Anuria is a serious medical condition characterized by the complete absence or severe reduction of urine production, typically defined as producing less than 50 milliliters of urine per day. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can indicate severe kidney dysfunction or other underlying health issues that need urgent treatment.
Understanding anuria is crucial because it often signals a significant problem with kidney function or urinary system blockage. Early recognition and proper medical intervention can help prevent severe complications and improve outcomes for patients affected by this condition.
What Is Anuria and How Does It Occur?
Anuria develops when the kidneys stop producing urine or when there's a complete blockage preventing urine from being expelled from the body. This condition differs from normal urinary patterns and can occur suddenly or develop gradually, depending on the underlying cause.
Types of Anuria
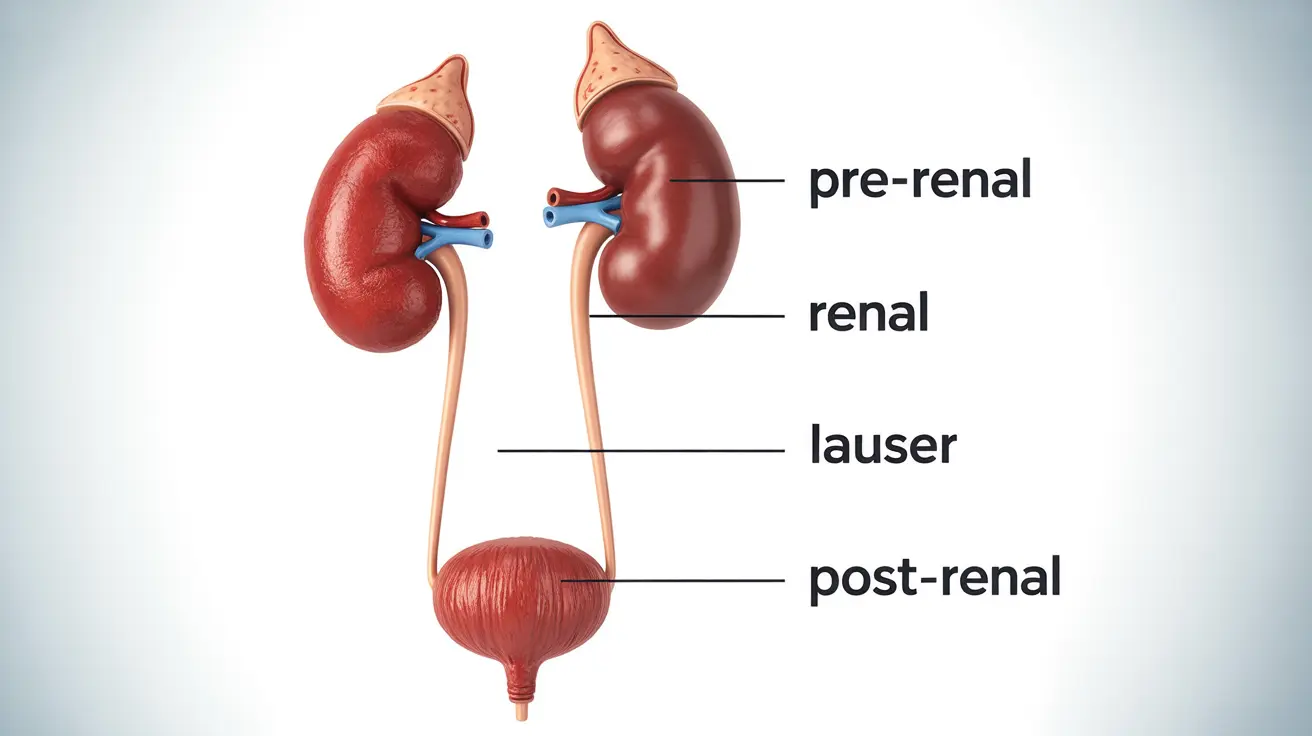
Medical professionals typically classify anuria into three main categories:
- Pre-renal anuria: Caused by reduced blood flow to the kidneys
- Renal anuria: Results from direct kidney damage or disease
- Post-renal anuria: Occurs due to blockages in the urinary tract
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several conditions can lead to the development of anuria:
- Severe dehydration
- Acute kidney injury
- Kidney stones or tumors
- Blood clots affecting kidney circulation
- Severe infections or sepsis
- Complications from certain medications
- Advanced heart failure
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose anuria and identify its underlying cause:
- Physical examination
- Urine output monitoring
- Blood tests to assess kidney function
- Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan)
- Kidney biopsy (in some cases)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for anuria focuses on addressing the underlying cause while maintaining proper kidney function. Common interventions include:
Immediate Interventions
- Intravenous fluid administration
- Medication adjustments
- Dialysis when necessary
- Removal of urinary blockages if present
Long-term Management
Long-term treatment typically involves:
- Regular monitoring of kidney function
- Blood pressure management
- Dietary modifications
- Ongoing medical supervision
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases of anuria can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce risk:
- Maintaining proper hydration
- Regular medical check-ups
- Managing underlying conditions like diabetes and hypertension
- Avoiding nephrotoxic medications when possible
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of anuria, and how can it be prevented?
The primary causes of anuria include severe dehydration, acute kidney injury, urinary tract obstruction, and serious infections. Prevention involves maintaining good hydration, managing underlying health conditions, and seeking prompt medical attention for kidney-related symptoms.
How is anuria diagnosed and treated, especially in cases of underlying kidney disease?
Diagnosis involves physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, and urine output monitoring. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include IV fluids, medication adjustments, dialysis, or surgery to remove blockages in cases of kidney disease.
What are the differences between oliguria and anuria, and how do their symptoms and treatments differ?
Oliguria involves decreased urine output (less than 400-500 mL/day), while anuria is the near-complete absence of urine production (less than 50 mL/day). While both conditions require medical attention, anuria typically indicates a more severe condition and may need more aggressive treatment approaches.
Can conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure lead to anuria, and what are the management options?
Yes, both diabetes and high blood pressure can contribute to kidney damage that may lead to anuria. Management includes strict control of blood sugar and blood pressure, medication compliance, regular medical monitoring, and lifestyle modifications.
What are the potential complications of untreated anuria, and how can they be avoided through early intervention?
Untreated anuria can lead to severe complications including electrolyte imbalances, fluid overload, heart problems, and potentially fatal kidney failure. Early intervention through prompt medical attention, regular monitoring, and appropriate treatment of underlying conditions is crucial for preventing these complications.