Upper right abdominal pain can be a concerning symptom that affects many people, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. This type of pain, located beneath the ribs on the right side of your abdomen, can signal various underlying conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the potential causes, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the common causes of upper right abdominal pain, how doctors diagnose it, available treatments, and when to seek immediate medical care. We'll also discuss lifestyle modifications that may help prevent or manage this type of pain.
Common Causes of Upper Right Abdominal Pain
Several conditions can trigger pain in the upper right abdomen, ranging from minor digestive issues to serious medical conditions:
Gallbladder Problems
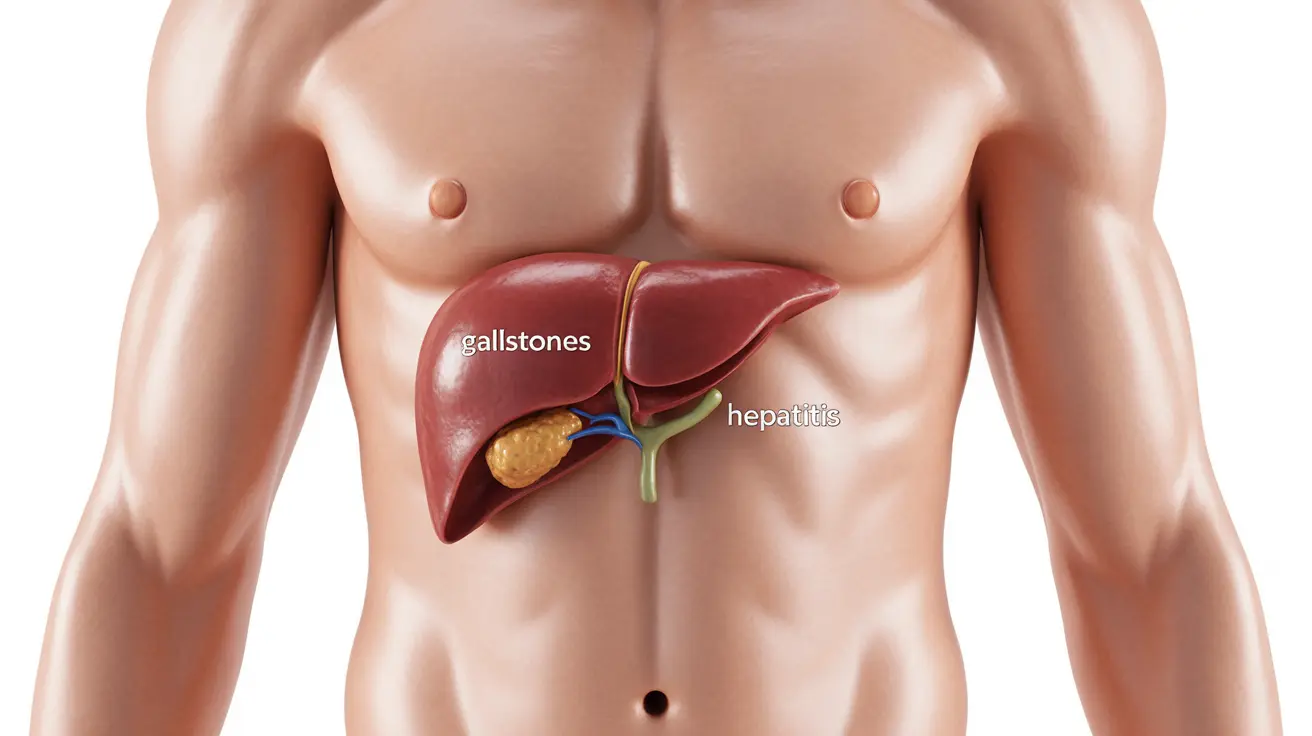
The gallbladder, located in the upper right abdomen, commonly causes pain in this area. Conditions include:
- Gallstones
- Cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation)
- Biliary colic
Liver Conditions
Various liver disorders can cause upper right quadrant pain:
- Hepatitis
- Fatty liver disease
- Liver abscess
- Cirrhosis complications
Digestive System Issues
Common digestive problems that may cause pain include:
- Gastritis
- Peptic ulcers
- Acid reflux (GERD)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose the cause of upper right abdominal pain:
Physical Examination
Doctors typically begin with a thorough physical examination and medical history review. They may check for tenderness, swelling, and other physical symptoms in the affected area.
Imaging Tests
Common diagnostic imaging procedures include:
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
- HIDA scan (for gallbladder function)
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests can help identify:
- Liver function abnormalities
- Inflammation markers
- Infection indicators
- Pancreatic enzyme levels
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include:
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics for infections
- Pain management medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Acid reducers for digestive issues
Surgical Interventions
Some conditions may require surgical treatment, such as:
- Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy)
- Liver abscess drainage
- Hernia repair
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes can often help manage symptoms:
- Dietary adjustments
- Weight management
- Stress reduction
- Regular exercise
Warning Signs and Emergency Care
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe, unbearable pain
- High fever
- Yellowing of skin or eyes
- Severe nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty breathing
- Dark-colored urine or pale stools
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of upper right abdominal pain under the ribs? Common causes include gallbladder problems, liver conditions, digestive issues like acid reflux or ulcers, and muscle strain. Some cases may be related to inflammation, infection, or underlying medical conditions affecting organs in this area.
How is upper right abdominal pain diagnosed by doctors? Doctors typically use a combination of physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI), and laboratory tests to diagnose the cause of upper right abdominal pain.
What treatments are available for pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen? Treatment options include medications for pain and inflammation, antibiotics for infections, surgical procedures when necessary, and lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and stress management techniques.
When should I seek emergency care for right upper abdominal pain? Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe, persistent pain, high fever, yellowing of skin or eyes, severe nausea and vomiting, difficulty breathing, or significant changes in urine or stool color.
Can dietary changes help relieve upper right abdominal pain caused by gallbladder or digestive issues? Yes, dietary modifications can often help manage symptoms. This may include reducing fatty foods, eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a balanced, healthy diet. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary recommendations.