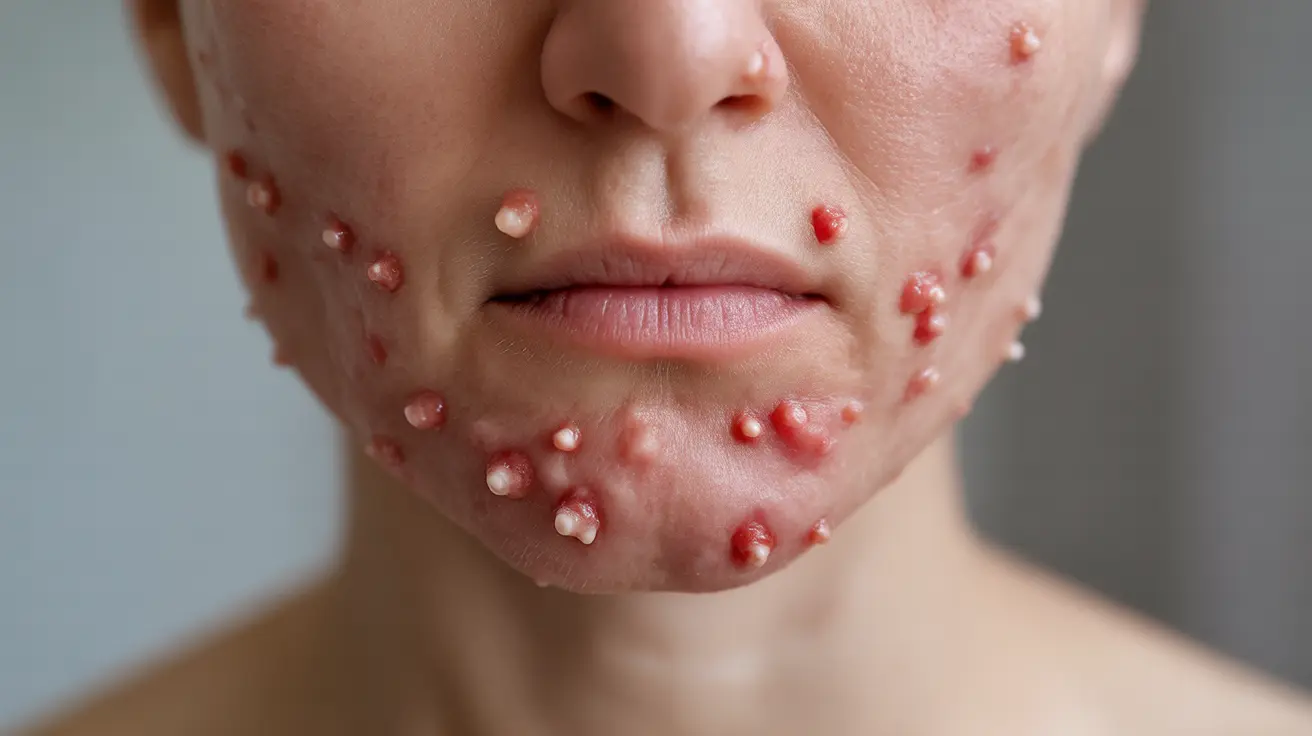
Folliculitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become infected or inflamed. This condition can affect anyone, appearing anywhere on the body where hair grows, but it's particularly common in areas subject to friction, sweating, or frequent shaving. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention.
While folliculitis often resolves on its own with proper care, knowing when to seek medical attention and how to prevent recurrences can significantly impact your skin health and overall well-being. Let's explore this condition in detail, from identification to treatment strategies.
Understanding Folliculitis and Its Types
Folliculitis presents as small, red, and sometimes painful bumps centered around hair follicles. The condition can be classified into several types, depending on the underlying cause and depth of inflammation:
- Superficial folliculitis (affecting the upper part of the hair follicle)
- Deep folliculitis (involving the entire hair follicle)
- Hot tub folliculitis (caused by bacterial contamination)
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae (often caused by ingrown hairs)
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what triggers folliculitis can help in both treatment and prevention. Common causes include:
- Bacterial infections (especially Staphylococcus aureus)
- Fungal infections
- Physical damage to hair follicles
- Tight clothing or equipment that causes friction
- Extended exposure to hot tubs or pools with improper chemical balance
- Certain medications or medical conditions
Recognizing Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of folliculitis can vary in severity but typically include:
- Clusters of small, red bumps or white-headed pimples
- Itching or burning sensation
- Tender or painful skin
- Possible spreading or worsening of existing bumps
- Potential scarring in severe cases
Diagnosis and Differentiation
While folliculitis may resemble other skin conditions, certain characteristics help distinguish it. Healthcare providers typically diagnose folliculitis through:
- Physical examination of the affected area
- Review of medical history and potential triggers
- Sometimes, laboratory testing of skin samples
- Assessment of pattern and distribution of lesions
Treatment Approaches
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Many cases of mild folliculitis respond well to home treatment methods:
- Warm compresses to relieve discomfort
- Gentle cleansing with antibacterial soap
- Over-the-counter antibiotic ointments
- Avoiding tight clothing and irritants
Medical Treatments
More severe or persistent cases may require professional medical intervention:
- Prescription oral or topical antibiotics
- Antifungal medications for fungal folliculitis
- Specialized medicated shampoos or body washes
- In rare cases, laser hair removal for chronic conditions
Prevention Strategies
Preventing folliculitis involves several key practices:
- Using clean, sharp razors and proper shaving technique
- Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing
- Maintaining good hygiene, especially in hot, humid conditions
- Regular cleaning of hot tubs and pools
- Avoiding sharing personal care items
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes and symptoms of folliculitis?
The most common causes include bacterial infections, friction from tight clothing, and damage from shaving. Primary symptoms include clusters of red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles, itching, and tenderness.
How is folliculitis diagnosed and how can I tell it apart from acne or other skin conditions?
Folliculitis is diagnosed through physical examination and sometimes laboratory testing. Unlike acne, folliculitis bumps are always centered around hair follicles and often appear in clusters in areas subject to friction or shaving.
What treatments are effective for bacterial versus fungal folliculitis?
Bacterial folliculitis typically responds to antibiotic treatments, while fungal folliculitis requires antifungal medications. The specific treatment approach depends on the confirmed cause and severity of the condition.
How can I prevent folliculitis caused by shaving or wearing tight clothing?
Use proper shaving techniques with clean, sharp razors, shave in the direction of hair growth, and wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing. Always keep skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to sweating.
When should I see a doctor for folliculitis that is severe, spreading, or recurrent?
Seek medical attention if folliculitis persists beyond a week, spreads, causes severe pain or fever, or returns frequently. Also consult a healthcare provider if home remedies aren't effective or if you develop large, painful bumps or scarring.