The sensation of heavy legs can significantly impact your daily activities, making simple tasks like walking up stairs or standing for extended periods feel exhausting. This common condition affects millions of people and can range from mild discomfort to debilitating symptoms that interfere with quality of life.
Heavy legs often signal underlying circulatory issues or venous insufficiency, but the good news is that many cases can be effectively managed through lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, or a combination of both. Understanding the root causes and available treatment options is essential for finding relief and preventing the condition from worsening.
What Causes Heavy Legs?
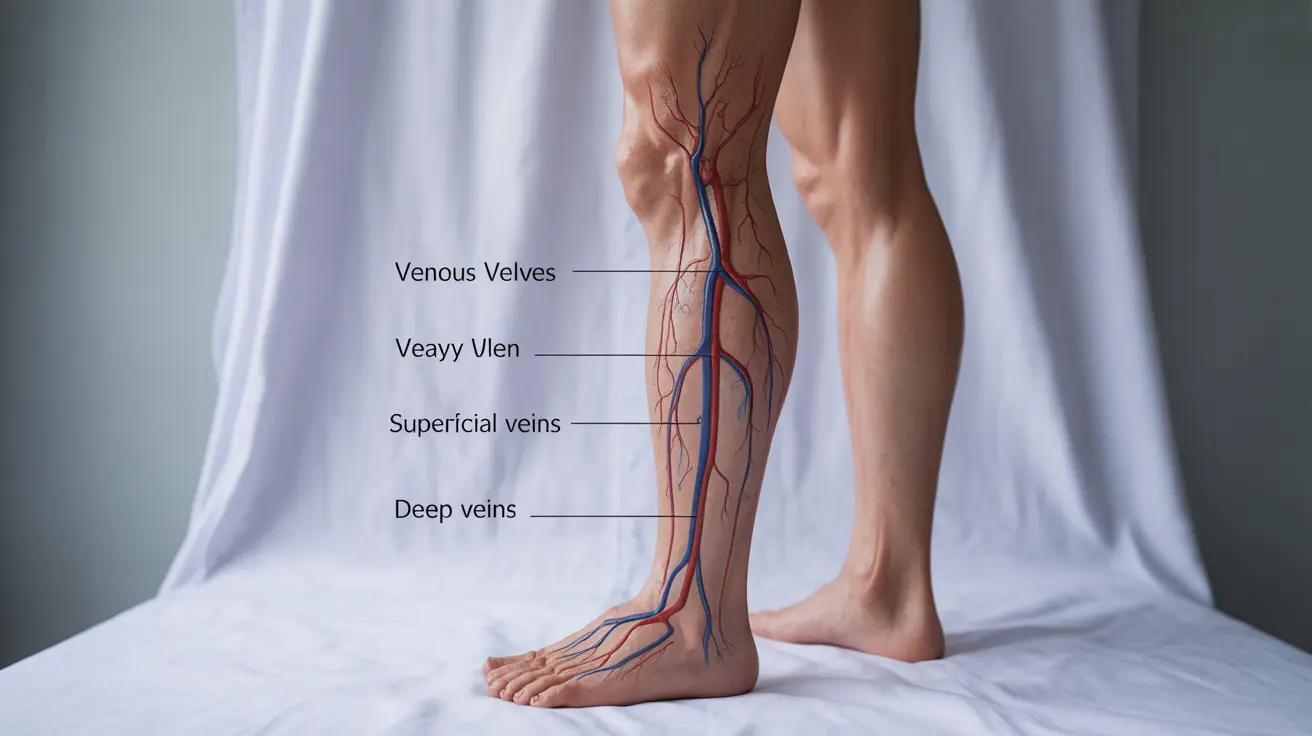
The feeling of heaviness in your legs typically stems from problems with blood circulation, particularly when blood has difficulty returning from the lower extremities back to the heart. This condition, known as venous insufficiency, occurs when the valves in your leg veins become weakened or damaged, causing blood to pool in the lower legs.
Several medical conditions can contribute to heavy legs. Varicose veins are among the most common culprits, developing when vein walls weaken and valves fail to function properly. Deep vein thrombosis, a serious condition involving blood clots in deep veins, can also cause leg heaviness along with swelling and pain.
Peripheral artery disease affects the arteries that supply blood to your legs, reducing oxygen-rich blood flow and creating sensations of heaviness, especially during physical activity. Heart conditions, kidney disease, and liver problems can also lead to fluid retention and the accompanying heavy leg sensation.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Understanding your risk factors for developing heavy legs can help you take proactive steps toward prevention. Age is a significant factor, as vein walls naturally lose elasticity over time, and valve function may deteriorate. Women face higher risks due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause, which can affect circulation.
