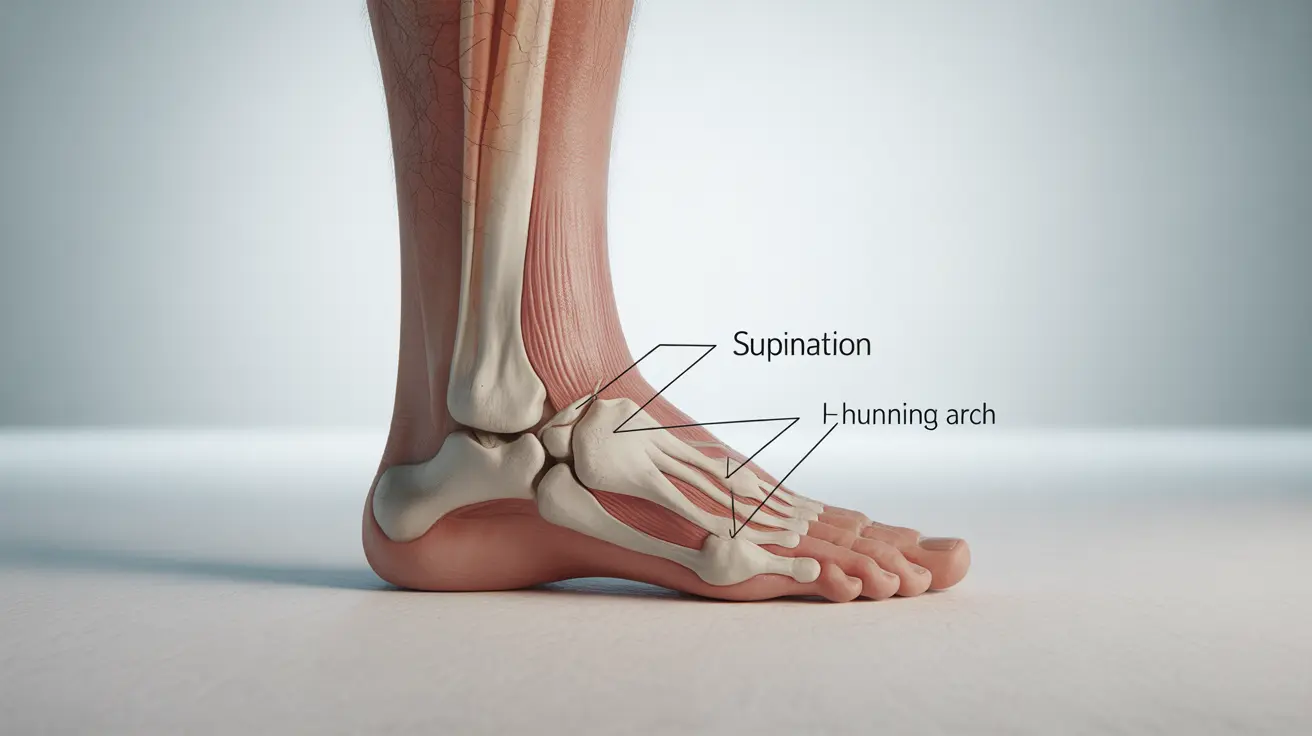
Foot supination, also known as underpronation, is a common biomechanical condition where the feet roll excessively outward during movement. This natural motion becomes problematic when excessive, potentially leading to discomfort and various musculoskeletal issues. Understanding the signs and proper management of supination is crucial for maintaining healthy foot mechanics and preventing related complications.
Whether you're an athlete experiencing foot pain or someone noticing unusual wear patterns on your shoes, learning about supination can help you take appropriate steps toward better foot health and overall comfort during daily activities.
Understanding Foot Supination
Supination occurs when the foot's outer edge bears most of the weight during movement. While some degree of supination is normal during the push-off phase of walking or running, excessive supination can create an imbalanced distribution of force throughout the foot and ankle.
This biomechanical pattern differs significantly from pronation, where the foot rolls inward. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Supination
Several indicators can help identify if you're experiencing excessive supination:
- Wear patterns on the outer edge of your shoes
- Frequent ankle sprains or instability
- Pain along the outer side of the foot
- Reduced shock absorption during walking or running
- Calluses or blisters on the outer side of the foot
- Higher, more rigid arch structure
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to excessive supination:
- Inherited foot structure and arch type
- Previous foot or ankle injuries
- Muscle imbalances or weakness
- Poor footwear choices
- High arch structure (pes cavus)
- Tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles
Treatment and Management Approaches
Proper Footwear Selection
Choosing appropriate footwear is crucial for managing supination:
- Shoes with good cushioning and flexibility
- Neutral running shoes with adequate shock absorption
- Proper fit with enough room in the toe box
- Regular replacement of worn-out shoes
Orthotic Solutions
Custom or over-the-counter orthotics can help address supination:
- Lateral wedge orthotics
- Cushioned insoles with arch support
- Custom-made orthotic devices for severe cases
- Shock-absorbing materials to reduce impact
Exercise and Stretching Programs
Specific exercises can help improve foot mechanics and reduce supination:
- Ankle mobility exercises
- Calf and Achilles tendon stretches
- Foot strengthening exercises
- Balance and proprioception training
Prevention and Long-term Care
Maintaining proper foot health and preventing complications from supination requires ongoing attention:
- Regular foot strength and flexibility exercises
- Proper warm-up before physical activities
- Gradual introduction of new exercise routines
- Regular monitoring of shoe wear patterns
- Professional assessment when needed
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs that indicate I have supination of the foot? Signs include wear on the outer edge of your shoes, frequent ankle sprains, pain along the outer foot, and visible high arches. You may also notice reduced shock absorption and calluses on the outer side of your foot.
What causes supination and how is it different from pronation? Supination is caused by genetic factors, foot structure, previous injuries, and muscle imbalances. While supination involves the foot rolling outward, pronation is when the foot rolls inward. Supination typically involves a high, rigid arch, whereas pronation often occurs with flat feet.
How can I treat or manage supination to prevent ankle, knee, or back pain? Treatment involves wearing appropriate supportive footwear, using custom or over-the-counter orthotics, performing specific stretching and strengthening exercises, and maintaining proper form during physical activities.
What type of shoes and orthotic insoles are best for people who supinate? People who supinate benefit from shoes with good cushioning, flexibility, and neutral support. Orthotic insoles should provide lateral support, shock absorption, and adequate arch support without forcing the foot to roll inward.
Are there exercises or stretches that help correct supination and strengthen the foot? Yes, beneficial exercises include ankle mobility work, calf stretches, foot strengthening exercises, and balance training. Regular practice of these exercises can help improve foot mechanics and reduce excessive supination.