Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a serious autoimmune condition that requires prompt medical attention and ongoing management. When left untreated, this progressive disease can lead to severe complications affecting not only the joints but multiple organ systems throughout the body.
Understanding the consequences of untreated rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent many of the serious complications that may develop when the condition goes unmanaged.
Initial Signs and Disease Progression
Untreated rheumatoid arthritis typically begins with subtle symptoms that gradually worsen over time. Early warning signs often include:
- Morning stiffness lasting more than an hour
- Symmetrical joint pain and swelling
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Low-grade fever
- Loss of appetite
Without proper medical intervention, these initial symptoms can escalate rapidly, leading to more severe manifestations of the disease.
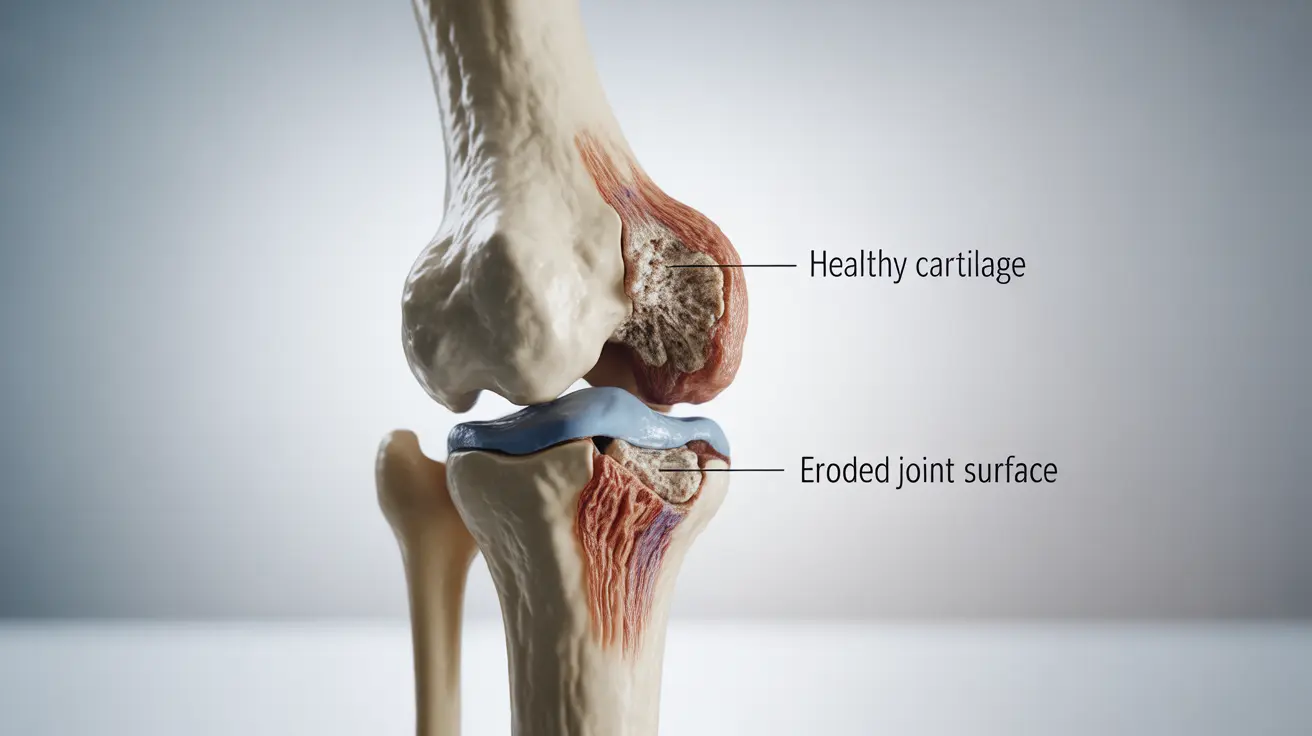
Joint Damage and Deformity
One of the most significant impacts of untreated rheumatoid arthritis occurs in the joints. The persistent inflammation can cause:
- Erosion of cartilage and bone
- Joint instability and misalignment
- Development of bone spurs
- Permanent joint deformities
- Limited range of motion
These changes can become irreversible, highlighting the importance of early treatment in preventing long-term disability.
Systemic Complications
Cardiovascular Impact
Untreated rheumatoid arthritis significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular problems, including:
- Atherosclerosis
- Heart disease
- Increased risk of heart attacks
- Inflammation of the heart muscle
Respiratory System Effects
The lungs can become severely affected, leading to:
- Interstitial lung disease
- Pleural effusion
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Reduced lung function
Other Organ Systems
The inflammatory process can affect multiple body systems, causing:
- Kidney damage
- Skin complications
- Eye problems, including scleritis
- Increased risk of lymphoma
- Bone loss and osteoporosis
Impact on Daily Life and Function
Untreated rheumatoid arthritis can severely impact a person's quality of life through:
- Difficulty performing basic daily tasks
- Reduced work capability
- Limited social participation
- Increased dependency on others
- Depression and anxiety
Treatment Importance and Options
Early intervention is crucial in managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. Modern treatment approaches include:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Biological response modifiers
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of untreated rheumatoid arthritis and how do they progress?
Untreated rheumatoid arthritis typically begins with morning stiffness, joint pain, and fatigue. These symptoms progressively worsen, leading to joint deformity, reduced mobility, and systemic complications affecting multiple organ systems.
How does untreated rheumatoid arthritis affect the joints and mobility in the long term?
Without treatment, RA causes progressive joint destruction, leading to permanent deformities, loss of function, and severe mobility limitations. The damage can affect both small and large joints throughout the body, potentially resulting in disability.
What serious complications can arise in the heart, lungs, skin, and kidneys if rheumatoid arthritis is left untreated?
Untreated RA can cause cardiovascular disease, interstitial lung disease, skin nodules, and kidney inflammation. These complications can significantly impact overall health and life expectancy.
Why is early treatment important for rheumatoid arthritis and what are the typical treatment options?
Early treatment is crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage and systemic complications. Treatment typically includes DMARDs, biologics, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy to control inflammation and maintain joint function.
How does untreated rheumatoid arthritis impact quality of life and daily activities?
Untreated RA significantly impacts daily activities, from basic self-care to work performance. It can lead to reduced independence, social isolation, and emotional challenges, substantially decreasing overall quality of life.