Fungal infections are a widespread health concern affecting millions of people worldwide. These infections can range from minor skin irritations to more serious systemic conditions, making it crucial to understand their various types, symptoms, and treatment options. This guide will help you identify different fungal infections and know when to seek medical attention.
Common Types of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections typically fall into several main categories, each affecting different parts of the body and requiring specific treatment approaches:
Skin Infections
The most common fungal skin infections include:
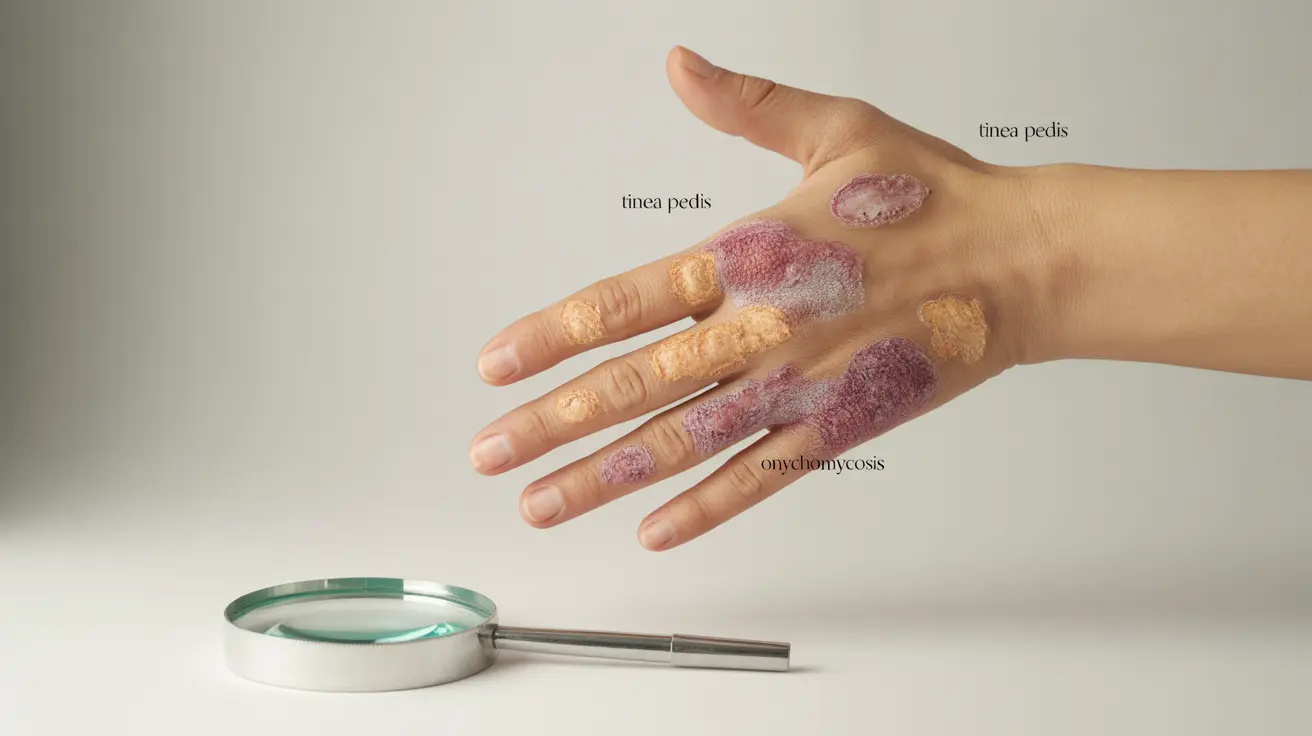
- Athlete's foot (tinea pedis)
- Ringworm (tinea corporis)
- Jock itch (tinea cruris)
- Candida skin infections
Nail Infections
Fungal nail infections (onychomycosis) can affect both fingernails and toenails, causing discoloration, thickening, and brittleness of the nails.
Scalp Infections
Tinea capitis primarily affects the scalp and hair shafts, causing patches of hair loss and scaliness. This condition is particularly common in children.
Identifying Superficial vs. Systemic Infections
Understanding the difference between superficial and systemic fungal infections is crucial for proper treatment:
Superficial Infections
These typically affect the outer layers of skin, hair, or nails and present with:
- Redness and irritation
- Itching or burning sensation
- Scaling or flaking skin
- Clear borders around affected areas
Systemic Infections
These more serious infections can affect internal organs and show symptoms such as:
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Unexplained weight loss
Treatment Options and Prevention
Most superficial fungal infections respond well to antifungal medications, which come in various forms:
- Topical creams and ointments
- Oral medications
- Medicated shampoos
- Antifungal nail solutions
Prevention Strategies
To reduce your risk of developing fungal infections:
- Keep skin clean and dry
- Wear breathable fabrics
- Change socks and underwear daily
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas
- Don't share personal items like towels or brushes
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your susceptibility to fungal infections:
- Compromised immune system
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Excessive sweating
- Prolonged antibiotic use
- Tight-fitting clothing
- Hot, humid environments
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the most common types of fungal infections that affect the skin and nails? A: The most common fungal infections include athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, candida infections, and fungal nail infections (onychomycosis). These conditions typically affect the skin's surface and nails, causing symptoms like itching, redness, and scaling.
Q: How can you tell if a fungal infection is superficial or systemic and requires medical treatment? A: Superficial infections typically show localized symptoms like itching, redness, and scaling on the skin or nails. Systemic infections, which require immediate medical attention, often present with severe symptoms like fever, fatigue, difficulty breathing, and widespread bodily effects.
Q: What are effective treatments for athlete's foot, ringworm, and other common fungal skin infections? A: Most common fungal skin infections can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications in cream, powder, or spray form. For more persistent cases, prescription oral medications may be necessary. Treatment should be continued for the full recommended duration, even if symptoms improve.
Q: What factors increase the risk of developing fungal infections, and how can they be prevented? A: Risk factors include poor hygiene, compromised immunity, diabetes, obesity, and exposure to warm, moist environments. Prevention involves maintaining good hygiene, keeping skin dry, wearing breathable clothing, and avoiding sharing personal items.
Q: When should someone see a doctor for a fungal infection that doesn't improve with over-the-counter remedies? A: Seek medical attention if an infection persists after two weeks of over-the-counter treatment, spreads to other areas, becomes painful or severely uncomfortable, or is accompanied by fever or other systemic symptoms.