Hip pain can significantly impact your daily life, affecting everything from walking and climbing stairs to simply getting out of bed. Whether you're experiencing occasional discomfort or chronic pain, understanding the causes, treatments, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining your mobility and quality of life.
This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of hip pain, including common causes, effective treatments, and when to seek medical attention. We'll also discuss practical strategies to manage and prevent hip pain through lifestyle modifications and targeted exercises.
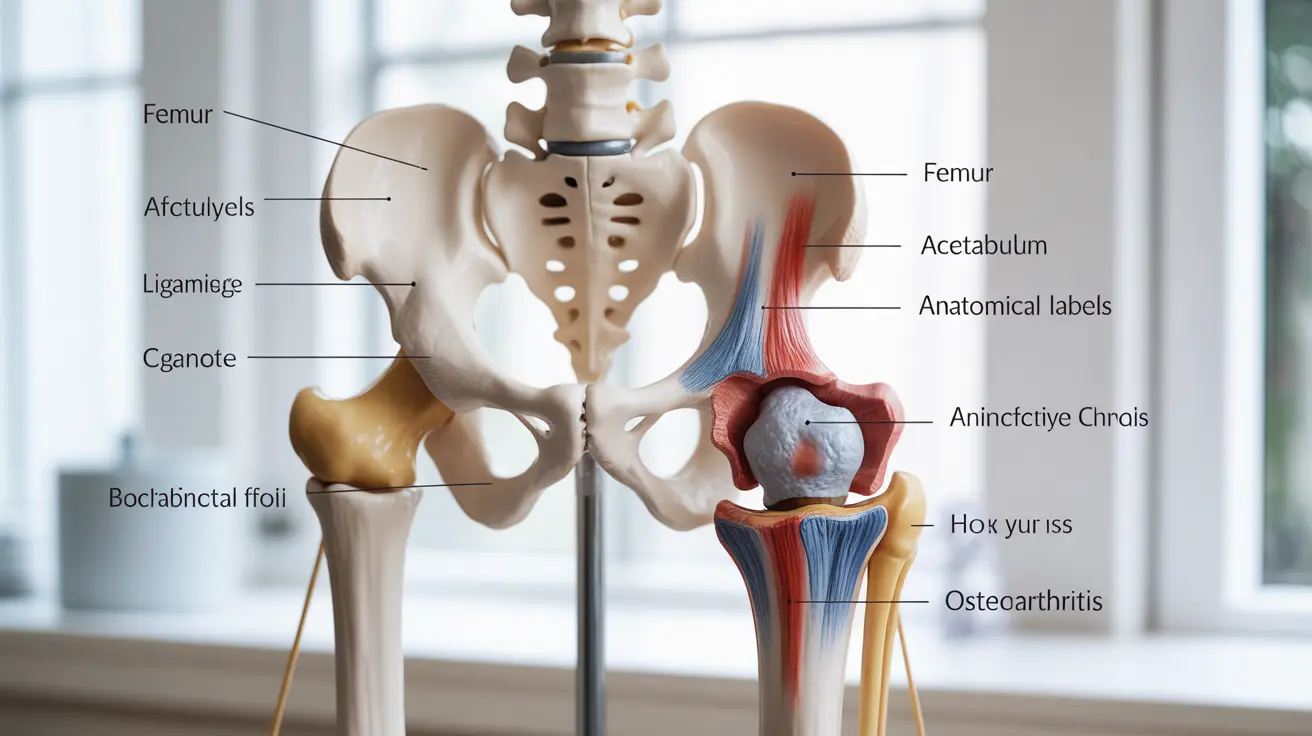
Common Causes of Hip Pain
Hip pain can stem from various conditions and factors, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. Understanding these causes is the first step in finding effective relief:
Arthritis
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are leading causes of hip pain, particularly in older adults. These conditions cause inflammation and deterioration of the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
Injuries and Trauma
Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can cause hip pain through:
- Fractures
- Sprains and strains
- Bursitis
- Tendinitis
- Labral tears
Other Medical Conditions
Several other conditions can contribute to hip pain:
- Sciatica
- Hip impingement
- Avascular necrosis
- Bone tumors (rare)
- Referred pain from back problems
Treatment Options for Hip Pain
Treatment approaches vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of hip pain. Common treatment options include:
Conservative Treatments
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice or heat therapy
- Over-the-counter pain medications
- Prescription anti-inflammatory drugs
- Supportive devices like canes or walkers
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in hip pain management through:
- Targeted stretching exercises
- Strength training
- Range of motion exercises
- Gait training
- Manual therapy techniques
Advanced Treatment Options
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, healthcare providers might recommend:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Platelet-rich plasma therapy
- Surgery (in severe cases)
- Joint replacement surgery
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
Taking proactive steps can help prevent hip pain or reduce its impact:
Exercise and Movement
- Maintain a regular exercise routine
- Focus on low-impact activities
- Include flexibility and strength training
- Practice proper form during physical activities
- Avoid overexertion
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on hip joints and can prevent or alleviate pain. Even modest weight loss can make a significant difference in symptoms.
Ergonomic Considerations
- Use proper posture when sitting and standing
- Ensure your workspace is ergonomically arranged
- Wear appropriate footwear
- Use proper lifting techniques
When to Seek Medical Attention
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe pain following an injury
- Inability to bear weight on the affected hip
- Significant swelling or redness
- Signs of infection (fever, chills)
- Progressive weakness or numbness
- Pain that significantly impacts daily activities
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of hip pain and how can I identify them?
The most common causes include arthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, and injuries. Each condition typically presents with specific symptoms: arthritis causes chronic pain and stiffness, bursitis often results in sharp pain on the outside of the hip, and injuries usually cause sudden, acute pain with specific triggers.
What treatments are available for hip pain caused by arthritis or injury?
Treatment options range from conservative approaches like medication and physical therapy to more advanced interventions such as injections or surgery. The specific treatment plan depends on the cause and severity of the pain.
How can physical therapy help relieve hip pain and improve mobility?
Physical therapy helps through targeted exercises that strengthen supporting muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance range of motion. Therapists also teach proper movement patterns and provide techniques for pain management.
When should I see a doctor for hip pain, and what are the warning signs for urgent medical attention?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, inability to move the hip, significant swelling, or signs of infection. Chronic pain that interferes with daily activities also warrants medical evaluation.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent or reduce hip pain over time?
Key lifestyle modifications include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly with proper form, using good posture, wearing appropriate footwear, and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain. Regular stretching and strength training can also help prevent hip problems.