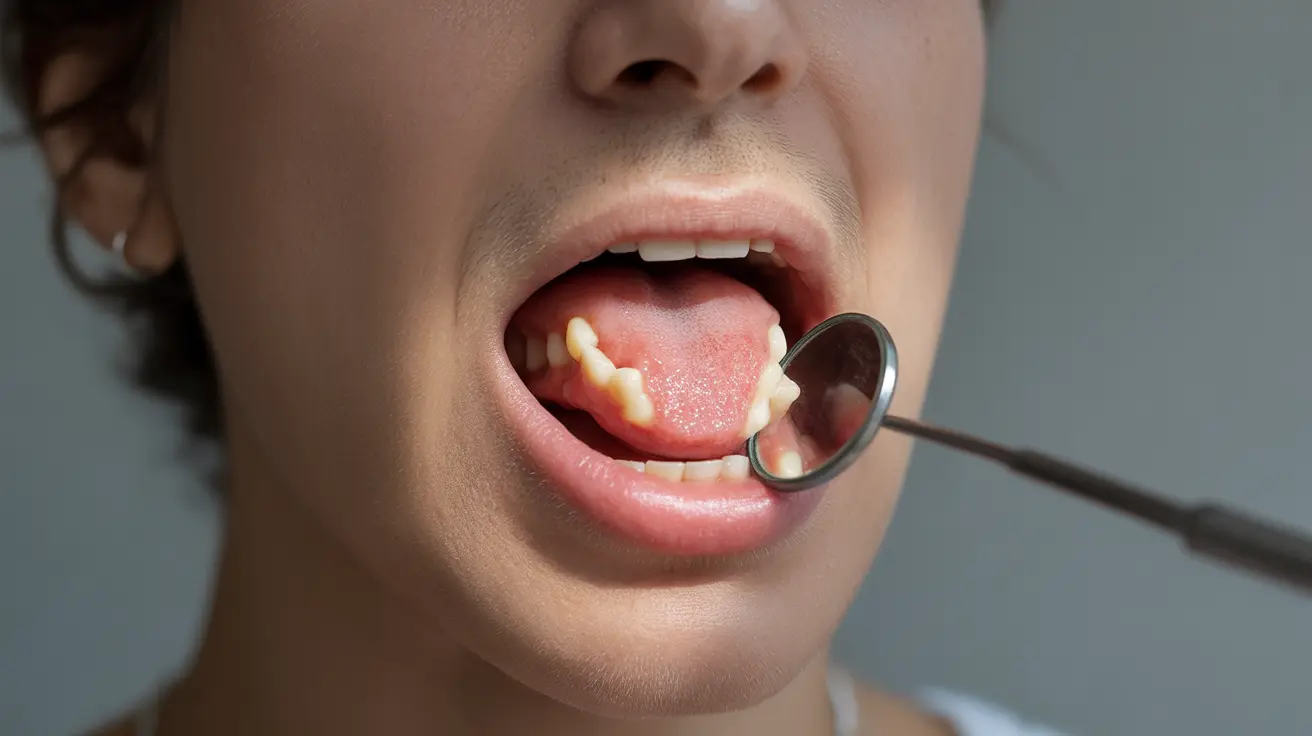
Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by thick, white patches that develop on the soft tissues of the mouth, gums, or tongue. These patches cannot be scraped off and may indicate potential pre-cancerous changes in the mouth. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and proper treatment.
While most cases of leukoplakia are benign, it's essential to have any unusual mouth patches evaluated by a healthcare professional, as some cases may develop into oral cancer. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for leukoplakia.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia typically presents with distinctive characteristics that set it apart from other oral conditions:
- White or grayish patches in the mouth
- Patches that cannot be wiped away
- Irregular or flat-textured areas
- Firm and rough spots to the touch
- Areas that may be slightly raised
- Patches that develop gradually over time
In some cases, red patches (erythroplakia) may appear alongside the white patches, which can indicate a higher risk of cancerous development and should be evaluated immediately.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of leukoplakia:
Tobacco Use
Smoking or chewing tobacco products is the leading cause of leukoplakia. The longer and more frequently you use tobacco, the higher your risk of developing these patches.
Alcohol Consumption
Regular alcohol use, especially when combined with tobacco, can significantly increase your risk of developing leukoplakia.
Other Risk Factors
- Chronic irritation from rough teeth or dental work
- Inflammatory conditions of the mouth
- Immune system suppression
- Long-term sun exposure to the lips
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosis of leukoplakia typically involves several steps:
Initial Examination
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination of your mouth and throat, looking for characteristic white patches and other suspicious areas.
Biopsy Procedure
If the patches appear suspicious or have concerning features, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. This involves removing a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis to rule out cancer or pre-cancerous conditions.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for leukoplakia focuses on addressing the underlying causes and removing the patches when necessary:
Conservative Management
- Stopping tobacco use
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Removing irritating factors
- Regular monitoring of patches
Medical Interventions
Your healthcare provider may recommend various treatment options:
- Surgical removal of patches
- Laser therapy
- Cryotherapy (freezing the affected tissue)
- Topical medications in some cases
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Several preventive measures can help reduce your risk of developing leukoplakia:
- Quit smoking and avoid all tobacco products
- Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption
- Maintain good oral hygiene
- Have regular dental check-ups
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Protect your lips from excessive sun exposure
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes leukoplakia and how can I reduce my risk of developing it?
Leukoplakia is primarily caused by tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic irritation of mouth tissues. To reduce your risk, quit tobacco products, limit alcohol intake, maintain good oral hygiene, and have regular dental check-ups.
What are the common symptoms and appearance of leukoplakia patches in the mouth?
Leukoplakia appears as thick, white patches in the mouth that cannot be scraped off. These patches may be slightly raised, firm to the touch, and can have irregular textures. They typically develop gradually and may be accompanied by red patches in some cases.
How is leukoplakia diagnosed and when should I see a doctor for a biopsy?
Diagnosis involves a thorough oral examination and possibly a biopsy if the patches appear suspicious. See a doctor immediately if you notice persistent white patches in your mouth, especially if they're accompanied by red areas or don't heal within two weeks.
What treatment options are available for leukoplakia, including surgical and non-surgical methods?
Treatment options include removing risk factors (like tobacco use), surgical removal of patches, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and topical medications. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and characteristics of the patches.
Can natural remedies or lifestyle changes help prevent or manage leukoplakia?
While natural remedies aren't proven to treat leukoplakia directly, lifestyle changes can help prevent and manage the condition. These include quitting tobacco, reducing alcohol consumption, maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a healthy diet, and protecting your lips from sun exposure.