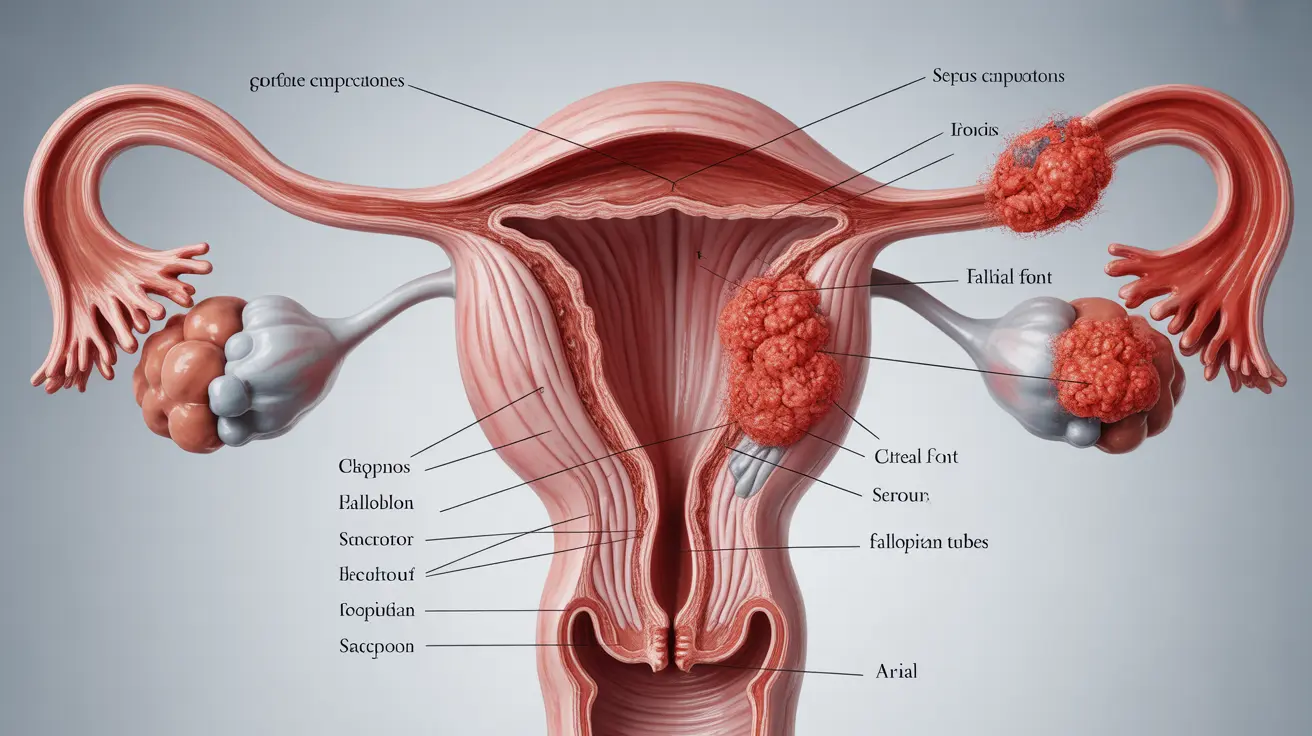
Serous carcinoma is a significant type of cancer that primarily affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes, though it can also develop in other parts of the female reproductive system. This aggressive form of cancer requires prompt diagnosis and treatment for the best possible outcomes. Understanding its characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
As one of the most common subtypes of ovarian cancer, serous carcinoma demands particular attention due to its potential for rapid progression, especially in its high-grade form. Early recognition of symptoms and proper medical intervention can significantly impact survival rates and quality of life.
Types of Serous Carcinoma
Serous carcinoma presents in two main forms, each with distinct characteristics and behaviors:
High-Grade Serous Carcinoma
High-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC) is the more aggressive and common form. It typically grows and spreads rapidly, accounting for approximately 70-80% of ovarian cancer deaths. This type often develops from cells in the fallopian tubes rather than the ovaries themselves.
Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma
Low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSC) is less common and typically grows more slowly. While it may be less aggressive, it often responds differently to traditional treatments and requires a specialized approach.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Early detection of serous carcinoma can be challenging due to its subtle initial symptoms. Common warning signs include:
- Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel habits
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Increased urinary frequency
- Unexplained fatigue
- Unexpected weight loss
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing serous carcinoma typically involves multiple steps and testing methods:
- Physical examination and medical history review
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- CT or MRI scans
- Blood tests for tumor markers (CA-125)
- Surgical biopsy for definitive diagnosis
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for serous carcinoma usually involves a combination of therapies:
Surgical Intervention
Surgery often serves as the primary treatment, involving removal of visible tumors and affected tissues. The extent of surgery depends on the cancer's stage and spread.
Chemotherapy
Most patients receive chemotherapy, either before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after (adjuvant). Platinum-based chemotherapy combinations are typically the standard of care.
Targeted Therapies
Newer treatment options may include targeted therapies such as PARP inhibitors, particularly effective in cases with specific genetic mutations.
Prognosis and Survival Factors
Several factors influence the prognosis of serous carcinoma:
- Stage at diagnosis
- Response to initial treatment
- Presence of specific genetic mutations
- Overall health status
- Access to specialized care
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of serous carcinoma and how can I recognize them early?
Common early symptoms include persistent bloating, pelvic pain, changes in bowel habits, and feeling full quickly when eating. Other signs may include increased urinary frequency and unexplained fatigue. Since these symptoms can be subtle, it's important to pay attention to persistent changes lasting more than two weeks.
What is the difference between high-grade and low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary?
High-grade serous carcinoma grows and spreads more rapidly, is more common, and typically responds well to platinum-based chemotherapy. Low-grade serous carcinoma grows more slowly, is less common, and often requires different treatment approaches due to its resistance to standard chemotherapy.
How is serous carcinoma diagnosed and what tests are typically performed?
Diagnosis involves multiple steps including physical examination, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT, MRI), blood tests for tumor markers like CA-125, and ultimately a surgical biopsy for definitive diagnosis. Genetic testing may also be performed to guide treatment decisions.
What are the current treatment options for high-grade serous carcinoma?
Treatment typically involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Surgery aims to remove all visible cancer, while chemotherapy helps eliminate remaining cancer cells. Targeted therapies, such as PARP inhibitors, may be used in certain cases, especially for patients with BRCA mutations.
How does the stage of serous carcinoma affect prognosis and survival rates?
The stage at diagnosis significantly impacts prognosis. Early-stage disease (confined to the ovaries) has better survival rates, while advanced stages (spread beyond the pelvis) have lower survival rates. Other factors affecting prognosis include response to treatment, age, and overall health status.