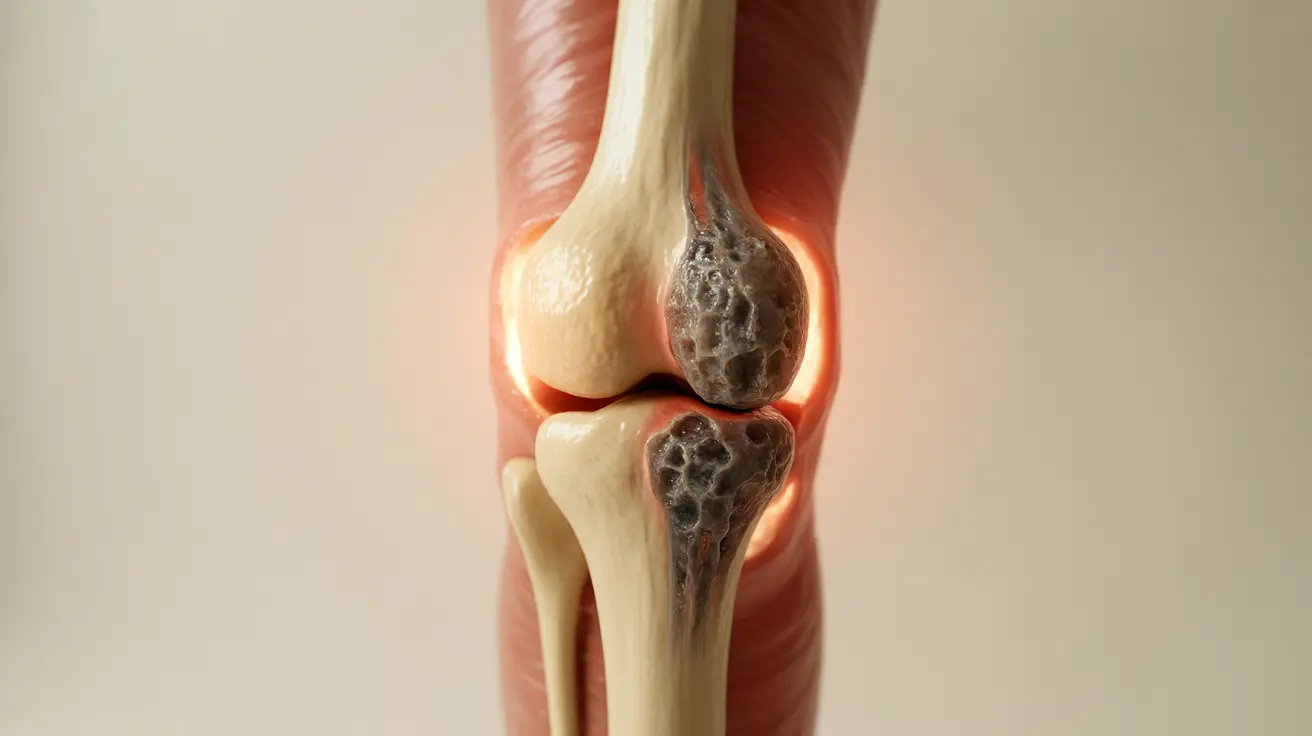
Arthralgia, commonly known as joint pain, affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. While often confused with arthritis, arthralgia specifically refers to pain in the joints without accompanying inflammation. Understanding this condition is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of arthralgia, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and when to seek medical attention. Whether you're experiencing joint pain yourself or seeking information for a loved one, this article will help you better understand and manage this condition.
What Is Arthralgia and How Does It Differ from Arthritis?
Arthralgia is characterized by joint pain without the presence of inflammation. Unlike arthritis, which involves both pain and inflammation, arthralgia can occur without swelling, redness, or warmth in the affected joints. This distinction is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Common locations for arthralgia include:
- Knees
- Hips
- Shoulders
- Elbows
- Wrists
- Ankles
Common Causes of Arthralgia
Arthralgia can develop from various underlying conditions and factors. Understanding these causes is essential for effective treatment:
Physical Causes
- Overuse or injury
- Poor posture
- Muscle strain
- Physical trauma
Medical Conditions
- Viral infections
- Autoimmune disorders
- Fibromyalgia
- Lyme disease
- Depression and anxiety
Lifestyle Factors
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor nutrition
- Dehydration
Treatment Options for Arthralgia
Medical Treatments
Healthcare providers may recommend various medical interventions to manage arthralgia:
- Pain medications (NSAIDs)
- Physical therapy
- Prescription medications
- Joint injections
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Several self-care measures can help alleviate joint pain:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice or heat therapy
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Proper posture maintenance
- Adequate hydration
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Taking proactive steps can help reduce the risk of developing arthralgia:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Proper ergonomics
- Balanced nutrition
- Stress management
When to Seek Medical Attention
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation:
- Severe or persistent joint pain
- Limited range of motion
- Joint instability
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever accompanying joint pain
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between arthralgia and arthritis, and how do their symptoms vary?
Arthralgia refers to joint pain without inflammation, while arthritis involves both pain and inflammation. Arthritis typically presents with swelling, redness, and warmth in affected joints, while arthralgia manifests primarily as pain without these inflammatory symptoms.
What are some common causes of arthralgia, and can it be a sign of an underlying condition?
Arthralgia can be caused by various factors, including physical trauma, viral infections, autoimmune conditions, and lifestyle factors. It can indeed signal underlying conditions such as fibromyalgia, Lyme disease, or autoimmune disorders, making proper medical evaluation important.
How is arthralgia typically treated, and what home remedies can help alleviate joint pain?
Treatment typically involves a combination of medical interventions (such as pain medications and physical therapy) and home remedies. Effective home remedies include rest, ice/heat therapy, gentle exercises, and maintaining proper posture. Some people also find relief through lifestyle modifications and stress management techniques.
What are some risk factors for developing arthralgia, and how can I prevent it?
Risk factors include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, poor posture, and certain medical conditions. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, proper ergonomics, and good nutrition. Staying physically active and practicing joint-protective behaviors can help reduce risk.
When should I seek medical attention if I'm experiencing persistent or severe joint pain?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe or persistent joint pain, limited range of motion, joint instability, unexplained weight loss, or fever accompanying joint pain. These symptoms may indicate a serious underlying condition requiring professional evaluation and treatment.