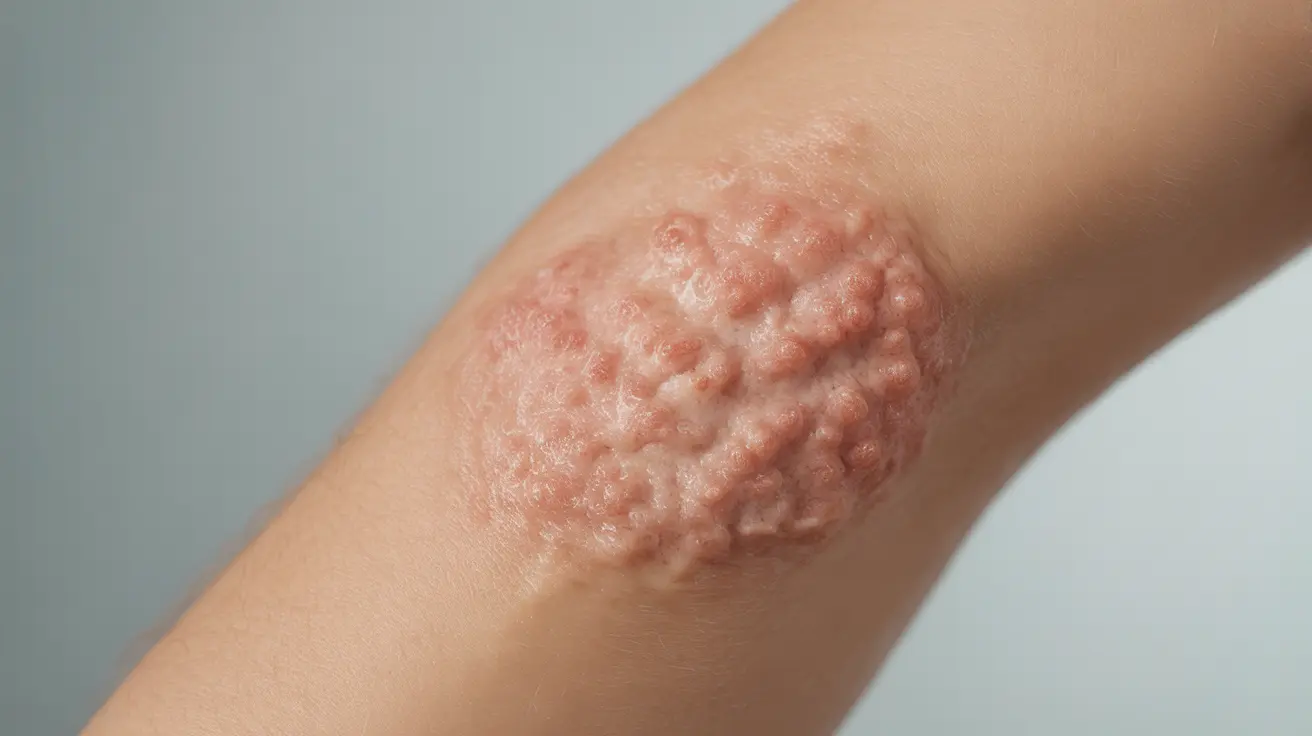
Dermatosis is a broad medical term that encompasses various skin conditions affecting the appearance, texture, or health of the skin. This comprehensive condition can manifest in numerous ways, impacting people of all ages and backgrounds. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and improved quality of life.
Whether you're experiencing skin changes yourself or seeking information for a loved one, this guide will help you understand the complexities of dermatosis and the various ways it can be addressed through medical intervention and lifestyle modifications.
Common Symptoms and Appearance
Dermatosis can present with various symptoms, depending on the specific type and underlying cause. Common manifestations include:
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- Scaling or flaking of the skin surface
- Itching or burning sensations
- Raised bumps or blisters
- Changes in skin texture
- Dry or cracked skin
- Skin thickening
The appearance of these symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, and they may affect different parts of the body. Some forms of dermatosis are localized to specific areas, while others can be more widespread.
Understanding the Causes
Dermatosis can develop due to multiple factors, often working in combination. Key contributors include:
Genetic Factors
Some forms of dermatosis have a hereditary component, making certain individuals more susceptible to developing specific skin conditions based on their genetic makeup.
Environmental Triggers
External factors that can trigger or worsen dermatosis include:
- Exposure to irritants or allergens
- Changes in weather or humidity
- UV radiation exposure
- Chemical exposure
- Occupational factors
Medical Conditions
Various underlying health conditions can contribute to the development of dermatosis, including autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, and certain infections.
Diagnosis and Testing
Healthcare providers typically diagnose dermatosis through a combination of methods:
Physical Examination
A thorough visual inspection of the affected skin areas is usually the first step in diagnosis. Doctors will examine the appearance, distribution, and characteristics of the skin changes.
Diagnostic Tests
When necessary, additional testing may include:
- Skin biopsy
- Blood tests
- Patch testing for allergies
- Wood's lamp examination
- Culture samples for bacterial or fungal infections
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for dermatosis varies depending on the specific type and underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
Medical Treatments
- Topical medications (corticosteroids, antibiotics, or antifungals)
- Oral medications when necessary
- Phototherapy for certain conditions
- Immunomodulating drugs for severe cases
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Care
Supporting medical treatments with lifestyle changes can improve outcomes:
- Regular moisturizing
- Gentle skincare routine
- Avoiding known triggers
- Proper sun protection
- Stress management
- Dietary modifications when relevant
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of dermatosis and how do they look on the skin?
Dermatosis commonly appears as redness, scaling, itching, or changes in skin texture. Symptoms can range from mild discoloration to more severe manifestations like blistering or skin thickening, varying by the specific type of dermatosis.
What are the main causes of dermatosis, and can infections or genes increase my risk?
Dermatosis can be caused by genetic factors, environmental triggers, infections, or underlying medical conditions. Both genetic predisposition and infections can significantly increase the risk of developing certain types of dermatosis.
How is dermatosis diagnosed by doctors, and what tests might be used if symptoms are unclear?
Doctors typically diagnose dermatosis through physical examination and patient history. When symptoms are unclear, they may perform additional tests such as skin biopsies, blood tests, or patch testing to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for dermatosis, and are there home remedies or lifestyle changes that can help?
Treatment options include topical and oral medications, phototherapy, and immunomodulating drugs. Home remedies and lifestyle changes like regular moisturizing, trigger avoidance, and proper skincare can complement medical treatments.
What's the difference between dermatosis and dermatitis, and how are they managed differently?
Dermatosis is a broader term encompassing various skin conditions, while dermatitis specifically refers to skin inflammation. While management strategies may overlap, treatment approaches are tailored to the specific condition and its underlying cause.