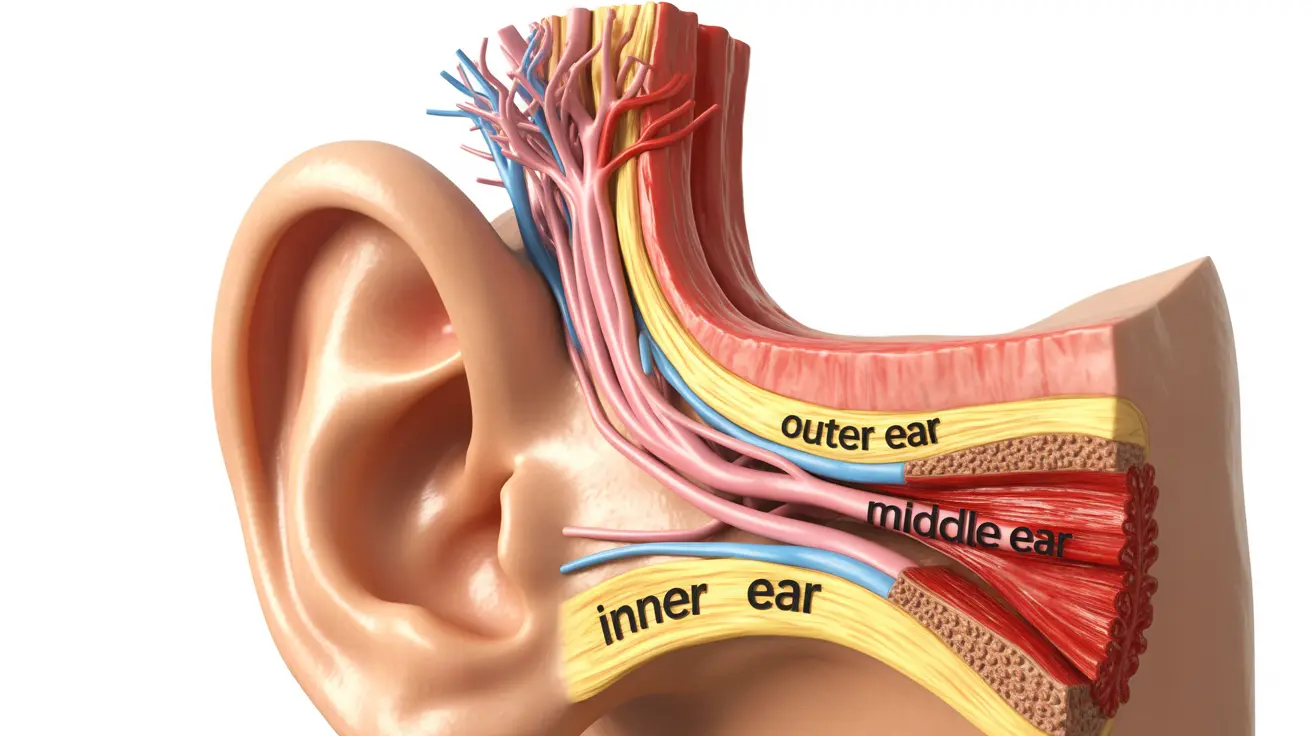
Tinnitus, often described as ringing, buzzing, or humming in the ears, affects millions of people worldwide. While many think of tinnitus as a single condition, it actually encompasses several distinct types, each with unique characteristics and causes. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
This comprehensive guide will explore the various types of tinnitus, their causes, and how healthcare providers approach diagnosis and treatment for each form. Whether you're experiencing tinnitus symptoms or seeking to understand the condition better, this information will help you navigate your healthcare journey more effectively.
Main Types of Tinnitus
Tinnitus manifests in several distinct forms, each requiring different approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these variations is essential for proper medical care.
Subjective Tinnitus
Subjective tinnitus is the most common form, affecting approximately 95% of tinnitus cases. This type is only audible to the person experiencing it and typically results from issues in the outer, middle, or inner ear, or problems with auditory nerves and the way your brain processes sound.
Common causes of subjective tinnitus include:
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- Age-related hearing loss
- Ear wax blockage
- Medications (ototoxic drugs)
- Head or neck injuries
- Acoustic neuroma
Objective Tinnitus
Objective tinnitus is rare and unique because healthcare providers can actually hear the sounds during an examination. This form often results from internal biological functions or disorders affecting blood vessels, muscles, or bones near the ear.
Key characteristics of objective tinnitus include:
- Clicking or crackling sounds
- Rhythmic pulsing in sync with heartbeat
- Sounds that can be recorded by medical professionals
- Often treatable by addressing the underlying cause
Pulsatile Tinnitus
Pulsatile tinnitus produces rhythmic sounds that match your heartbeat. This type often indicates underlying vascular issues or blood flow problems near the ears. It can be either subjective or objective, depending on whether healthcare providers can detect the sound.
Common causes of pulsatile tinnitus include:
- High blood pressure
- Atherosclerosis
- Tumors affecting blood vessels
- Abnormal capillary formations
- Pregnancy or anemia
Classification by Duration
Acute Tinnitus
Acute tinnitus is temporary, typically lasting a few days to several weeks. It often occurs after exposure to loud noise or during temporary illness, and usually resolves on its own.
Chronic Tinnitus
Chronic tinnitus persists for months or years and may require ongoing management strategies. This type often significantly impacts quality of life and requires comprehensive treatment approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of tinnitus and how do they differ from each other?
The main types of tinnitus are subjective (heard only by the patient), objective (can be heard by examiners), and pulsatile (rhythmic sounds matching heartbeat). They differ in their causes, characteristics, and treatment approaches. Subjective tinnitus is most common and stems from auditory system issues, while objective tinnitus often relates to physical conditions that create actual sounds in the ear.
What causes pulsatile tinnitus and how is it different from regular tinnitus?
Pulsatile tinnitus is caused by blood flow issues near the ears, such as high blood pressure, vascular tumors, or abnormal blood vessel formations. Unlike regular tinnitus, it produces rhythmic sounds that sync with the heartbeat and often indicates underlying cardiovascular conditions requiring medical attention.
How can I tell if my tinnitus is objective, subjective, or pulsatile?
Subjective tinnitus is only heard by you and typically presents as constant ringing or buzzing. Pulsatile tinnitus produces rhythmic sounds matching your pulse. Objective tinnitus is rare and can be heard by healthcare providers during examination. A medical professional can help determine which type you have through proper examination and testing.
What medical conditions and factors are commonly linked to different types of tinnitus?
Different types of tinnitus are linked to various conditions: subjective tinnitus often relates to hearing loss, ear wax blockage, or medication side effects; objective tinnitus may be caused by middle ear bone conditions or muscle contractions; and pulsatile tinnitus frequently connects to blood vessel disorders, high blood pressure, or tumors.
How is tinnitus diagnosed and what treatment options are available based on its type?
Diagnosis typically involves a complete medical history, physical examination, hearing tests, and possibly imaging studies. Treatment varies by type: subjective tinnitus might be managed with sound therapy, counseling, or hearing aids; objective tinnitus often involves treating the underlying physical condition; and pulsatile tinnitus treatment focuses on addressing cardiovascular issues or other vascular abnormalities.