A hysterectomy is a major surgical procedure that involves removing a woman's uterus. Understanding the different types of hysterectomy surgery and approaches available can help patients make informed decisions about their healthcare. This comprehensive guide explores the various surgical options, recovery expectations, and important considerations for women facing this procedure.
Types of Hysterectomy Procedures
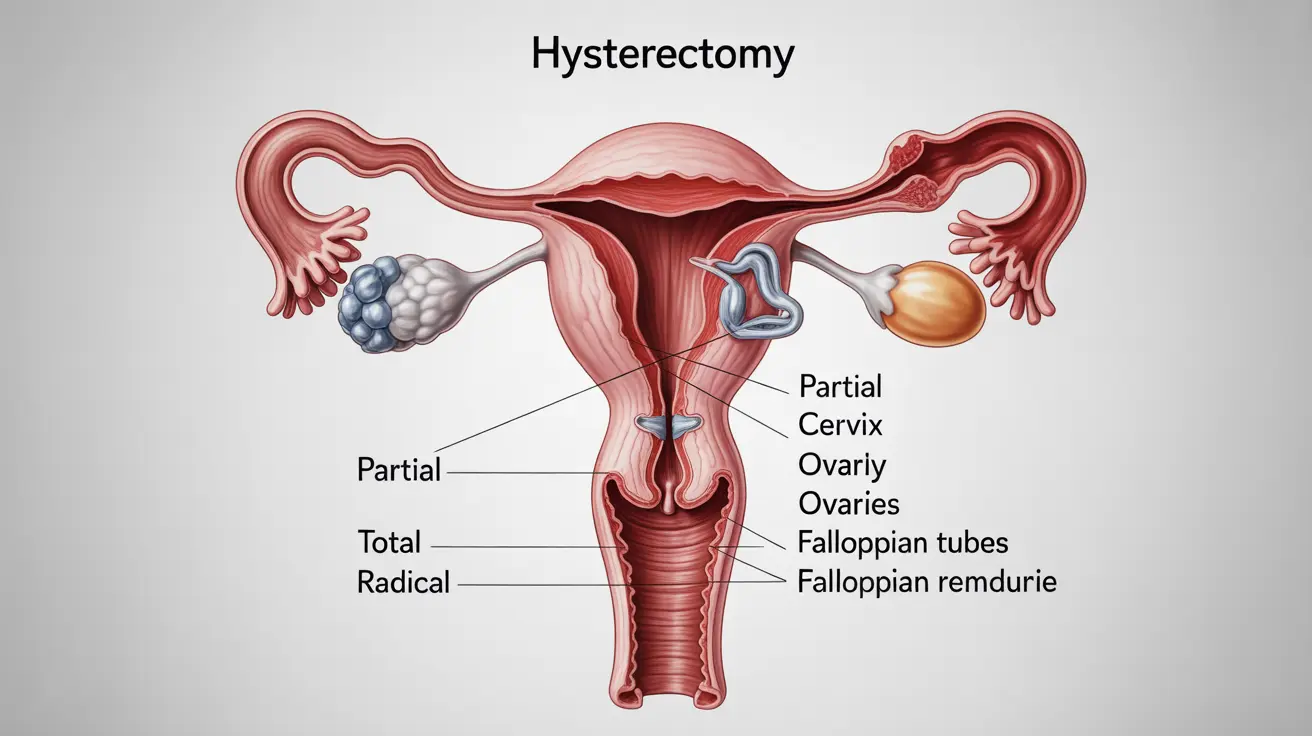
There are three main types of hysterectomy procedures, each varying in the amount of tissue removed during surgery:
Partial (Supracervical) Hysterectomy
In a partial hysterectomy, surgeons remove only the upper portion of the uterus while leaving the cervix in place. This option may be suitable for women who have benign conditions and wish to maintain cervical support for pelvic floor strength.
Total Hysterectomy
A total hysterectomy involves removing both the uterus and cervix completely. This is the most common type of hysterectomy performed and may be recommended for various conditions, including cancer prevention and treatment of severe endometriosis.
Radical Hysterectomy
This most extensive form of hysterectomy removes the uterus, cervix, parts of the vagina, and surrounding tissues. Doctors typically reserve this procedure for treating certain types of gynecologic cancers.
Surgical Approaches for Hysterectomy
Abdominal Hysterectomy
This traditional approach involves making a horizontal or vertical incision in the lower abdomen. While it offers excellent surgical visibility, it typically requires a longer recovery period of 4-6 weeks.
Vaginal Hysterectomy
Performed entirely through the vagina with no external incisions, this approach typically offers the fastest recovery time and minimal scarring. However, it may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with very large fibroids or limited vaginal access.
Laparoscopic and Robotic Approaches
These minimally invasive techniques use small abdominal incisions and specialized instruments. Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures often result in shorter hospital stays, less post-operative pain, and faster recovery compared to traditional abdominal surgery.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery time varies significantly based on the type of procedure and surgical approach chosen. Minimally invasive procedures typically allow patients to return to normal activities within 2-4 weeks, while traditional abdominal surgery may require 4-6 weeks of recovery.
Managing Post-Operative Symptoms
Patients should expect some discomfort, vaginal bleeding, and fatigue during the initial recovery period. Following your surgeon's instructions regarding activity restrictions, pain management, and wound care is crucial for optimal healing.
Hormonal Considerations
If the ovaries are removed during surgery (oophorectomy), patients will experience immediate surgical menopause. This may necessitate hormone replacement therapy to manage symptoms and protect long-term health. Women who retain their ovaries will continue to produce hormones naturally, even after the uterus is removed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of hysterectomy surgery and how do they vary?
The three main types are partial (removing just the upper uterus), total (removing the entire uterus and cervix), and radical (removing the uterus, cervix, part of the vagina, and surrounding tissue). Each type serves different medical needs and conditions.
How do surgeons decide whether to perform a total, partial, or radical hysterectomy?
Surgeons base their decision on several factors, including the underlying medical condition, cancer risk, patient age, desired outcomes, and overall health status. Radical hysterectomies are typically reserved for cancer cases, while partial or total hysterectomies address benign conditions.
What are the common surgical approaches for hysterectomy and how do recovery times compare?
Common approaches include abdominal (4-6 weeks recovery), vaginal (2-4 weeks), and laparoscopic/robotic (2-4 weeks). Minimally invasive approaches generally offer faster recovery times and less post-operative pain compared to traditional abdominal surgery.
What should I expect during recovery after a laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy?
Expect mild to moderate pain, light vaginal bleeding, and fatigue for several weeks. Most patients can return to light activities within 1-2 weeks and full activities within 4 weeks. Follow-up appointments typically occur at 2 and 6 weeks post-surgery.
How does removal of ovaries during hysterectomy affect menopause and hormone replacement needs?
Removing the ovaries during hysterectomy (oophorectomy) causes immediate surgical menopause, requiring careful consideration of hormone replacement therapy. If ovaries are preserved, they continue producing hormones naturally, and natural menopause will occur at the typical age.