Inflammatory PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) represents a distinct variation of this common hormonal disorder, characterized by chronic inflammation that can significantly impact overall health and symptom severity. Understanding the inflammatory component of PCOS is crucial for developing effective management strategies and improving quality of life for those affected.
While PCOS affects approximately 1 in 10 women of reproductive age, the inflammatory variant presents unique challenges and requires specific attention to inflammation-related symptoms and treatment approaches. This comprehensive guide explores the connection between inflammation and PCOS, along with evidence-based strategies for management.
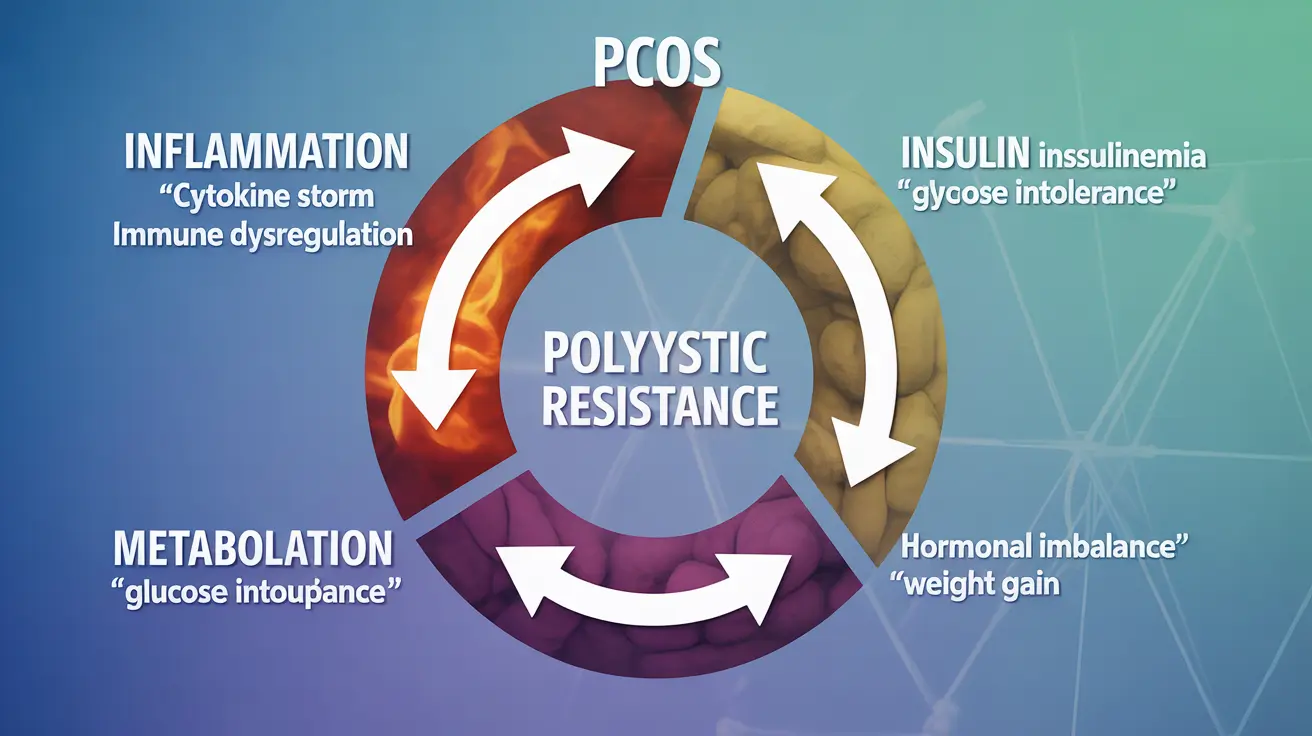
Understanding Inflammatory PCOS
Inflammatory PCOS differs from traditional PCOS presentations through its heightened inflammatory responses and specific symptom patterns. This variation often involves more pronounced metabolic disruptions and can lead to more severe health complications if left unaddressed.
Key Characteristics and Symptoms
The inflammatory form of PCOS typically presents with several distinct features:
- Elevated inflammatory markers in blood tests
- More severe acne and skin inflammation
- Increased abdominal fat
- Greater insulin resistance
- Higher risk of cardiovascular issues
- More pronounced fatigue and mood disturbances
The Inflammation-Insulin Connection
Chronic inflammation plays a central role in developing and maintaining insulin resistance, a key feature of PCOS. This creates a challenging cycle where inflammation worsens insulin resistance, which in turn promotes more inflammation. Understanding this relationship is crucial for effective treatment approaches.
Dietary Approaches for Managing Inflammatory PCOS
An anti-inflammatory diet can significantly impact PCOS symptoms and overall health. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods
- Including abundant colorful vegetables and fruits
- Incorporating omega-3 rich foods
- Limiting refined carbohydrates and sugars
- Adding anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric and ginger
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in managing inflammatory PCOS by:
- Reducing systemic inflammation
- Improving insulin sensitivity
- Supporting healthy weight management
- Enhancing mood and energy levels
- Promoting better sleep quality
Supplement and Treatment Options
Several evidence-based supplements and treatments can help manage inflammatory PCOS:
- Omega-3 fatty acid supplements
- Vitamin D supplementation
- N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)
- Inositol
- Anti-inflammatory herbs and botanicals
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of inflammatory PCOS and how do they differ from regular PCOS?
Inflammatory PCOS typically presents with more severe symptoms including pronounced acne, increased abdominal fat, greater insulin resistance, and higher levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Unlike regular PCOS, inflammatory PCOS often shows more significant metabolic disruptions and more severe skin-related symptoms.
How does chronic inflammation affect insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes risk in people with PCOS?
Chronic inflammation directly impacts insulin sensitivity, creating a harmful cycle where inflammation increases insulin resistance, which in turn promotes more inflammation. This relationship significantly elevates the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in people with inflammatory PCOS.
What lifestyle and dietary changes can help reduce inflammation in PCOS?
Key lifestyle changes include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in whole foods, colorful vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, while limiting processed foods and refined sugars. Regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep are also crucial for reducing inflammation.
Are there specific treatments or supplements recommended to manage inflammation in PCOS?
Several evidence-based supplements can help manage inflammatory PCOS, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, NAC, and inositol. These should be combined with appropriate medical treatments as recommended by healthcare providers.
How can regular exercise influence inflammation and metabolic health in individuals with PCOS?
Regular exercise helps reduce systemic inflammation, improves insulin sensitivity, and supports healthy weight management. Both moderate-intensity cardio and strength training can be beneficial, with research showing that consistent physical activity helps regulate hormones and reduce PCOS symptoms.