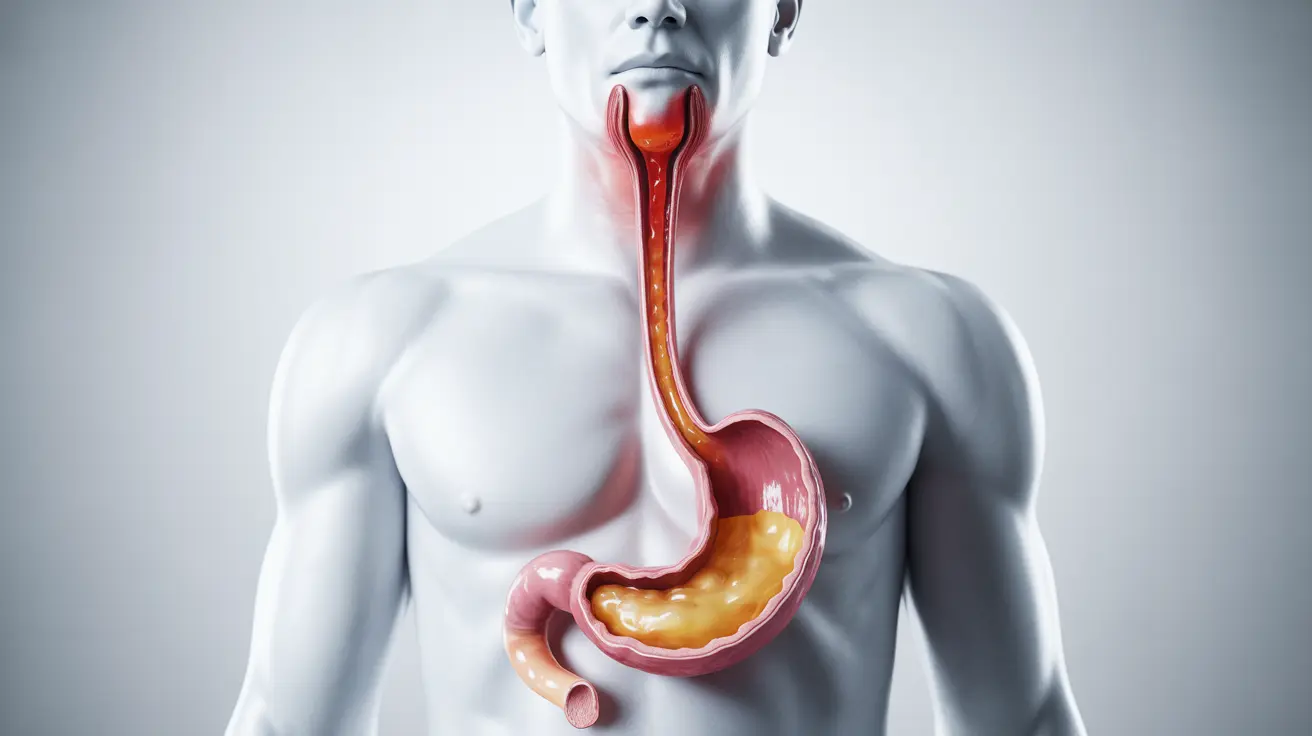
Heartburn affects millions of Americans, causing that familiar burning sensation in the chest that can make eating and daily activities uncomfortable. While the name might suggest a heart problem, heartburn actually occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, creating irritation and discomfort. Understanding this common condition is crucial for effective management and knowing when to seek medical attention.
Whether you experience heartburn occasionally or frequently, this guide will help you recognize symptoms, identify triggers, and discover effective treatment options. We'll also explore when heartburn might signal a more serious condition requiring medical evaluation.
Common Symptoms and Recognition
The primary symptom of heartburn is a burning sensation that typically begins in the chest, behind the breastbone. This discomfort may:
- Worsen when lying down or bending over
- Last for several hours
- Intensify after eating
- Move upward toward your throat
- Be accompanied by a bitter or sour taste in your mouth
Some people also experience difficulty swallowing, chronic cough, or the sensation of food stuck in their throat. Understanding these symptoms helps distinguish heartburn from other conditions and guides appropriate treatment choices.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors
Certain foods and lifestyle habits frequently trigger heartburn episodes. Common dietary triggers include:
- Spicy, fatty, or acidic foods
- Citrus fruits and tomatoes
- Chocolate and mint
- Coffee and alcoholic beverages
- Large or late-night meals
Lifestyle factors that can increase your risk of heartburn include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Eating close to bedtime
- Wearing tight-fitting clothes
Treatment Options and Relief Strategies
Several effective treatment approaches exist for managing heartburn, ranging from lifestyle modifications to medication. Over-the-counter options include:
- Antacids for quick, temporary relief
- H2 blockers to reduce acid production
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) for more persistent symptoms
For immediate relief, try these natural approaches:
- Remaining upright for at least three hours after eating
- Elevating the head of your bed
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes
- Chewing sugar-free gum after meals
- Drinking ginger tea
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional heartburn is common, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation:
- Persistent heartburn that doesn't respond to over-the-counter medications
- Difficulty swallowing or painful swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath or arm pain
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
Prevention Strategies
Preventing heartburn often involves making sustainable lifestyle changes:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoiding known trigger foods
- Not lying down for 2-3 hours after eating
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of heartburn and how can I recognize them?
The most common symptoms include a burning sensation in the chest, difficulty swallowing, and a sour taste in the mouth. The discomfort typically worsens when lying down or after meals and can last for several hours.
What foods and lifestyle habits commonly trigger heartburn?
Common triggers include spicy foods, citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee, and large meals. Lifestyle habits like eating late at night, smoking, and being overweight can also contribute to frequent heartburn episodes.
How can I treat heartburn at home and what over-the-counter medications work best?
Over-the-counter treatments include antacids for quick relief, H2 blockers, and PPIs for longer-term management. Natural remedies like elevating your head while sleeping and avoiding trigger foods can also help manage symptoms.
When should I see a doctor because my heartburn might be more serious?
Seek medical attention if you experience persistent heartburn unresponsive to over-the-counter medications, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, or chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent frequent heartburn and acid reflux?
Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, not lying down after eating, quitting smoking, and managing stress effectively.