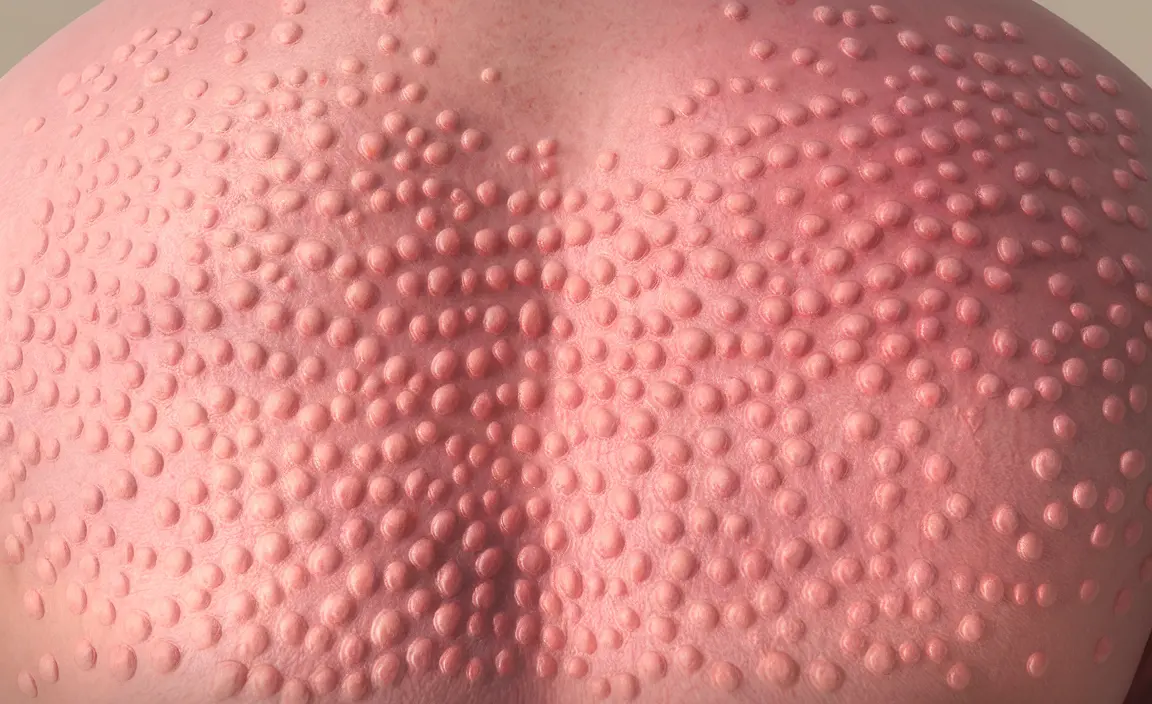
Hives, also known as urticaria, are itchy, raised welts on the skin that can appear suddenly and cause significant discomfort. These distinctive skin reactions affect millions of people worldwide and can range from mild, temporary outbreaks to severe, chronic conditions requiring medical attention.
Whether you're experiencing hives for the first time or dealing with recurring episodes, understanding their causes, treatments, and warning signs is crucial for effective management. This comprehensive guide will address common concerns and provide evidence-based information about this common skin condition.
What Causes Hives to Develop?
Hives occur when your body releases histamine and other chemicals in response to various triggers. These substances cause small blood vessels to leak, leading to swelling in the skin. Common triggers include:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings
- Physical stimuli like pressure, cold, heat, or exercise
- Stress or emotional factors
- Infections and illnesses
- Exposure to certain plants or chemicals
- Autoimmune conditions
Understanding your specific triggers is essential for preventing future outbreaks and managing symptoms effectively.
Home Treatment and Relief Options
While hives can be uncomfortable, several home remedies and over-the-counter treatments can help provide relief:
- Cool compresses to reduce itching and inflammation
- Over-the-counter antihistamines
- Loose, comfortable clothing
- Lukewarm baths with colloidal oatmeal
- Avoiding hot showers and harsh soaps
These measures can help manage symptoms while the hives naturally resolve or until you can seek medical attention if needed.
Warning Signs and Emergency Symptoms
While most cases of hives are not dangerous, some situations require immediate medical attention. Watch for these warning signs:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Dizziness or fainting
- Severe chest tightness
- Rapid pulse
These symptoms could indicate anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires emergency treatment.
The Connection Between Infections and Hives
Various infections, including viral infections like the common cold, COVID-19, and bacterial infections, can trigger hives. This occurs because infections activate your immune system, which can lead to skin reactions as part of the body's defense response.
These infection-related hives typically resolve as the underlying infection clears, though treatment may be needed to manage symptoms in the meantime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are hives contagious or can they spread from person to person? No, hives are not contagious and cannot spread from one person to another. They are an individual allergic or immune response to specific triggers.
What are the most common causes and triggers of hives? The most common triggers include allergic reactions to foods, medications, or insect stings; physical stimuli like pressure or temperature changes; stress; infections; and exposure to certain environmental factors.
How can I treat and relieve the itching from hives at home? You can manage hive symptoms at home using cool compresses, over-the-counter antihistamines, wearing loose clothing, taking lukewarm oatmeal baths, and avoiding known triggers.
When should I see a doctor for hives or seek emergency care? Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, throat swelling, dizziness, or chest tightness. Also consult a doctor if hives persist for more than six weeks or if over-the-counter treatments aren't effective.
Can infections like colds or COVID-19 cause hives to appear? Yes, various infections, including colds and COVID-19, can trigger hives as part of the body's immune response. These hives typically resolve as the infection clears up.