Skin ulcers are open sores that develop when the skin and underlying tissues break down, often due to poor circulation, pressure, or other underlying health conditions. These wounds can be painful, slow to heal, and potentially serious if not properly treated. Understanding the different types, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Whether you're dealing with a skin ulcer yourself or caring for someone who has one, this comprehensive guide will help you understand what to look for, when to seek medical attention, and how to promote proper healing.
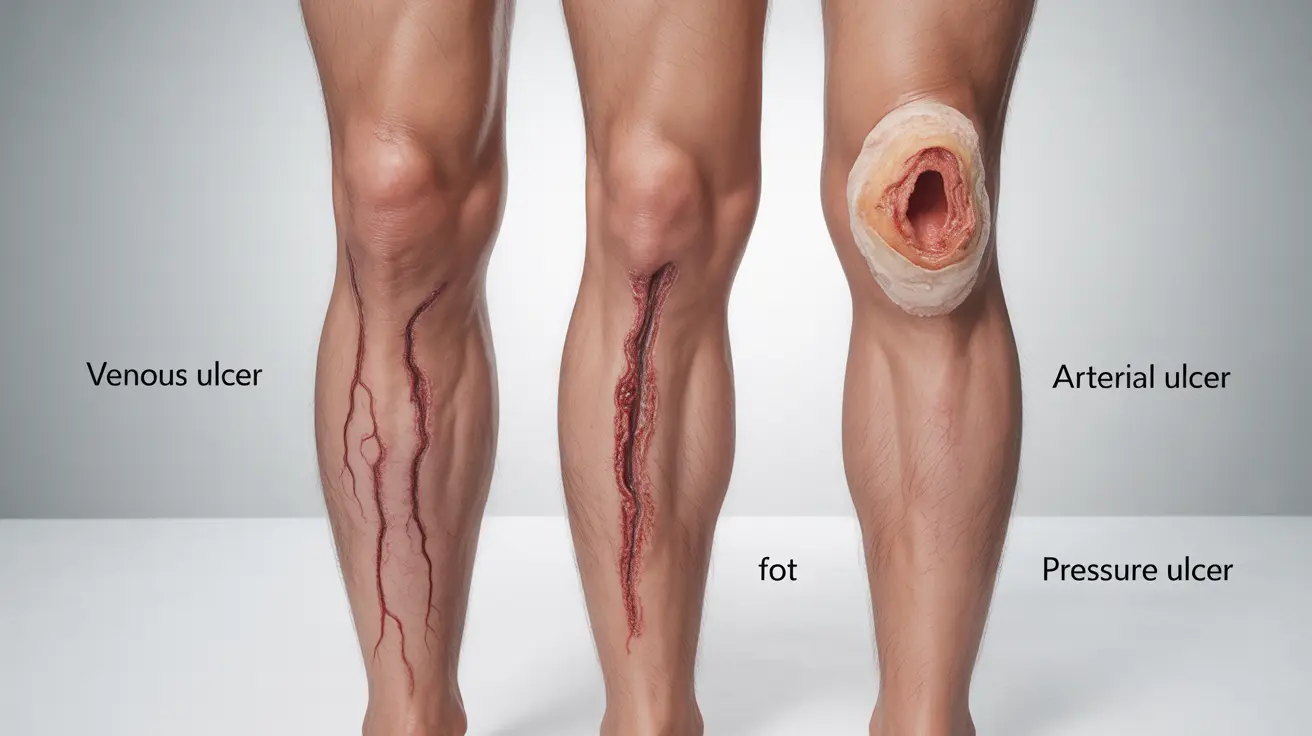
Types of Skin Ulcers
There are several distinct types of skin ulcers, each with unique characteristics and causes:
Venous Ulcers
These are the most common type of skin ulcers, typically occurring on the lower legs and ankles. They develop when blood flow in the veins becomes compromised, leading to fluid buildup and tissue damage.
Arterial Ulcers
These ulcers form when arteries fail to deliver sufficient oxygen-rich blood to the extremities. They often appear on the feet, toes, and lower legs, characterized by a punched-out appearance and severe pain.
Pressure Ulcers (Decubitus)
Also known as bedsores, these develop when prolonged pressure damages the skin and underlying tissues. Common locations include the tailbone, hips, heels, and other bony areas.
Signs and Symptoms
Common indicators of a skin ulcer include:
- Discoloration of the affected area
- Open wounds or sores
- Pain or tenderness
- Drainage or discharge
- Swelling around the wound
- Warm or hot skin near the ulcer
- Foul odor (if infected)
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase your risk of developing skin ulcers:
- Diabetes
- Poor circulation
- Limited mobility
- Advanced age
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Nutritional deficiencies
Prevention strategies include maintaining good skin hygiene, regular position changes for immobile individuals, proper diabetes management, and wearing appropriate footwear.
Treatment Approaches
Medical Treatments
Professional medical care may include:
- Wound debridement
- Specialized dressings
- Compression therapy
- Antibiotics for infections
- Surgery in severe cases
Home Care
Essential home care practices include:
- Regular cleaning with prescribed solutions
- Careful dressing changes
- Keeping the wound area dry
- Following dietary recommendations
- Monitoring for signs of infection
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes and risk factors for developing a skin ulcer?
Skin ulcers primarily develop due to poor circulation, pressure on the skin, diabetes, and venous insufficiency. Risk factors include obesity, smoking, advanced age, immobility, and certain medical conditions that affect blood flow or nerve function.
How can I tell if a skin ulcer is infected and what are the symptoms to watch for?
Signs of infection include increased pain, redness spreading beyond the ulcer, warmth around the wound, foul odor, fever, increased drainage or pus, and swelling. If you notice these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
What are the most effective treatments and home care tips for healing a skin ulcer?
Effective treatment involves proper wound cleaning, appropriate dressing changes, pressure relief, and addressing underlying conditions. Home care includes keeping the wound clean and dry, following prescribed treatment plans, maintaining good nutrition, and monitoring for complications.
What is the difference between a venous, arterial, and pressure (decubitus) skin ulcer?
Venous ulcers result from poor vein function and typically occur on lower legs. Arterial ulcers develop from poor arterial blood flow and often affect the feet and toes. Pressure ulcers form when sustained pressure damages skin and underlying tissues, commonly occurring over bony areas.
What steps can I take to prevent skin ulcers, especially if I have diabetes or poor circulation?
Prevention includes regular skin inspection, maintaining good hygiene, managing underlying conditions like diabetes, wearing proper footwear, avoiding pressure on vulnerable areas, staying active, maintaining a healthy diet, and quitting smoking if applicable.