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in leg heaviness. Prolonged sitting or standing, particularly in occupations that require maintaining one position for hours, can impair circulation. Excess weight puts additional pressure on leg veins, while a sedentary lifestyle weakens the muscle pump that helps blood return to the heart.
Prevention strategies focus on improving circulation and reducing strain on leg veins. Regular exercise, particularly activities that engage the calf muscles like walking or swimming, helps maintain healthy blood flow. Elevating your legs above heart level when resting allows gravity to assist blood return, while avoiding prolonged periods in one position prevents blood pooling.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Modifications
Many people find significant relief from heavy legs through simple home remedies and lifestyle adjustments. Compression stockings are among the most effective tools, providing graduated pressure that helps blood flow upward from the legs. These specially designed garments are available in various compression levels, from mild support hosiery to medical-grade compression wear.
Exercise modifications can make a substantial difference in managing symptoms. Low-impact activities like walking, cycling, or swimming promote circulation without putting excessive strain on leg veins. Simple exercises like calf raises, ankle pumps, and leg elevation can be performed throughout the day to combat the effects of prolonged sitting or standing.
Dietary changes may also help reduce leg heaviness. Limiting sodium intake helps prevent fluid retention, while staying well-hydrated supports healthy circulation. Foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, such as berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish, may support vascular health.
Medical Treatment Options
When home remedies prove insufficient, various medical treatments can address the underlying causes of heavy legs. Prescription-strength compression therapy offers more significant pressure than over-the-counter options and may be necessary for severe cases of venous insufficiency.
Minimally invasive procedures have revolutionized the treatment of varicose veins and underlying venous problems. Endovenous laser therapy uses laser energy to close problematic veins, while radiofrequency ablation achieves similar results using radiofrequency waves. Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution that causes damaged veins to close and eventually disappear.
For cases involving arterial problems, treatments may focus on improving blood flow through medications that help dilate blood vessels or prevent blood clots. In severe cases of peripheral artery disease, surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore adequate blood flow.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
While mild leg heaviness may respond well to home treatment, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical attention. Seek immediate care if you experience sudden onset of severe leg pain, significant swelling, warmth or redness in the leg, or difficulty breathing, as these may indicate a blood clot.
Schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider if heavy legs persist despite lifestyle modifications, worsen over time, or interfere with daily activities. Additional concerning symptoms include skin changes, leg ulcers, or pain that occurs with walking and improves with rest, which may suggest peripheral artery disease.
A thorough evaluation typically includes a physical examination, medical history review, and potentially diagnostic tests such as duplex ultrasound to assess blood flow and detect any structural problems in the veins or arteries. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes and can prevent complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of heavy legs and how do they affect circulation?
Common causes of heavy legs include venous insufficiency, varicose veins, deep vein thrombosis, and peripheral artery disease. These conditions affect circulation by impairing blood flow back to the heart or reducing arterial blood supply to the legs. When vein valves malfunction, blood pools in the lower legs, creating pressure and heaviness. Similarly, arterial problems reduce oxygen delivery to leg muscles, causing fatigue and discomfort during activity.
How can I relieve the sensation of heavy legs at home through lifestyle changes or compression stockings?
Home relief strategies include wearing graduated compression stockings, which provide external pressure to help blood flow upward. Elevate your legs above heart level for 15-20 minutes several times daily, engage in regular low-impact exercise like walking or swimming, and perform simple leg exercises throughout the day. Maintain a healthy weight, stay hydrated, limit sodium intake, and avoid prolonged sitting or standing to improve circulation naturally.
When should I see a doctor for persistent heavy legs and what medical treatments are available?
Consult a doctor if heavy legs persist despite home treatments, worsen over time, or include symptoms like severe swelling, skin changes, or leg ulcers. Seek immediate care for sudden severe pain, warmth, redness, or breathing difficulties. Medical treatments include prescription compression therapy, minimally invasive procedures like endovenous laser therapy or sclerotherapy for varicose veins, medications for arterial problems, and surgical interventions for severe cases.
Can varicose veins or peripheral artery disease cause heavy legs, and how are these conditions diagnosed?
Yes, both conditions commonly cause heavy legs. Varicose veins result from weakened vein walls and faulty valves, causing blood pooling and heaviness. Peripheral artery disease reduces arterial blood flow, leading to muscle fatigue and heaviness during activity. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, medical history, and duplex ultrasound to visualize blood flow and detect structural abnormalities. Additional tests like ankle-brachial index may assess arterial circulation.
What risk factors increase the likelihood of developing heavy legs, and how can I prevent it?
Risk factors include advancing age, female gender, pregnancy, prolonged sitting or standing, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of vein problems, and certain medical conditions. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining active lifestyle with regular exercise, avoiding prolonged static positions, maintaining healthy weight, wearing supportive footwear, staying hydrated, and using compression stockings if you have risk factors or early symptoms.