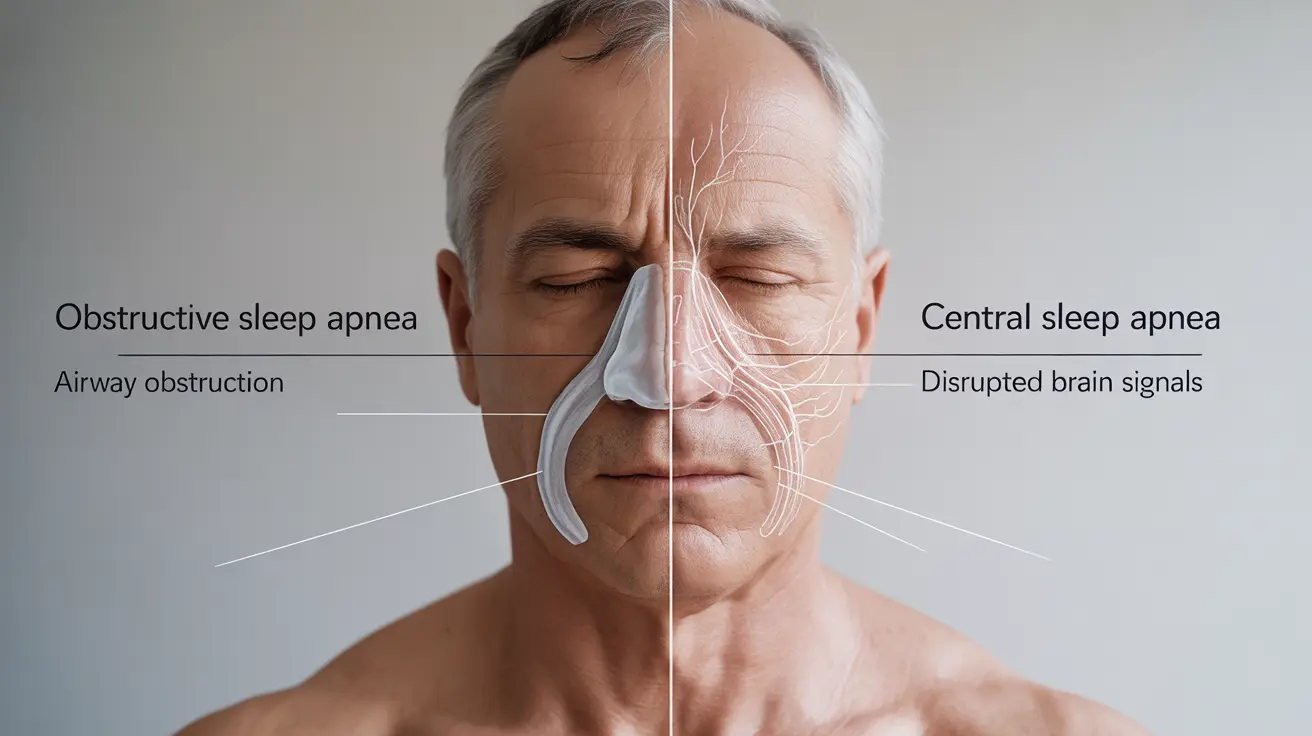
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that affects millions of Americans, causing breathing interruptions during sleep that can significantly impact health and quality of life. Understanding the two main types of sleep apnea is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Let's explore the key differences between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA), their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Distinguishing Between Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway during sleep. This physical obstruction leads to repeated breathing pauses throughout the night. In contrast, central sleep apnea happens when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing, resulting in breathing interruptions without any physical blockage.
Understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to OSA development, including:
- Excess weight and obesity
- Large neck circumference
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids
- Family history
- Aging
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Nasal congestion or anatomical features
Common Symptoms
Key indicators of OSA include:
- Loud snoring
- Witnessed breathing pauses during sleep
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Morning headaches
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability or mood changes
Understanding Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Causes and Risk Factors
CSA typically develops due to:
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Opioid medication use
- High altitude
- Certain medical conditions affecting the brainstem
Distinctive Symptoms
CSA symptoms often include:
- Periodic breathing pauses without snoring
- Shortness of breath that awakens you
- Difficulty staying asleep
- Excessive daytime fatigue
- Morning headaches
- Mood changes
Treatment Approaches
Treating Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Treatment options for OSA include:
- CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) therapy
- Oral appliances
- Weight loss programs
- Position therapy
- Surgery in select cases
- Lifestyle modifications
Managing Central Sleep Apnea
CSA treatment typically involves:
- Treating underlying medical conditions
- Bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP)
- Adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV)
- Supplemental oxygen
- Medication adjustments if needed
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Several lifestyle modifications can help manage both types of sleep apnea:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding alcohol and sedatives
- Establishing good sleep habits
- Sleeping on your side
- Quitting smoking
- Managing allergies and nasal congestion
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea involves physical blockage of the airway due to relaxed throat muscles, while central sleep apnea occurs when the brain fails to send proper breathing signals. OSA typically involves snoring, while CSA usually doesn't.
What causes the two types of sleep apnea and how can they be identified?
OSA is primarily caused by physical factors like obesity, anatomical features, and lifestyle habits. CSA is usually related to underlying medical conditions affecting the brain's breathing control center. Both can be identified through sleep studies and careful evaluation of symptoms.
How is obstructive sleep apnea treated compared to central sleep apnea?
OSA is primarily treated with CPAP therapy, oral appliances, and lifestyle changes. CSA treatment focuses on addressing underlying medical conditions and may require specialized breathing devices like BiPAP or ASV.
What symptoms should make me suspect I have obstructive or central sleep apnea?
For OSA, watch for loud snoring, witnessed breathing pauses, and daytime sleepiness. CSA symptoms include breathing pauses without snoring, sudden awakenings with shortness of breath, and difficulty staying asleep.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent or reduce obstructive sleep apnea symptoms?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly impact OSA symptoms. Weight loss, regular exercise, sleeping position changes, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives can help reduce symptom severity and improve sleep quality.