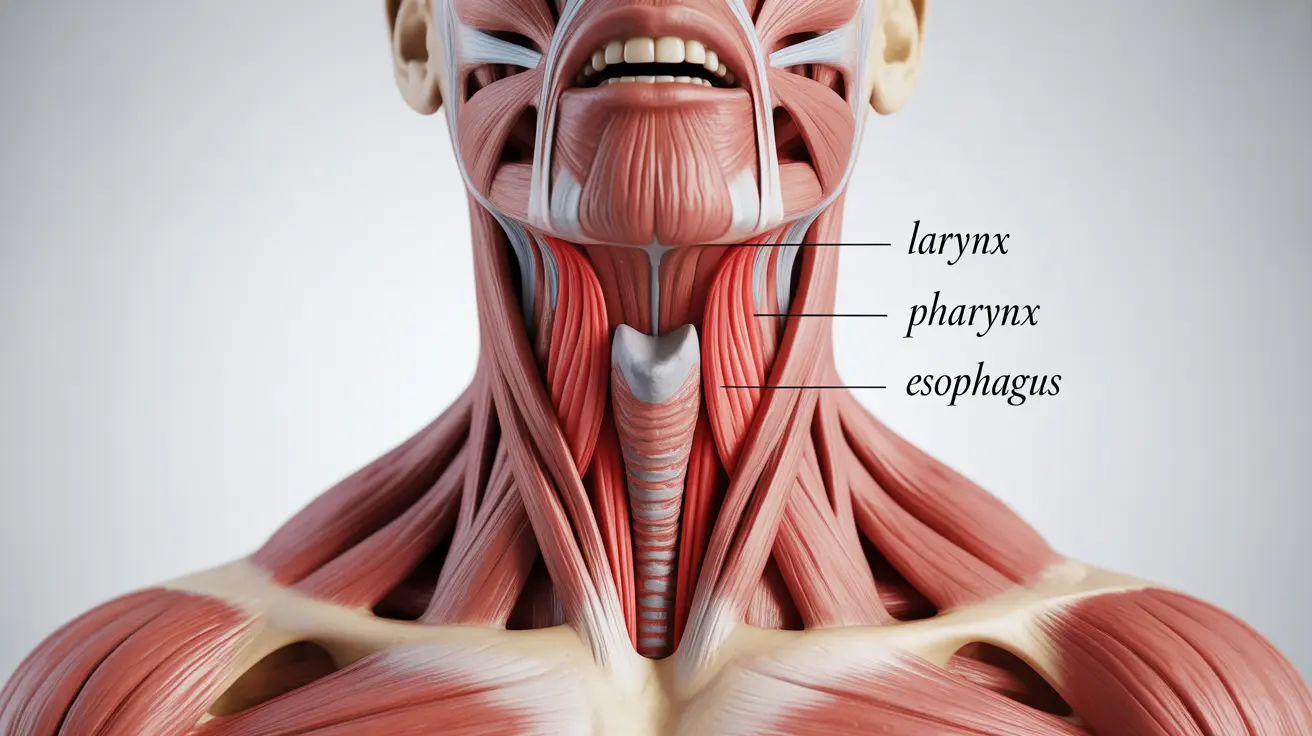
Throat spasms can be an uncomfortable and sometimes alarming experience, causing sudden tightness, difficulty swallowing, and a sensation of something stuck in the throat. These involuntary muscle contractions in the throat region can affect anyone, though they're particularly common in certain medical conditions or stress-related situations.
Understanding the nature of throat spasms, their various causes, and available treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about throat spasms and how to address them.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Throat spasms can manifest in several distinct ways, making recognition of symptoms important for proper diagnosis and treatment:
- Sudden tightness in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Sensation of food getting stuck
- Coughing or choking sensation
- Throat pain or discomfort
- Voice changes or hoarseness
Understanding the Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of throat spasms:
Medical Conditions
Various underlying health conditions may trigger throat spasms:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Anxiety and stress disorders
- Neurological conditions
- Muscle tension dysphonia
- Autoimmune disorders
Environmental Triggers
External factors that might precipitate throat spasms include:
- Dry air or dehydration
- Allergies or irritants
- Excessive talking or voice strain
- Temperature changes
- Certain medications
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically use several methods to diagnose throat spasms accurately:
Physical Examination
The initial evaluation usually includes a thorough examination of the throat and neck area, along with a detailed review of symptoms and medical history.
Diagnostic Tests
Various tests may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis:
- Videofluoroscopy
- Endoscopy
- Manometry
- pH monitoring
- EMG studies
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for throat spasms vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms:
Medical Interventions
- Muscle relaxants
- Anti-reflux medications
- Botulinum toxin injections
- Speech therapy
- Physical therapy
Self-Care Measures
Several self-management techniques can help alleviate symptoms:
- Proper hydration
- Stress reduction techniques
- Throat exercises
- Dietary modifications
- Proper posture maintenance
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Implementing certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent or reduce the frequency of throat spasms:
- Regular exercise and stress management
- Maintaining good posture
- Avoiding trigger foods
- Staying well-hydrated
- Getting adequate rest
- Practice proper breathing techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of throat spasms caused by cricopharyngeal spasm?
Common symptoms include sudden throat tightness, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of food getting stuck, coughing, and occasional voice changes. Some people may also experience throat pain or discomfort during episodes.
What factors or conditions can trigger cricopharyngeal spasms and throat tightness?
Triggers can include GERD, anxiety, stress, neurological conditions, dry air, dehydration, allergies, and certain medications. Medical conditions like muscle tension dysphonia and autoimmune disorders may also contribute to symptoms.
How are throat spasms diagnosed and what tests might be involved?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and specialized tests such as videofluoroscopy, endoscopy, manometry, pH monitoring, and EMG studies when necessary.
What treatment options are available for managing or relieving cricopharyngeal spasm symptoms?
Treatment options include muscle relaxants, anti-reflux medications, botulinum toxin injections, speech therapy, and physical therapy. Self-care measures like proper hydration and stress reduction techniques can also be effective.
Can lifestyle changes or stress reduction help prevent or reduce throat spasms?
Yes, lifestyle modifications can significantly impact throat spasm frequency and severity. Regular exercise, stress management, maintaining good posture, proper hydration, and avoiding trigger foods can help prevent or reduce episodes.