Joint hyperextension occurs when a joint moves beyond its normal range of motion in a backward direction, potentially leading to injury and pain. This common orthopedic issue can affect various joints in the body, most notably the knee, elbow, and fingers, and often happens during sports activities or accidents.
Whether you're an athlete concerned about injury prevention or someone recovering from a hyperextension injury, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining joint health and preventing long-term complications.
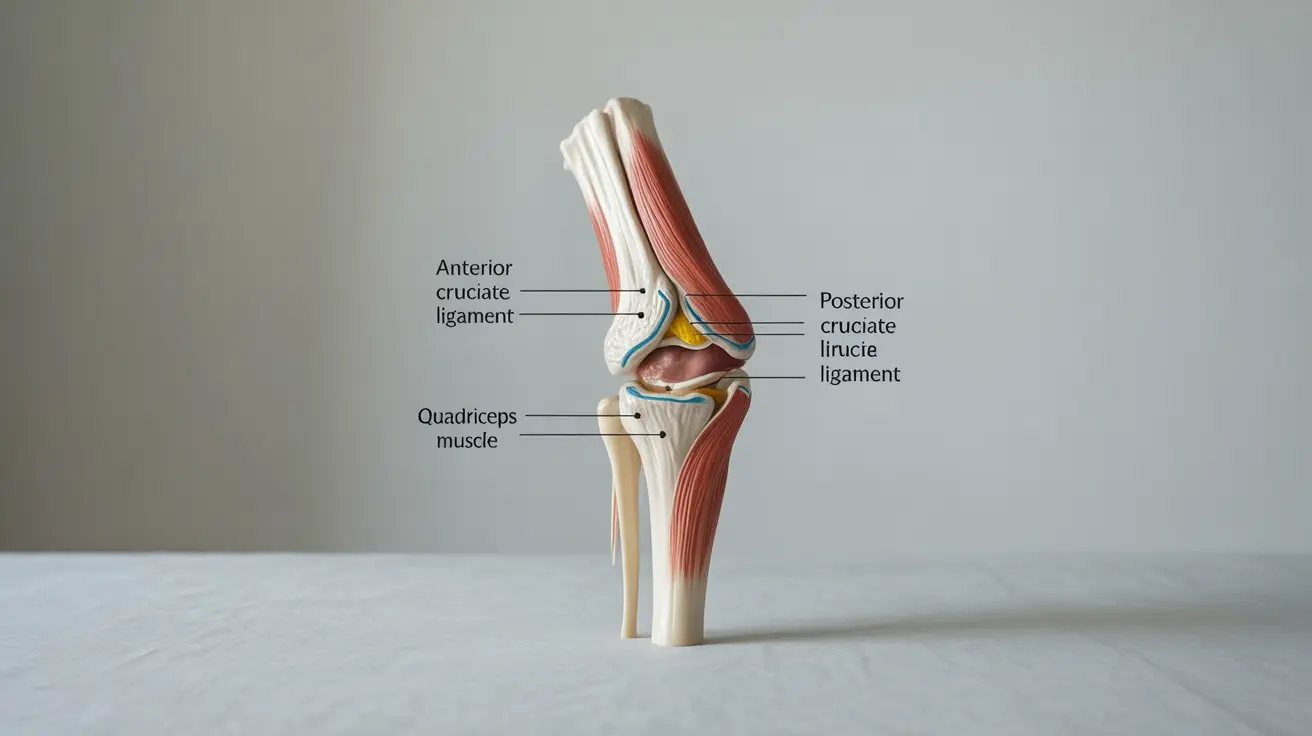
What Is Joint Hyperextension?
Hyperextension refers to the excessive backward movement of a joint beyond its typical range. While some individuals naturally have more flexible joints, sudden or forceful hyperextension can cause significant damage to ligaments, tendons, and other surrounding tissues.
Common Causes of Hyperextension Injuries
Hyperextension injuries typically occur due to several factors:
- Direct impact or trauma to the joint
- Sudden stops or changes in direction during sports
- Landing awkwardly from a jump
- Falls or accidents
- Poor form during exercise
- Natural joint laxity or hypermobility
Identifying Hyperextension Symptoms
When a joint becomes hyperextended, several symptoms may appear immediately or develop over time:
- Immediate pain at the injury site
- Swelling around the affected joint
- Bruising or discoloration
- Reduced range of motion
- Joint instability
- Difficulty bearing weight (especially in knee injuries)
- Muscle spasms around the affected area
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers typically diagnose hyperextension injuries through:
- Physical examination
- Range of motion tests
- Imaging studies (X-rays, MRI)
- Stability assessments
Conservative Treatment Approaches
Most hyperextension injuries respond well to conservative treatment methods:
- RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Physical therapy exercises
- Protective bracing or taping
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Modified activity levels during recovery
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
While most hyperextension injuries heal with conservative treatment, surgery may be required in cases involving:
- Complete ligament tears
- Significant joint instability
- Associated fractures
- Failed conservative treatment
- Chronic joint problems
Prevention Strategies
Preventing hyperextension injuries involves several key approaches:
- Proper warm-up before physical activity
- Maintaining good form during exercise
- Strengthening muscles around joints
- Using appropriate protective equipment
- Regular flexibility training
- Avoiding overtraining
- Learning proper landing techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes hyperextension injuries in joints like the knee, elbow, and fingers? Hyperextension injuries typically occur from sudden trauma, sports accidents, falls, or forceful impact that pushes a joint backward beyond its normal range of motion. Poor technique during exercise and natural joint laxity can also contribute to these injuries.
What are the common symptoms of a hyperextended joint? Common symptoms include immediate pain, swelling, bruising, reduced range of motion, joint instability, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected joint. Muscle spasms and inflammation around the injury site are also typical.
How is a hyperextended knee or elbow diagnosed and treated? Diagnosis involves physical examination, range of motion tests, and possibly imaging studies like X-rays or MRI. Treatment typically includes the RICE protocol, physical therapy, bracing, and anti-inflammatory medications. More severe cases may require specialized treatment approaches.
When is surgery necessary for a hyperextension injury? Surgery becomes necessary when there are complete ligament tears, significant joint instability, associated fractures, or when conservative treatment fails to resolve the injury. The decision for surgery is based on injury severity and individual patient factors.
How can I prevent hyperextension injuries during sports or exercise? Prevention includes proper warm-up, maintaining good form during exercise, strengthening muscles around joints, using appropriate protective equipment, and practicing proper technique. Regular flexibility training and avoiding overtraining are also important preventive measures.