Labored breathing, medically known as dyspnea, is a condition where breathing becomes difficult, uncomfortable, or requires more effort than usual. This breathing difficulty can range from mild discomfort during physical activity to severe respiratory distress that occurs even at rest. Understanding the various causes and warning signs of labored breathing is crucial for determining when medical intervention is necessary and how to manage this concerning symptom effectively.
While occasional shortness of breath during intense exercise is normal, persistent or sudden onset of labored breathing can indicate underlying health conditions that require prompt medical attention. From respiratory infections to heart problems, numerous factors can contribute to breathing difficulties, making it essential to recognize the symptoms and understand when professional medical care is needed.
Common Causes of Labored Breathing
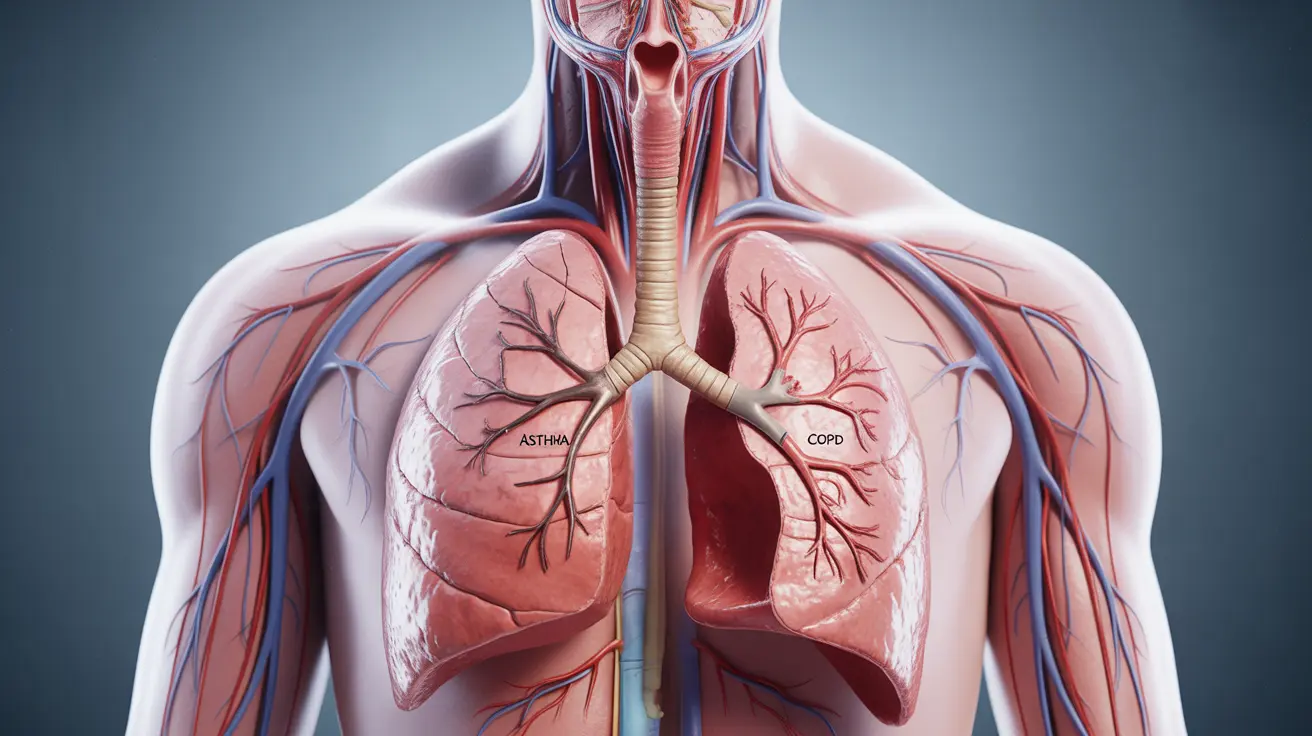
Labored breathing can result from various underlying conditions affecting different body systems. Respiratory causes include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism. These conditions directly impact the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, leading to breathing difficulties.
Cardiovascular causes represent another significant category, including heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmias. When the heart cannot pump blood effectively, fluid may accumulate in the lungs, making breathing labored and difficult. Additionally, conditions like anemia reduce the blood's oxygen-carrying capacity, forcing the respiratory system to work harder to meet the body's oxygen demands.
Environmental factors and lifestyle choices can also contribute to breathing difficulties. Exposure to allergens, pollution, or irritants may trigger respiratory symptoms. Obesity places additional strain on the respiratory system, while smoking damages lung tissue and airways, leading to chronic breathing problems.
Identifying Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of labored breathing involves understanding both physical symptoms and accompanying warning signs. Primary indicators include increased breathing rate, using accessory muscles for breathing (visible chest and neck muscle use), shallow or rapid breathing patterns, and feeling unable to catch one's breath during normal activities.
Associated symptoms that often accompany labored breathing include chest pain or tightness, wheezing or crackling sounds, persistent coughing, fatigue, dizziness, and changes in skin color, particularly bluish discoloration around the lips or fingertips (cyanosis). These additional symptoms can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause of breathing difficulties.
