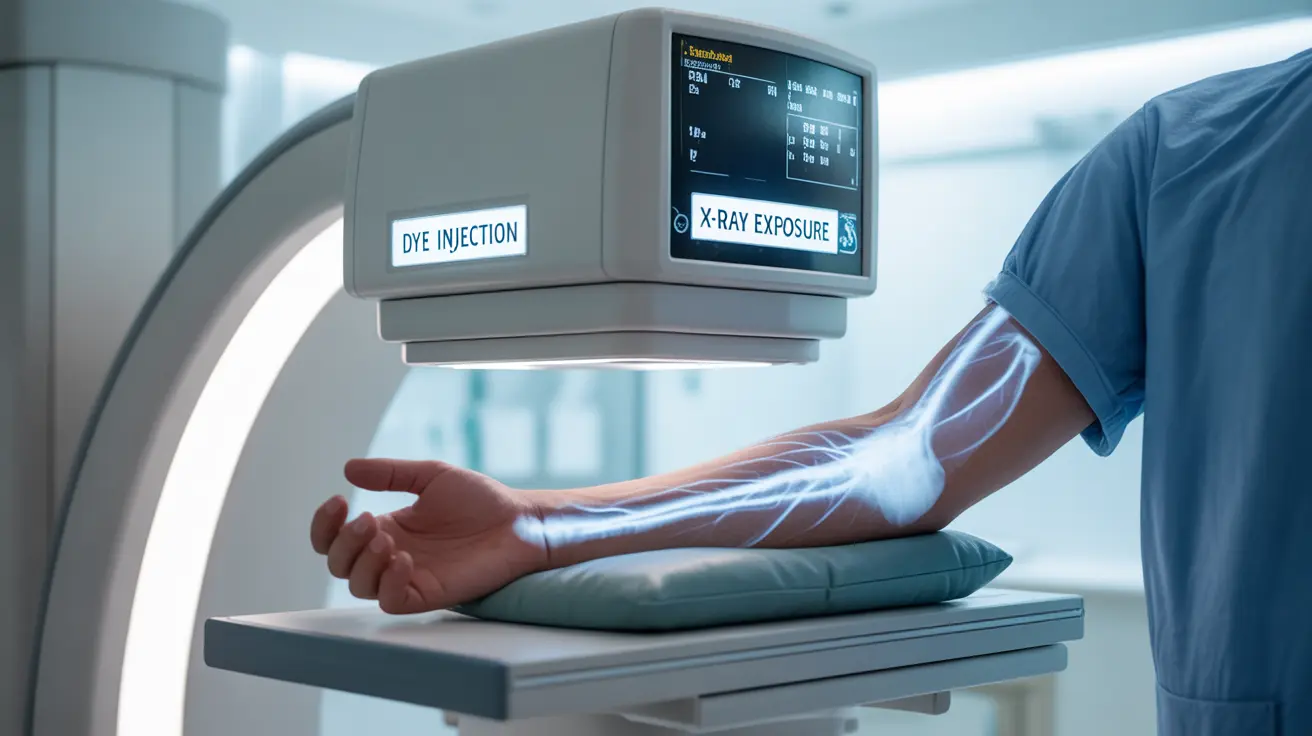
An arteriogram is a sophisticated medical imaging procedure that provides detailed visualization of blood vessels and arteries throughout the body. This specialized X-ray examination helps healthcare providers diagnose and evaluate various cardiovascular conditions by creating clear images of blood flow patterns and potential blockages.
For patients facing potential arterial health issues, understanding this vital diagnostic tool can help reduce anxiety and prepare for the procedure effectively. Let's explore everything you need to know about arteriograms, from preparation to recovery.
What is an Arteriogram?
An arteriogram, also known as an arteriography or angiogram, is a medical imaging technique that uses contrast dye and X-ray technology to examine blood vessels in detail. The procedure creates real-time images called angiograms, allowing doctors to identify narrowing, blockages, or other abnormalities in the arteries.
During the procedure, a special contrast material is injected into the bloodstream, making blood vessels visible on X-ray images. This helps physicians evaluate blood flow and detect various cardiovascular conditions with high precision.
Preparing for Your Arteriogram
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful arteriogram procedure. Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions, which typically include:
- Fasting for 6-8 hours before the procedure
- Discussing current medications with your doctor
- Arranging transportation home
- Informing your doctor about any allergies
- Completing necessary blood tests beforehand
You may need to temporarily stop taking certain medications, particularly blood thinners or diabetes medications. Always follow your doctor's specific instructions regarding medication management.
The Arteriogram Procedure Process
The procedure is performed by a specialized healthcare team in a hospital's radiology department or cardiac catheterization laboratory. Here's what to expect:
Before the Procedure
The medical team will:
- Check your vital signs
- Place an IV line
- Clean and prepare the insertion site
- Administer local anesthesia
During the Procedure
The main steps include:
- Insertion of a catheter through a small incision
- Guidance of the catheter to the target area
- Injection of contrast dye
- Taking multiple X-ray images
- Possible immediate treatment of identified issues
Medical Conditions Diagnosed Through Arteriogram
Arteriograms help diagnose various cardiovascular conditions, including:
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries)
- Aneurysms
- Peripheral artery disease
- Blood vessel malformations
- Coronary artery disease
- Blood clots
Risks and Safety Considerations
While arteriograms are generally safe, understanding potential risks is important. Possible complications may include:
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye
- Bleeding or bruising at the insertion site
- Kidney problems
- Blood clots
- Infection
- Damage to blood vessels
Your healthcare provider will discuss these risks and help determine if an arteriogram is the right diagnostic tool for your situation.
Recovery and Aftercare
After the procedure, patients typically need to:
- Rest for several hours
- Keep the insertion site clean and dry
- Monitor for unusual bleeding or swelling
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Avoid strenuous activities for 24-48 hours
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an arteriogram and how is it used to detect artery problems?
An arteriogram is a specialized X-ray examination that uses contrast dye to create detailed images of blood vessels. It helps detect problems like blockages, narrowing, and other arterial abnormalities by providing clear visualization of blood flow patterns.
How should I prepare for an arteriogram procedure?
Preparation includes fasting for 6-8 hours before the procedure, discussing current medications with your doctor, arranging transportation, and completing any required pre-procedure tests. Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions based on your situation.
What are the risks and possible side effects of having an arteriogram?
Common risks include allergic reactions to contrast dye, bleeding or bruising at the insertion site, kidney problems, and rare complications like blood clots or infection. Most patients experience minimal side effects when proper precautions are taken.
How is an arteriogram performed and what can I expect during the test?
The procedure involves inserting a catheter through a small incision, usually in the groin area, and guiding it to the target area. Contrast dye is injected, and X-ray images are taken. The procedure typically takes 1-2 hours and is performed under local anesthesia.
What types of medical conditions can an arteriogram help diagnose?
An arteriogram can diagnose conditions such as atherosclerosis, aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, blood vessel malformations, coronary artery disease, and blood clots. It's particularly useful for evaluating cardiovascular health and planning treatments.