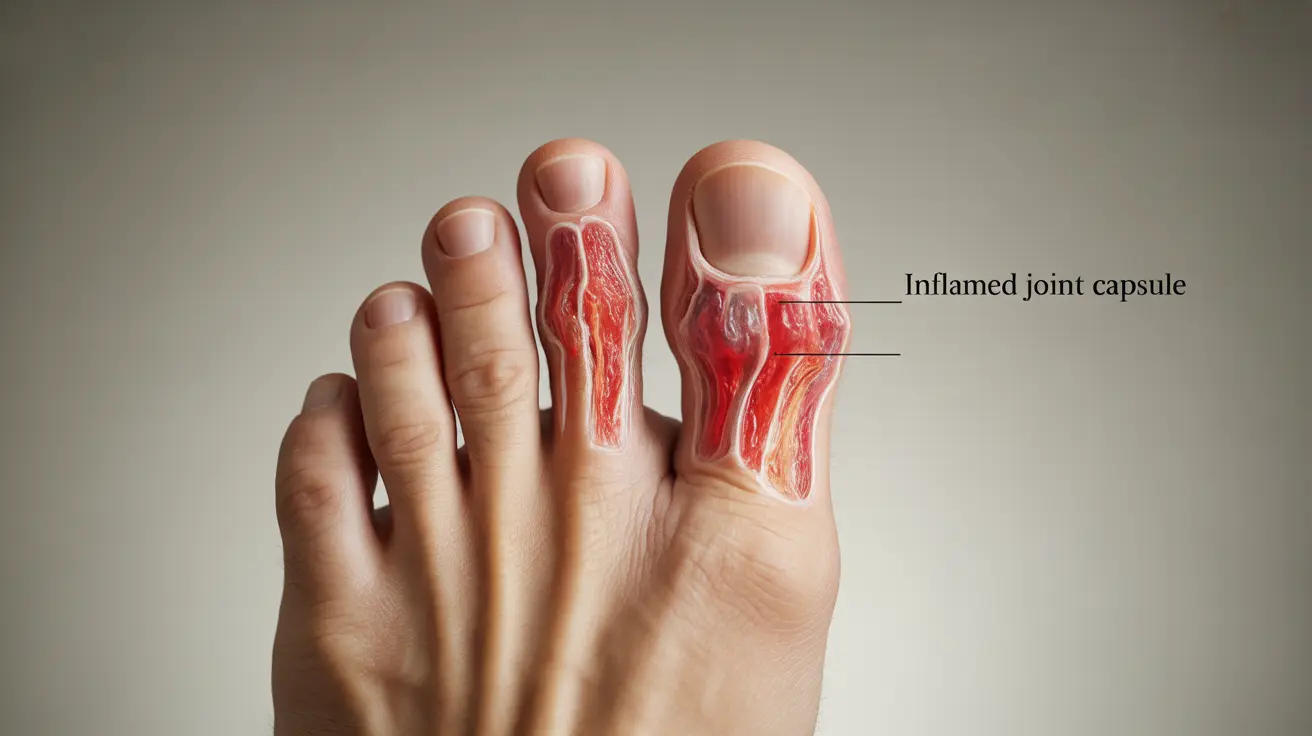
Capsulitis is a painful condition affecting the joints of the toes, particularly the second toe, where inflammation develops in the surrounding ligaments and soft tissue capsule. This condition can significantly impact daily activities and mobility if left untreated. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention.
While capsulitis can affect any toe joint, it most commonly occurs in the second toe, often referred to as second toe capsulitis. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about managing and treating this challenging condition.
Understanding Capsulitis Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the early signs of capsulitis is crucial for prompt treatment and better outcomes. The condition typically develops gradually, with symptoms becoming progressively more noticeable over time.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The primary indicators of capsulitis include:
- Pain under the ball of the foot, especially near the affected toe
- Swelling around the toe joint
- Difficulty wearing shoes comfortably
- Pain that worsens when walking barefoot
- A feeling of walking on a marble or pebble
- Gradual drifting or crossing of the affected toe
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of capsulitis:
Anatomical Factors
- Abnormal foot mechanics
- Second toe longer than the big toe
- High arch or flat feet
- Bunion deformity
External Factors
- Wearing inappropriate footwear
- High-impact activities
- Excessive weight-bearing exercises
- Being overweight or obese
Treatment Approaches for Capsulitis
Conservative Management
Initial treatment typically focuses on non-invasive approaches:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice therapy for inflammation
- Proper footwear selection
- Toe taping or splinting
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications
Medical Interventions
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, medical professionals may recommend:
- Custom orthotics
- Cortisone injections
- Physical therapy
- In severe cases, surgical intervention
Prevention and Long-term Management
Taking proactive steps can help prevent capsulitis or prevent it from worsening:
Footwear Recommendations
- Choose shoes with adequate toe box space
- Avoid high heels over 2 inches
- Use supportive insoles
- Ensure proper shoe fit
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice proper foot exercises
- Avoid activities that cause excessive foot stress
- Regular foot health check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of capsulitis in the foot, and what does it feel like?
Capsulitis typically presents as pain and swelling under the ball of the foot, particularly near the affected toe joint. Patients often describe a sensation of walking on a marble or pebble, and pain tends to worsen when walking barefoot or wearing unsupportive shoes.
What causes capsulitis of the toe, and what activities or conditions increase my risk?
Capsulitis can be caused by abnormal foot mechanics, improper footwear, high-impact activities, and anatomical factors like having a second toe longer than the big toe. Risk increases with obesity, bunion deformities, and activities that put excessive pressure on the ball of the foot.
How do you treat capsulitis at home, and what treatments do doctors recommend?
Home treatments include rest, ice therapy, proper footwear, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications. Medical professionals may recommend custom orthotics, cortisone injections, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Can capsulitis heal on its own, or is medical treatment always needed?
While mild cases of capsulitis may improve with conservative treatment and rest, medical intervention is often necessary to prevent progression and ensure proper healing. Ignoring symptoms can lead to permanent joint damage and deformity.
What kind of shoes and lifestyle changes can help prevent or relieve capsulitis pain?
Wear shoes with adequate toe box space and good arch support, avoid high heels, and use supportive insoles. Maintain a healthy weight, practice foot-strengthening exercises, and modify activities that cause excessive foot stress to help prevent and manage capsulitis.