The onset and pattern of symptoms also provide important diagnostic information. Sudden, severe breathing difficulty may indicate a medical emergency, while gradual onset over days or weeks might suggest chronic conditions requiring ongoing management.
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain symptoms accompanying labored breathing require immediate emergency medical attention. These critical warning signs include sudden, severe shortness of breath, chest pain or pressure, rapid heartbeat, confusion or altered mental state, and significant skin color changes indicating oxygen deprivation.
Other emergency indicators include inability to speak in full sentences due to breathlessness, severe wheezing or stridor (high-pitched breathing sounds), profuse sweating combined with breathing difficulty, and feeling of impending doom or panic that accompanies respiratory distress.
Individuals with known respiratory or cardiac conditions should be particularly vigilant for changes in their baseline symptoms. Worsening of chronic conditions or new symptoms developing rapidly should prompt immediate medical evaluation to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use various diagnostic tools and techniques to identify the underlying cause of labored breathing. The evaluation typically begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination, focusing on the onset, duration, and characteristics of breathing difficulties.
Diagnostic tests commonly include pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen levels, chest X-rays to visualize lung structure and identify abnormalities, and arterial blood gas analysis to assess oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. More specialized tests may include echocardiograms to evaluate heart function, pulmonary function tests to assess lung capacity and airflow, and CT scans for detailed imaging of chest structures.
Laboratory tests such as complete blood count, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels for heart failure assessment, and D-dimer tests for pulmonary embolism may also be necessary depending on the suspected underlying condition.
Treatment Options and Management
Treatment for labored breathing varies significantly based on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Immediate interventions may include oxygen therapy to improve blood oxygen levels, bronchodilators for airway constriction, and positioning techniques to ease breathing effort.
For chronic conditions like asthma or COPD, long-term management strategies include daily medications such as inhaled corticosteroids, lifestyle modifications including smoking cessation and weight management, and pulmonary rehabilitation programs to improve breathing efficiency and overall respiratory health.
Cardiac-related breathing difficulties may require heart medications, dietary changes to reduce sodium intake, fluid restriction, and in some cases, surgical interventions. Treatment plans are individualized based on the specific diagnosis, symptom severity, and patient's overall health status.
Anxiety and Panic-Related Breathing Difficulties
Anxiety and panic attacks can indeed cause labored breathing through hyperventilation and increased respiratory rate. During anxiety episodes, individuals may experience rapid, shallow breathing, feeling of suffocation, chest tightness, and tingling sensations in hands or around the mouth due to changes in blood chemistry.
Management of anxiety-related breathing difficulties involves both immediate coping strategies and long-term treatment approaches. Immediate techniques include controlled breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and grounding techniques to help regulate breathing patterns during panic episodes.
Long-term management may include cognitive behavioral therapy to address underlying anxiety, stress management techniques, regular exercise to improve overall cardiovascular and respiratory health, and in some cases, anti-anxiety medications prescribed by healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of labored breathing and how can I identify them?
The most common causes of labored breathing include asthma, COPD, heart failure, pneumonia, and anxiety disorders. You can identify potential causes by noting associated symptoms: wheezing and chest tightness may indicate asthma, while swelling in legs and fatigue might suggest heart problems. Fever and cough often accompany respiratory infections, while sudden onset during stressful situations may indicate anxiety-related breathing difficulties.
When should I seek emergency medical help for labored or difficult breathing?
Seek immediate emergency care if you experience sudden, severe shortness of breath, chest pain, blue discoloration of lips or fingertips, inability to speak in full sentences, severe wheezing, rapid heartbeat with breathing difficulty, or confusion. Also seek emergency help if breathing problems worsen rapidly or if you have a feeling of impending doom accompanying respiratory distress.
How do doctors diagnose the underlying cause of labored breathing?
Doctors diagnose labored breathing through medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Common tests include pulse oximetry, chest X-rays, blood tests, arterial blood gas analysis, and electrocardiograms. Depending on suspected causes, additional tests like echocardiograms, pulmonary function tests, or CT scans may be ordered to identify specific conditions affecting breathing.
What treatment options are available for labored breathing depending on its cause?
Treatment varies by underlying cause: asthma may require bronchodilators and corticosteroids; heart failure might need diuretics and heart medications; infections typically require antibiotics or antiviral medications; COPD management includes bronchodilators and pulmonary rehabilitation. Oxygen therapy, breathing exercises, and lifestyle modifications are often part of comprehensive treatment plans regardless of the specific cause.
Can anxiety or panic attacks cause labored breathing, and how is it managed?
Yes, anxiety and panic attacks commonly cause labored breathing through hyperventilation and rapid, shallow breathing patterns. Management includes immediate techniques like controlled breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and grounding methods. Long-term management involves cognitive behavioral therapy, stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and sometimes anti-anxiety medications prescribed by healthcare providers to address underlying anxiety disorders.