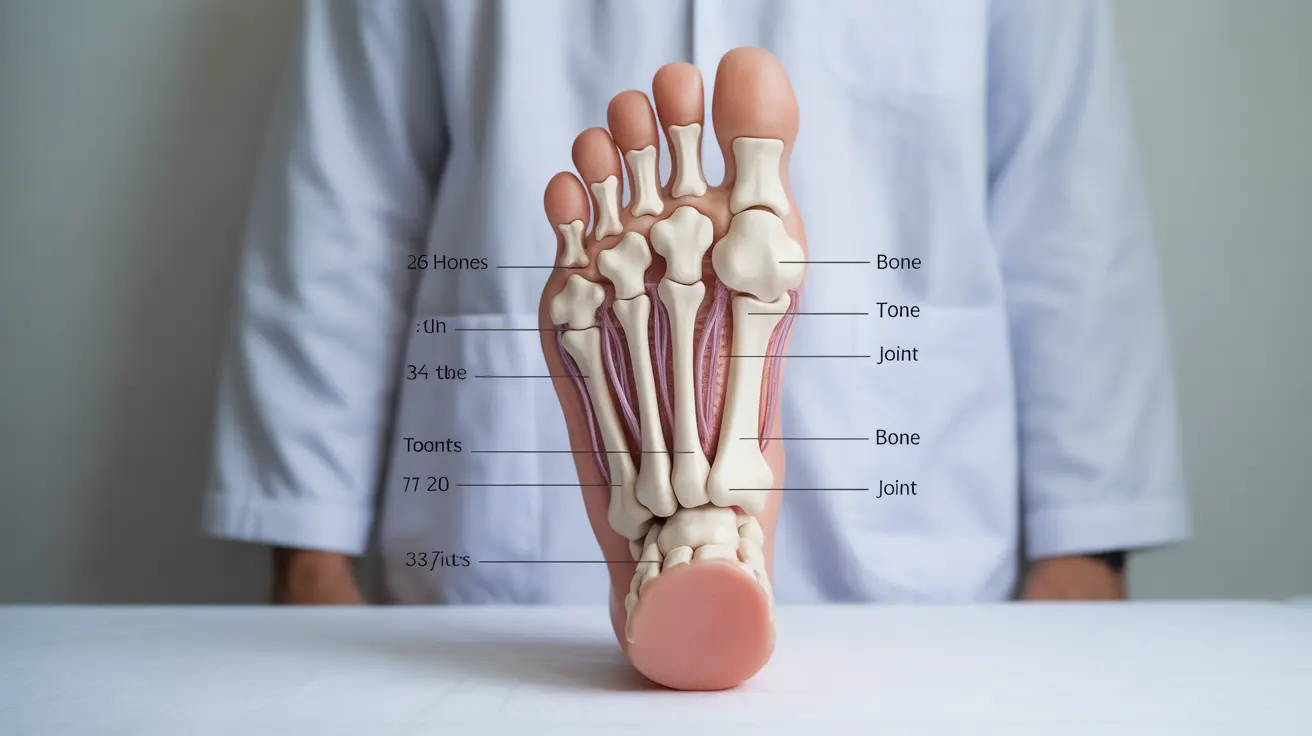
The human foot is a remarkable feat of biological engineering, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This complex structure supports our entire body weight, facilitates movement, and helps maintain balance in our daily activities. Understanding foot anatomy is crucial for anyone interested in foot health, whether you're an athlete, healthcare professional, or someone experiencing foot problems.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the intricate components of foot anatomy, their functions, and how they work together to keep us mobile and stable. We'll also examine common foot problems and the importance of anatomical knowledge in treating foot conditions.
The Structural Framework of the Foot
The foot's structure can be divided into three main sections: the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot. Each section plays a vital role in supporting body weight and enabling movement.
Forefoot Structure
The forefoot contains the metatarsal bones and phalanges (toes). The five metatarsals form the ball of the foot, while the fourteen phalanges make up the toes. This section is crucial for push-off during walking and running.
Midfoot Architecture
The midfoot consists of five tarsal bones that form the foot's arch. These bones act as a shock absorber and help distribute weight evenly across the foot during movement.
Hindfoot Components
The hindfoot includes the talus and calcaneus (heel bone). The talus connects the foot to the ankle, while the calcaneus forms the heel and bears much of our body weight when standing.
The Dynamic Arch System
The foot contains three distinct arches: the medial longitudinal arch, lateral longitudinal arch, and transverse arch. These architectural marvels provide essential support and flexibility during movement.
Functions of the Arch System
The arches help absorb shock during walking and running, store energy for propulsion, and adapt to different surface conditions. They also play a crucial role in maintaining balance and distributing body weight effectively.
Muscular and Tendon Network
The foot's complex network of muscles and tendons enables precise movements and maintains stability. Key structures include the Achilles tendon, plantar fascia, and various intrinsic foot muscles.
Essential Tendons and Ligaments
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel, while the plantar fascia supports the arch and aids in push-off. Numerous ligaments provide stability and maintain proper foot alignment.
Common Anatomical Issues and Prevention
Understanding foot anatomy helps identify and prevent various foot problems. Common issues include flat feet (fallen arches), high arches, plantar fasciitis, and bunions. Proper footwear, regular stretching, and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent many foot problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What bones and joints make up the different parts of the foot and what are their functions? A: The foot contains 26 bones and 33 joints divided into three sections: the forefoot (metatarsals and phalanges for push-off), midfoot (tarsal bones for shock absorption), and hindfoot (talus and calcaneus for weight-bearing and ankle connection).
Q: How do the arches of the foot support balance and absorb shock during movement? A: The foot's three arches work together to distribute weight, absorb impact, and provide stability. They flex and recoil during movement, storing and releasing energy while adapting to different surfaces and maintaining balance.
Q: What muscles and tendons are involved in foot movement and how do they maintain foot stability? A: The foot contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles, along with tendons like the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia. These structures work together to control movement, maintain arch height, and provide stability during walking and standing.
Q: What common foot problems are linked to issues with foot anatomy and how can they be prevented? A: Common anatomical issues include flat feet, high arches, plantar fasciitis, and bunions. Prevention strategies include wearing proper footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, regular stretching, and strengthening exercises.
Q: How does understanding foot anatomy help in diagnosing and treating foot injuries or pain? A: Knowledge of foot anatomy helps healthcare providers accurately identify the source of pain or injury, determine appropriate treatment methods, and develop effective rehabilitation plans. It also aids in selecting proper footwear and orthotic devices when needed.