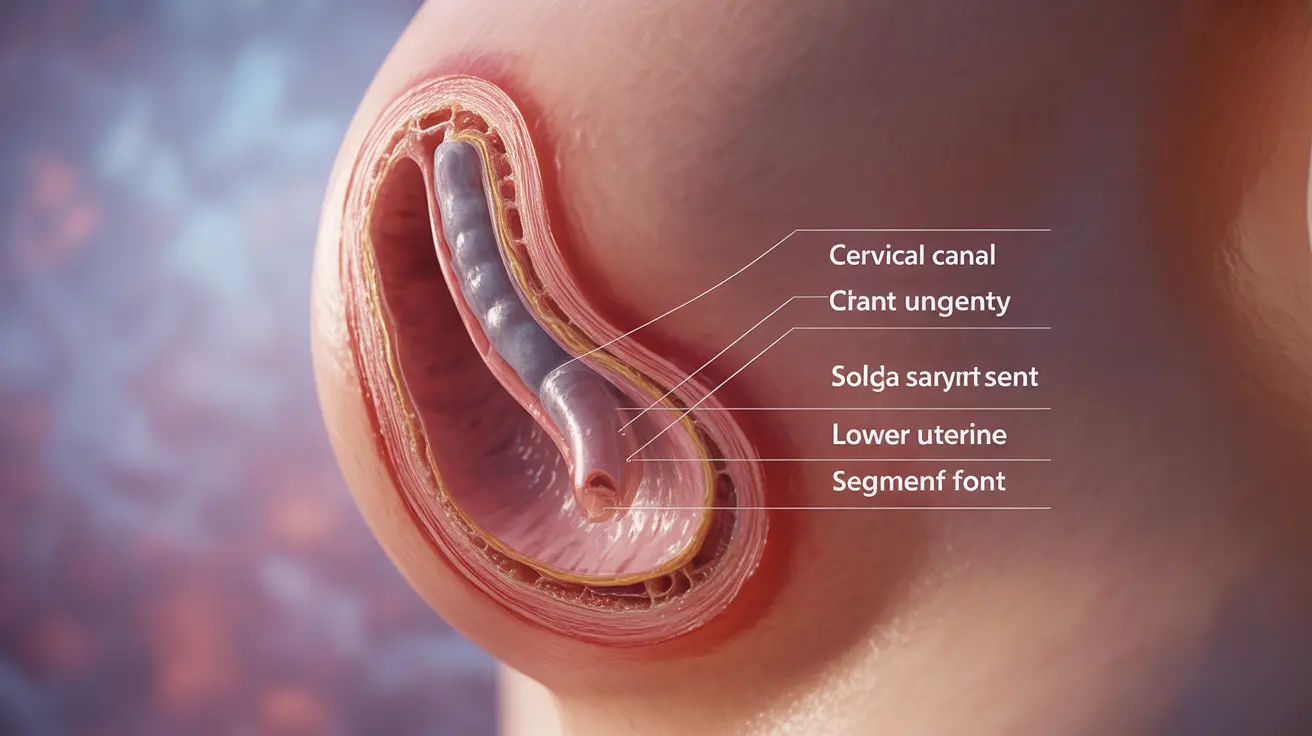
Cervical effacement is one of the most significant changes that occurs in a woman's body as it prepares for childbirth. This natural process involves the thinning and shortening of the cervix, which must occur before labor can progress effectively. Understanding effacement can help expectant mothers better recognize the signs that their bodies are preparing for delivery and feel more confident about the birthing process ahead.
As pregnancy advances toward its conclusion, the cervix undergoes remarkable transformations to facilitate the baby's passage through the birth canal. Effacement works alongside cervical dilation to create the optimal conditions for a successful delivery, making it an essential aspect of labor preparation that every pregnant woman should understand.
What Is Cervical Effacement?
Cervical effacement refers to the gradual thinning and shortening of the cervix that occurs during late pregnancy and early labor. Throughout most of pregnancy, the cervix remains thick, firm, and closed to protect the developing baby and maintain the pregnancy. However, as the body prepares for labor, hormonal changes and increasing pressure from the baby's head cause the cervix to soften and begin effacing.
This process involves the cervical tissue being drawn upward and incorporated into the lower part of the uterus. The cervix, which normally measures about 3 to 4 centimeters in length, gradually becomes thinner until it eventually disappears entirely into the uterine wall. This transformation is essential because it allows the cervix to open more easily during active labor.
Effacement typically begins weeks before active labor starts, especially in first-time mothers. The process is driven by prostaglandins, hormones that soften cervical tissue, and by the mechanical pressure exerted by the baby's presenting part, usually the head, against the cervix.
How Healthcare Providers Measure Effacement
Medical professionals measure cervical effacement as a percentage, with 0% representing a thick, uneffaced cervix and 100% indicating complete effacement. During prenatal appointments and labor assessments, healthcare providers perform cervical examinations to evaluate both effacement and dilation progress.
