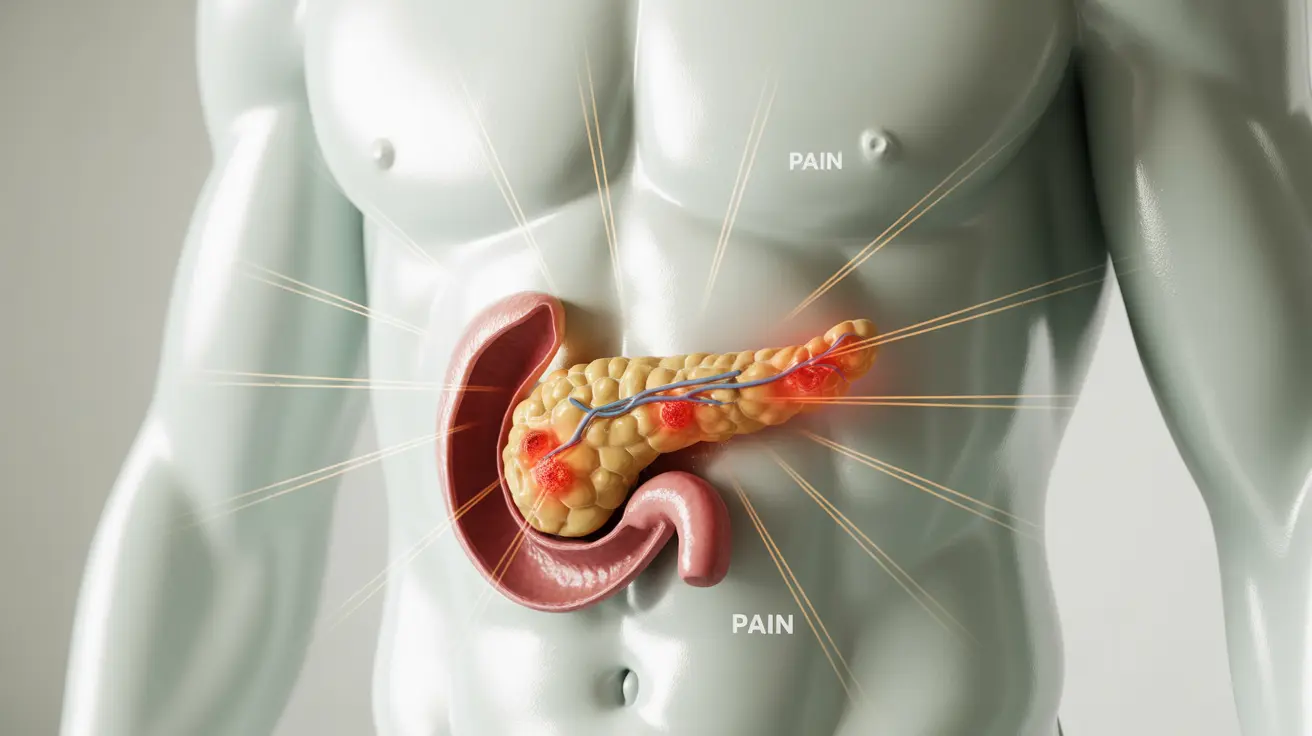
Upper left abdominal pain can be a concerning symptom, particularly when it's related to acute pancreatitis. This serious condition occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed, leading to intense discomfort and potentially severe complications if left untreated. Understanding the connection between upper left abdominal pain and pancreatitis is crucial for early recognition and proper medical care.
When pancreatitis develops, the pain typically manifests in the upper left or middle abdomen, often radiating to the back. This distinctive pattern of discomfort serves as a key indicator for healthcare providers in diagnosing the condition and determining appropriate treatment approaches.
Understanding Pancreatitis and Upper Left Abdominal Pain
The pancreas, located in the upper left portion of the abdomen, plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. When inflammation occurs, it typically causes severe pain in this area. The pain associated with pancreatitis often:
- Develops suddenly and intensifies rapidly
- Worsens after eating
- May persist for several days
- Can be accompanied by nausea and vomiting
- Might radiate to the back
Common Causes of Pancreatitis-Related Abdominal Pain
Several factors can trigger pancreatitis and its associated upper left abdominal pain:
- Gallstones
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- High triglyceride levels
- Certain medications
- Viral infections
- Trauma to the abdomen
Diagnostic Process for Upper Left Abdominal Pain
When patients present with upper left abdominal pain, doctors typically follow a comprehensive diagnostic approach:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to check pancreatic enzyme levels
- Imaging studies (CT scan, ultrasound, or MRI)
- Assessment of medical history and lifestyle factors
Treatment Approaches for Pancreatitis Pain
The management of upper left abdominal pain from pancreatitis typically involves several strategies:
Immediate Medical Care
Initial treatment usually focuses on pain management and preventing complications through:
- Intravenous fluid administration
- Pain medication
- Temporary restriction of food intake
- Monitoring vital signs
Long-term Management
Once the acute phase is controlled, long-term management may include:
- Dietary modifications
- Lifestyle changes
- Regular monitoring of pancreatic function
- Treatment of underlying conditions
Dietary Considerations
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in managing pancreatitis and preventing recurring upper left abdominal pain. Recommended dietary guidelines include:
- Low-fat food choices
- Small, frequent meals
- Adequate hydration
- Avoiding alcohol completely
- Limiting processed foods
Prevention Strategies
Several lifestyle modifications can help prevent recurring episodes of pancreatitis-related upper left abdominal pain:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Following a balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Managing underlying health conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and causes of upper left abdominal pain related to acute pancreatitis? The most common symptoms include severe upper left abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, nausea, vomiting, and tender abdomen. Common causes include gallstones, alcohol use, high triglycerides, and certain medications.
How is acute pancreatitis with upper left abdominal pain diagnosed by doctors? Doctors diagnose acute pancreatitis through physical examination, blood tests measuring pancreatic enzyme levels, and imaging studies such as CT scans or ultrasounds. They also review the patient's medical history and symptoms.
What treatments are available for severe upper left abdominal pain caused by acute pancreatitis? Treatment typically includes pain management, intravenous fluids, fasting to rest the pancreas, and addressing underlying causes. Severe cases may require hospitalization and intensive monitoring.
Can eating certain foods make upper left abdominal pain worse in pancreatitis? Yes, fatty, fried, and highly processed foods can worsen pancreatitis pain. A low-fat diet with small, frequent meals is recommended during recovery and for prevention.
How can lifestyle changes help prevent recurrent upper left abdominal pain from pancreatitis? Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol, following a low-fat diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying health conditions that could trigger pancreatitis.