Living with ulcerative colitis (UC) can be challenging, particularly when dealing with one of its most common and distressing symptoms: diarrhea. Understanding the connection between ulcerative colitis and diarrhea is crucial for effectively managing this inflammatory bowel disease and improving quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explores the causes of UC-related diarrhea, available treatment options, and practical strategies for symptom management. Whether you're newly diagnosed or looking for better ways to control your symptoms, we'll help you understand and address this challenging aspect of ulcerative colitis.
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis Diarrhea
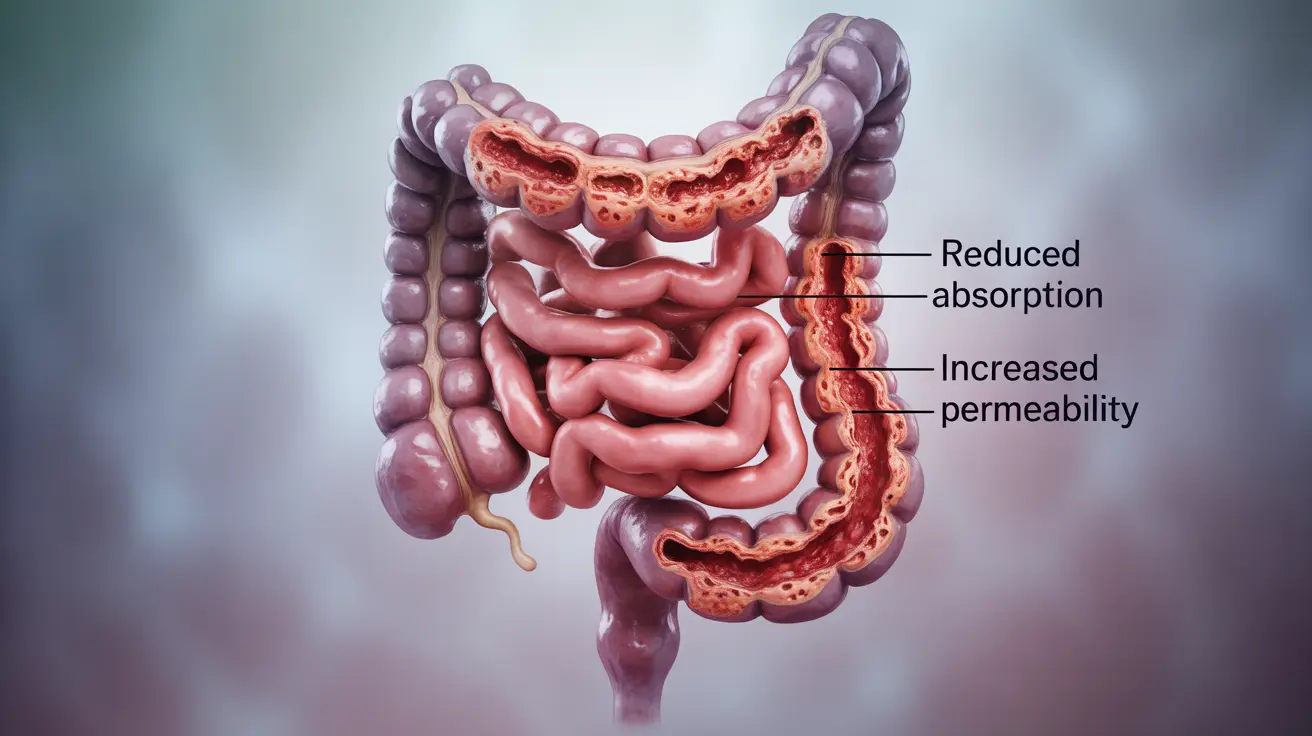
Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and ulcers in the large intestine (colon) and rectum. This inflammation disrupts normal bowel function, leading to frequent diarrhea. The condition can affect the colon's ability to absorb water and electrolytes, resulting in loose, urgent bowel movements that may contain blood or mucus.
During a flare-up, the inflamed intestinal lining becomes more sensitive and less efficient at processing waste, often leading to increased frequency and urgency of bowel movements. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
Medical Treatments for UC-Related Diarrhea
Several medication classes can help control ulcerative colitis diarrhea:
- Aminosalicylates (5-ASAs) to reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids for acute flare management
- Immunomodulators to suppress inflammatory responses
- Biologics for moderate to severe cases
- Anti-diarrheal medications (when approved by your healthcare provider)
It's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to find the most effective medication combination for your specific situation. Never start or stop medications without medical supervision.
Dietary Management Strategies
Diet plays a crucial role in managing ulcerative colitis diarrhea. Consider these evidence-based approaches:
- Keep a detailed food diary to identify trigger foods
- Choose low-fiber foods during flares
- Stay well-hydrated with water and electrolyte-rich beverages
- Consider a low-FODMAP diet under medical supervision
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals
Remember that dietary triggers can vary significantly between individuals. What works for one person may not work for another, so personalization is key.
Lifestyle Modifications and Coping Strategies
Implementing certain lifestyle changes can help manage UC-related diarrhea:
- Stress management through relaxation techniques
- Regular exercise when appropriate
- Adequate rest and sleep
- Planning ahead for outings
- Maintaining a support network
These modifications, combined with medical treatment and dietary management, can significantly improve symptom control and quality of life.
Warning Signs and Emergency Situations
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe, uncontrolled diarrhea
- Significant blood in stool
- High fever
- Severe abdominal pain
- Signs of dehydration
- Unexplained weight loss
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes diarrhea in people with ulcerative colitis and why does it sometimes contain blood or mucus?
Diarrhea in ulcerative colitis occurs due to inflammation of the colon's lining, which impairs normal water absorption and causes increased urgency. Blood and mucus appear when inflammation leads to ulcers and damage to the intestinal wall.
How can I manage or reduce diarrhea symptoms during an ulcerative colitis flare-up?
Managing flare-ups involves a combination of medication adherence, dietary modifications, stress reduction, and adequate rest. Stay hydrated, avoid trigger foods, and follow your healthcare provider's treatment plan carefully.
What medications are commonly used to treat diarrhea caused by ulcerative colitis?
Treatment typically includes anti-inflammatory medications (5-ASAs), corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics. Anti-diarrheal medications may be used under medical supervision during specific circumstances.
Are there specific foods or lifestyle changes that help control diarrhea in ulcerative colitis patients?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding trigger foods, staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting adequate rest can help control symptoms. Some patients benefit from following specific diets like low-FODMAP or low-fiber during flares.
When should I seek medical help if my ulcerative colitis diarrhea becomes severe or frequent?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe, uncontrolled diarrhea, significant bleeding, high fever, severe abdominal pain, signs of dehydration, or rapid weight loss.