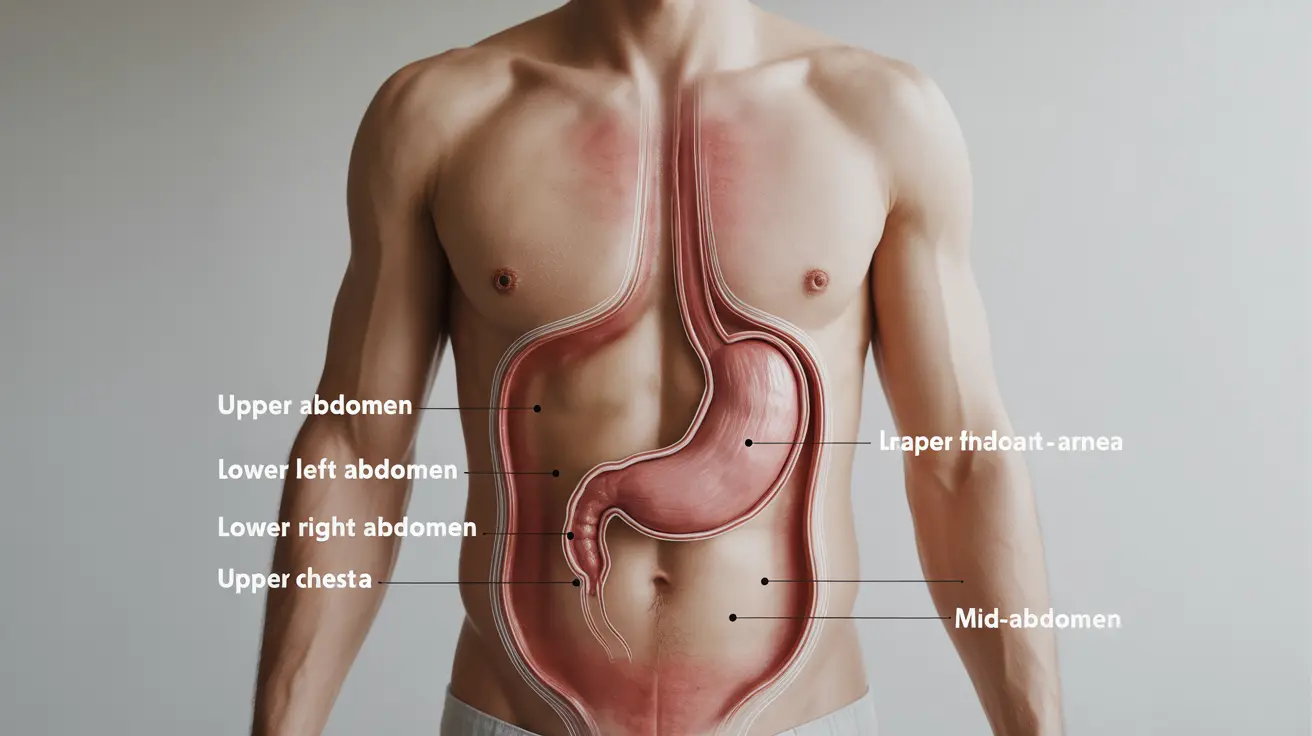
Common Locations of Trapped Gas Pain
Gas pain can manifest in various areas of your abdomen, often leading to confusion about its source. The most common locations include:
- Upper abdomen (epigastric region)
- Lower left abdomen
- Lower right abdomen
- Upper chest area
- General mid-abdomen area
Upper Abdominal Gas Pain
When gas becomes trapped in the upper abdomen, it often causes pressure and discomfort just below the rib cage. This pain can sometimes be mistaken for heart-related issues or indigestion. The pain typically feels sharp or burning and may worsen after eating.
Lower Abdominal Gas Pain
Gas pain in the lower abdomen can occur on either the left or right side. On the left side, it's often related to the sigmoid colon, while right-sided pain might be confused with appendicitis. The pain usually feels crampy and may move around as gas bubbles shift position.
Distinguishing Gas Pain from Other Conditions
Understanding the characteristics of gas pain can help differentiate it from more serious conditions:
- Gas pain typically moves or changes location
- Pain often improves with passing gas or bowel movements
- Symptoms may worsen after eating certain foods
- Position changes can affect pain intensity
Managing Trapped Gas Pain
Several strategies can help alleviate trapped gas pain:
- Gentle exercise or walking
- Over-the-counter gas relief medications
- Dietary modifications
- Proper eating habits
- Stress reduction techniques
Warning Signs and When to Seek Help
While gas pain is usually harmless, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe, persistent pain that doesn't move
- Fever accompanying abdominal pain
- Blood in stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common locations where trapped gas pain can occur in the abdomen?
Trapped gas pain commonly occurs in the upper abdomen below the rib cage, lower left abdomen near the sigmoid colon, and lower right abdomen. The pain can also present in the upper chest area and general mid-abdomen region.
How can I tell the difference between trapped gas pain and appendicitis pain based on pain location and symptoms?
Gas pain typically moves around and changes with position or passing gas, while appendicitis pain usually starts near the belly button and moves to the lower right abdomen, becoming more severe and constant. Appendicitis also often comes with fever, loss of appetite, and nausea.
Why does gas pain sometimes feel like it is on the left side or right side of the abdomen?
Gas pain can appear on either side due to the anatomy of the digestive system. Left-sided pain often relates to the sigmoid colon, while right-sided pain may occur due to gas in the ascending colon. The pain location can shift as gas moves through the intestines.
When should I seek medical help for abdominal pain that might be caused by trapped gas or appendicitis?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe, persistent pain that doesn't move, fever, blood in stool, unexplained weight loss, or persistent nausea and vomiting. These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition requiring professional evaluation.
What home remedies or treatments help relieve trapped gas pain effectively?
Effective home remedies include gentle exercise, walking, over-the-counter gas relief medications, dietary changes, and proper eating habits. Additionally, heat therapy, peppermint tea, and gentle abdominal massage can help relieve trapped gas pain.