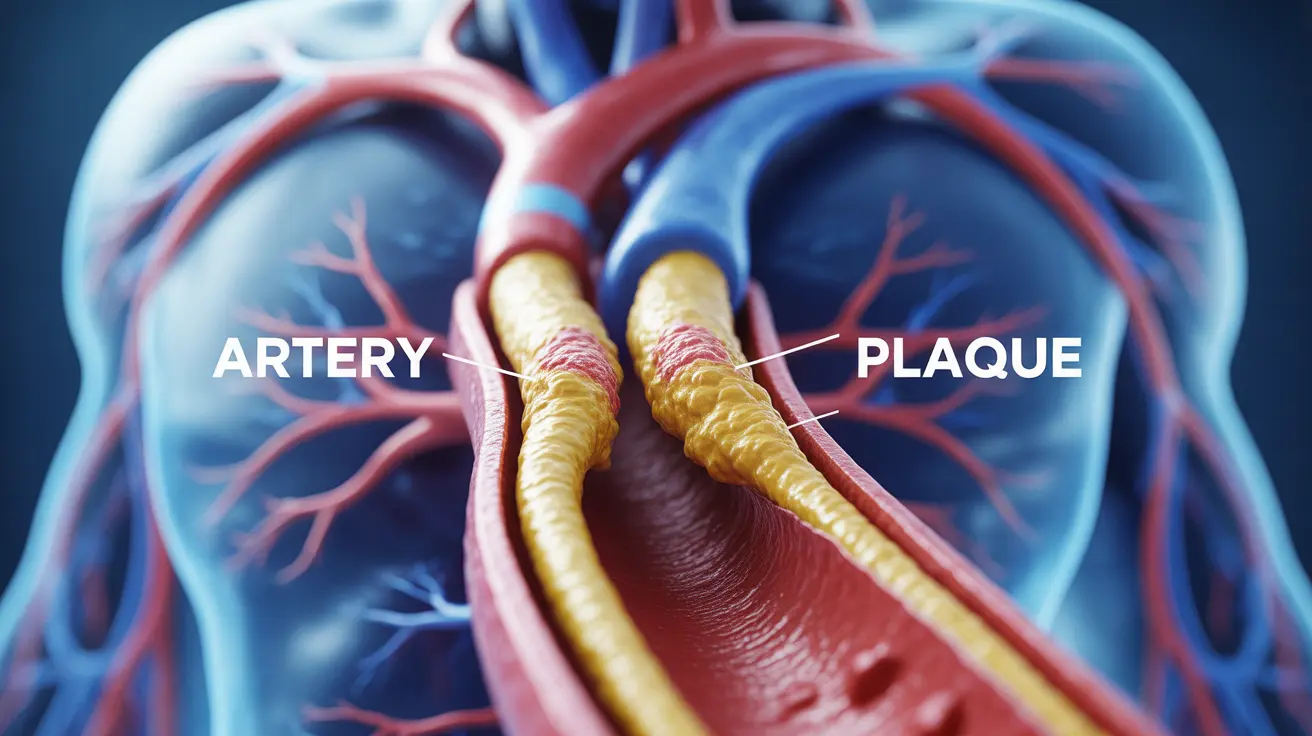
Atherosclerosis is a serious cardiovascular condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque along their walls. This progressive condition can significantly impact blood flow throughout the body, potentially leading to severe health complications if left unmanaged. Understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for both prevention and management.
While atherosclerosis develops gradually over many years, its effects can be far-reaching, affecting various organs and body systems depending on which arteries are involved. Early recognition and intervention are key to preventing serious complications such as heart attacks and strokes.
How Atherosclerosis Develops
The process of atherosclerosis begins when damage occurs to the inner layer of an artery. This damage can be triggered by various factors, including high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, inflammation, and lifestyle choices. Over time, substances like cholesterol, calcium, and cellular debris accumulate in the damaged areas, forming plaque that gradually narrows the arteries.
Common Symptoms Based on Affected Areas
Coronary Artery Symptoms
When atherosclerosis affects the heart's arteries, individuals may experience:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeat
- Fatigue during physical activity
Peripheral Artery Symptoms
Atherosclerosis in limb arteries often causes:
- Leg pain while walking
- Numbness in extremities
- Slow wound healing
- Cold hands or feet
Cerebral Artery Symptoms
When brain arteries are affected, symptoms may include:
- Temporary vision loss
- Difficulty speaking
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Severe headaches
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, some of which can be controlled through lifestyle modifications:
Controllable Risk Factors
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poorly managed diabetes
Preventive Measures
Implementing healthy lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerosis:
- Regular physical activity
- Heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress effectively
- Regular medical check-ups
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use various tests to diagnose and monitor atherosclerosis:
- Blood tests to check cholesterol levels
- Ultrasound imaging
- Cardiac CT scans
- Angiograms
- Stress tests
Treatment Options
Treatment typically involves a combination of approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary changes
- Regular exercise
- Stress management
- Smoking cessation
Medications
- Statins for cholesterol management
- Blood pressure medications
- Anti-platelet drugs
- Beta-blockers
Medical Procedures
- Angioplasty
- Stent placement
- Bypass surgery
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical symptoms of atherosclerosis, and how do they vary depending on the affected arteries?
Symptoms vary based on which arteries are affected. Coronary artery atherosclerosis typically causes chest pain and shortness of breath. Peripheral artery disease leads to leg pain and numbness, while cerebral artery involvement can cause stroke-like symptoms including temporary vision loss and weakness on one side of the body.
How can lifestyle changes like diet and exercise help prevent or manage atherosclerosis?
Regular exercise improves circulation and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels. A heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps manage cholesterol levels. These lifestyle changes, combined with stress management and smoking cessation, can significantly slow the progression of atherosclerosis.
What are the primary risk factors for developing atherosclerosis, and how can they be controlled?
Primary risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. These can be controlled through medication when necessary, regular exercise, healthy diet, weight management, and smoking cessation. Regular medical check-ups help monitor and manage these risk factors effectively.
What are some common diagnostic tests used to detect atherosclerosis, and how do they help in diagnosing the condition?
Common diagnostic tests include blood tests to check cholesterol levels, ultrasound imaging to visualize arteries, cardiac CT scans to detect calcium deposits, angiograms to show blood flow through arteries, and stress tests to evaluate heart function. These tests help determine the presence, location, and severity of arterial blockages.
Can atherosclerosis be reversed, and what treatments are available to slow its progression?
While complete reversal is challenging, atherosclerosis progression can be significantly slowed through a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures. Treatments include cholesterol-lowering medications, blood pressure management, antiplatelet drugs, and surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery when necessary.