A cervix that is 50% effaced means it has thinned to half its original thickness, while 100% effacement indicates the cervix has completely thinned out and merged with the uterine wall. At this stage, only the cervical opening remains, which can then dilate fully to allow the baby's passage.
Healthcare providers assess effacement through manual examination, feeling for changes in cervical thickness and consistency. This measurement, combined with dilation assessment, helps determine labor progression and timing for delivery decisions.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Many women experience subtle signs that cervical effacement is occurring, though the process can sometimes happen without noticeable symptoms. Common indicators include increased vaginal discharge, which may appear thicker or tinged with blood as the cervix changes. This discharge, known as the mucus plug, may be released gradually or all at once.
Some women notice mild cramping or pressure in the pelvic area as effacement progresses. These sensations often feel similar to menstrual cramps and may come and go irregularly. Back discomfort, particularly in the lower back, can also accompany cervical changes as the body adjusts to prepare for labor.
Braxton Hicks contractions may become more frequent or intense as effacement advances. While these practice contractions don't typically cause cervical dilation, they can contribute to the effacement process by applying gentle pressure to the cervix over time.
The Relationship Between Effacement and Dilation
While effacement and cervical dilation work together to prepare for childbirth, they represent distinct processes that often occur simultaneously but at different rates. Effacement involves the thinning of cervical tissue, while dilation refers to the opening of the cervical canal to allow the baby's passage.
In first-time mothers, effacement typically occurs before significant dilation begins. The cervix may reach 100% effacement while remaining only minimally dilated. For women who have given birth before, effacement and dilation often happen simultaneously, sometimes making labor progression appear faster.
Both processes are necessary for successful vaginal delivery. A cervix must be sufficiently effaced to dilate effectively, and complete dilation (10 centimeters) requires the cervix to be fully effaced and thinned out. Healthcare providers monitor both measurements to assess labor progress and make decisions about delivery timing and interventions.
Risks of Premature Effacement
When cervical effacement occurs too early in pregnancy, it can lead to complications including preterm labor and delivery. Premature effacement, particularly when accompanied by dilation before 37 weeks of pregnancy, may result in cervical insufficiency, a condition where the cervix cannot maintain the pregnancy to full term.
Risk factors for early effacement include previous cervical procedures, multiple pregnancies, infections, and certain medical conditions. Women with a history of preterm birth or cervical procedures should receive close monitoring throughout pregnancy to detect early cervical changes.
If premature effacement is detected, healthcare providers may recommend interventions such as bed rest, cervical cerclage (a surgical procedure to reinforce the cervix), or medications to delay labor. Early detection and management are crucial for preventing preterm delivery and ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and baby.
Supporting Natural Effacement
While effacement is a natural process that cannot be forced, certain activities may support healthy cervical changes as pregnancy progresses to term. Gentle exercise, such as walking, can help maintain optimal positioning for the baby and may encourage natural effacement through gravity and movement.
Prenatal yoga and specific stretches can promote relaxation and optimal pelvic positioning. However, it's important to avoid activities specifically intended to induce labor before the pregnancy reaches full term, as these may lead to complications.
Adequate rest, proper nutrition, and stress management support overall pregnancy health and may contribute to normal effacement timing. Regular prenatal care allows healthcare providers to monitor cervical changes and provide guidance specific to individual circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does cervical effacement mean and how does it prepare the body for labor?
Cervical effacement is the process where the cervix gradually thins out and shortens during late pregnancy and early labor. This preparation allows the cervix to open more easily during active labor by softening and drawing the cervical tissue upward into the uterine wall, creating optimal conditions for the baby's passage through the birth canal.
How is cervical effacement measured and what does 100% effacement mean?
Healthcare providers measure effacement as a percentage through manual cervical examination. Zero percent represents a thick, uneffaced cervix, while 100% effacement means the cervix has completely thinned out and merged with the uterine wall, leaving only the cervical opening that can then dilate for delivery.
What are the signs and symptoms that cervical effacement is happening?
Signs of effacement include increased vaginal discharge (possibly tinged with blood), mild pelvic cramping or pressure similar to menstrual cramps, lower back discomfort, and more frequent or intense Braxton Hicks contractions. Some women may experience these symptoms gradually, while others notice few changes.
What is the difference between cervical effacement and dilation during labor?
Effacement refers to the thinning of cervical tissue, while dilation involves the opening of the cervical canal. In first-time mothers, effacement typically occurs before significant dilation, whereas women who have given birth before often experience both processes simultaneously. Both are necessary for successful vaginal delivery.
Can cervical effacement happen too early and what are the risks?
Yes, premature effacement before 37 weeks can lead to preterm labor and delivery complications. Risk factors include previous cervical procedures, multiple pregnancies, and infections. Early effacement may require interventions such as bed rest, cervical cerclage, or medications to delay labor and prevent preterm birth.