Stomatitis is a common inflammatory condition affecting the mouth's soft tissues, causing discomfort and painful sores. This condition can impact people of all ages and may present in various forms, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types of stomatitis and their causes is crucial for proper management and prevention.
Types of Stomatitis
There are several main types of stomatitis that affect different areas of the mouth and have varying causes:
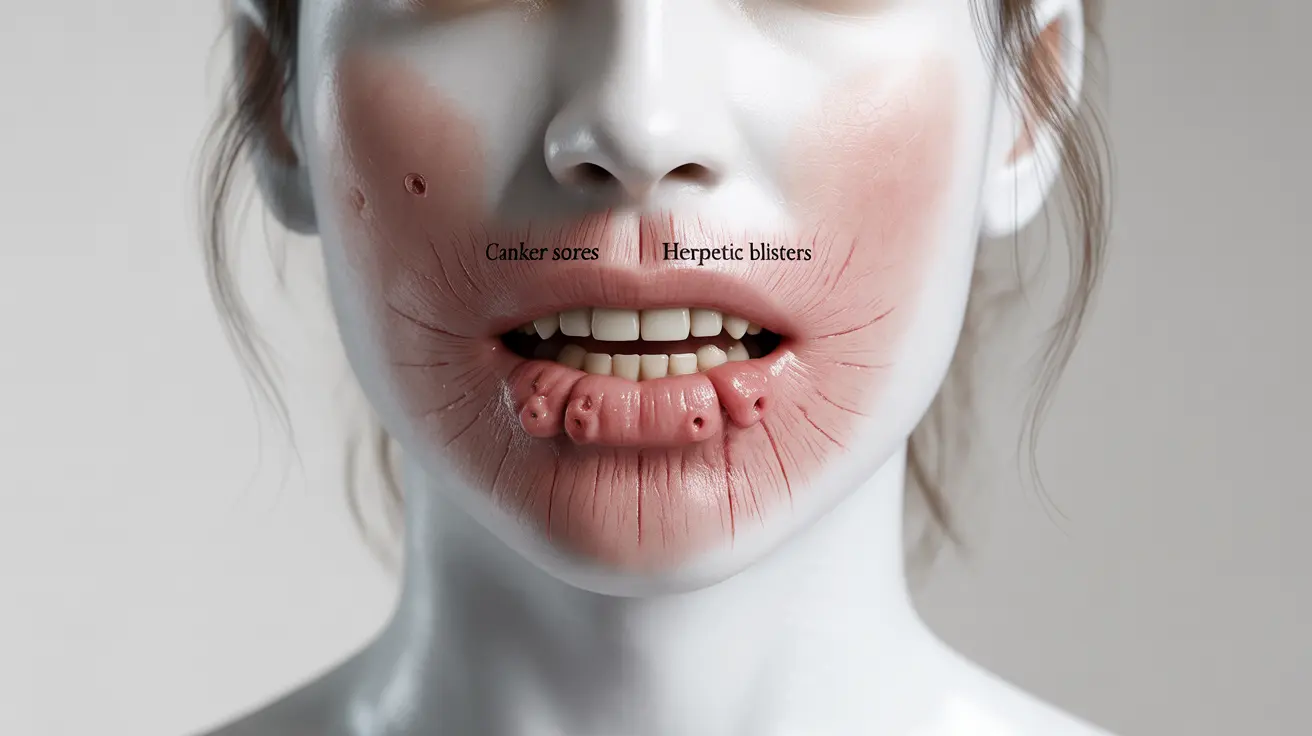
Aphthous Stomatitis (Canker Sores)
These are painful, shallow ulcers that appear inside the mouth. They typically have a white or yellow center with a red border and can occur on the inside of the cheeks, lips, or tongue. Unlike cold sores, canker sores aren't contagious and usually heal within 1-2 weeks.
Herpetic Stomatitis
Caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1), this type produces painful blisters and sores around and inside the mouth. It's particularly common in young children and can cause fever and swollen lymph nodes alongside mouth sores.
Denture Stomatitis
This form appears as inflammation under dentures, typically affecting the roof of the mouth. It's often associated with poor denture hygiene or ill-fitting dental appliances.
Common Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of stomatitis can vary depending on the type but commonly include:
- Pain or burning sensation in the mouth
- Difficulty eating or drinking
- Swollen or inflamed oral tissues
- White or red patches in the mouth
- Bleeding or crusting of oral sores
- Bad breath
- Fever (in some cases)
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of stomatitis:
- Viral infections (particularly HSV-1)
- Bacterial infections
- Nutritional deficiencies (especially vitamin B12, iron, and folate)
- Immune system disorders
- Allergic reactions
- Physical trauma to mouth tissues
- Stress and fatigue
- Hormonal changes
Treatment Options
Treatment for stomatitis focuses on symptom relief and addressing the underlying cause. Common approaches include:
Medical Treatments
- Topical anesthetics for pain relief
- Antimicrobial mouthwashes
- Antiviral medications (for herpetic stomatitis)
- Corticosteroid preparations
- Vitamin supplements when deficiencies are present
Self-Care Measures
- Maintaining good oral hygiene
- Using salt water rinses
- Avoiding spicy, acidic, or hot foods
- Applying ice to reduce inflammation
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing stomatitis:
- Practice excellent oral hygiene
- Avoid triggers that may cause outbreaks
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Replace toothbrushes regularly
- Manage stress levels effectively
- Keep dentures clean and well-fitting
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common causes and symptoms of stomatitis?
Common causes include viral infections, nutritional deficiencies, physical trauma, and immune system disorders. Primary symptoms include mouth pain, inflammation, sores, difficulty eating, and sometimes fever.
- How can I tell the difference between herpetic stomatitis (cold sores) and aphthous stomatitis (canker sores)?
Herpetic stomatitis typically appears on the outside of the mouth and is contagious, while canker sores occur inside the mouth and aren't contagious. Herpetic sores often begin as clusters of blisters, while canker sores are usually single ulcers with a white center and red border.
- What treatments are effective for relieving pain and healing stomatitis sores?
Effective treatments include topical anesthetics, antimicrobial mouthwashes, antiviral medications (for herpetic cases), and pain relievers. Salt water rinses and avoiding irritating foods can also help healing.
- Can nutritional deficiencies contribute to stomatitis and how can they be addressed?
Yes, deficiencies in vitamin B12, iron, and folate can contribute to stomatitis. These can be addressed through dietary changes and supplements as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- What steps can I take to prevent stomatitis or reduce the risk of recurring mouth sores?
Prevention includes maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a balanced diet, avoiding known triggers, managing stress, and keeping dentures clean and well-fitting. Regular dental check-ups can also help identify and address potential issues early.