Understanding urine glucose levels is crucial for monitoring diabetes and overall health. Whether you're managing diabetes, experiencing symptoms that concern you, or undergoing routine screening, knowing how to interpret urine glucose test results can provide valuable insights into your body's glucose metabolism.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand urine glucose testing, interpret test results using standard measurement charts, and know when to seek medical attention based on your findings.
What is a Urine Glucose Test?
A urine glucose test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in your urine. Under normal circumstances, very little or no glucose appears in urine because your kidneys typically reabsorb all glucose back into your bloodstream. When blood glucose levels become too high, however, the excess begins to spill into your urine.
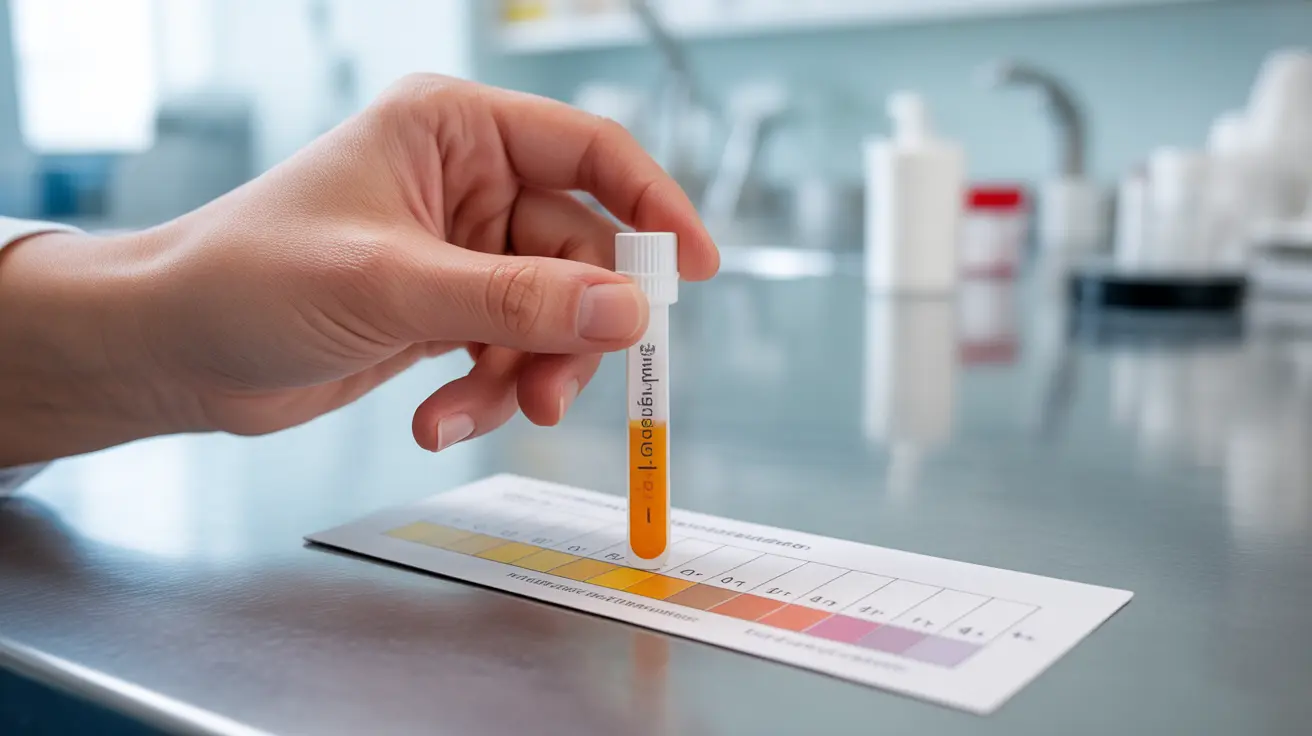
Understanding the Urine Glucose Levels Chart
Urine glucose levels are typically measured using dipstick tests and are reported on a scale from negative to 4+. Here's what different readings typically indicate:
- Negative (Normal): No glucose detected
- Trace: 100 mg/dL
- 1+: 250 mg/dL
- 2+: 500 mg/dL
- 3+: 1000 mg/dL
- 4+: Over 2000 mg/dL
Any reading above "negative" may warrant further investigation, especially if you're not already diagnosed with diabetes.
Testing Methods and Accuracy
Urine glucose testing can be performed using different methods, including:
- Dipstick tests (most common)
- Laboratory analysis
- Home testing kits
While convenient, urine glucose tests are considered less accurate than blood glucose tests for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. They primarily serve as screening tools or supplementary monitoring methods.
Factors Affecting Test Results
Medical Conditions
Several conditions can influence urine glucose levels:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Gestational diabetes
- Kidney disorders
- Hormonal imbalances
External Factors
Test results may be affected by:
- Certain medications
- Pregnancy
- Recent food intake
- Dehydration
- Time of day
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Consistently positive urine glucose readings
- Unexpected changes in glucose levels
- Symptoms like frequent urination, excessive thirst, or unexplained fatigue
- Pregnancy with positive glucose readings
Frequently Asked Questions
What do different urine glucose levels mean on a urine glucose levels chart?
Different levels on a urine glucose chart indicate varying amounts of glucose spillover into urine. Negative is normal, while readings from trace to 4+ (100-2000+ mg/dL) suggest increasingly elevated blood glucose levels that require medical attention.
How accurate is a urine glucose test compared to a blood glucose test for detecting diabetes?
Urine glucose tests are less accurate than blood glucose tests because they only detect glucose after it exceeds the kidney's reabsorption threshold. Blood glucose tests provide real-time, precise measurements and remain the gold standard for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring.
Can medications or pregnancy affect urine glucose test results?
Yes, certain medications, pregnancy hormones, and other factors can affect urine glucose test results. Vitamin C supplements, antibiotics, and pregnancy-related changes in kidney function can all influence test accuracy.
What should I do if my urine glucose test shows high levels of glucose?
If your urine glucose test shows high levels, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider for blood glucose testing and further evaluation. Don't make any changes to your medication regimen without professional medical advice.
How often should people at risk of diabetes get their urine glucose levels checked?
People at risk for diabetes should follow their healthcare provider's recommended screening schedule. Typically, this means annual check-ups, though some may need more frequent monitoring based on individual risk factors and symptoms.