Heart valve defects can significantly impact your cardiovascular health and quality of life. These conditions affect the crucial valves that control blood flow through your heart's chambers, potentially leading to various complications if left untreated. Understanding the signs, causes, and available treatments is essential for managing these conditions effectively.
Whether you're recently diagnosed or concerned about potential symptoms, this comprehensive guide will help you understand heart valve defects and the various options available for treatment and management.
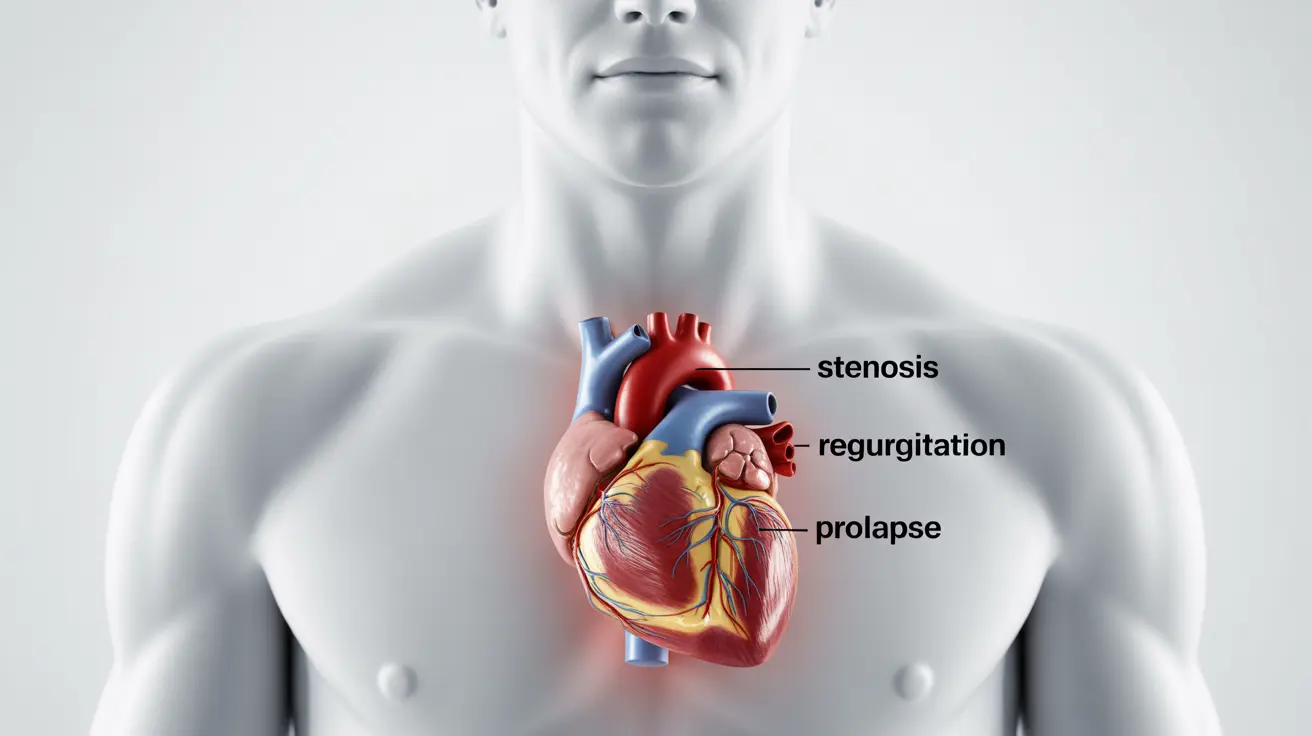
Types of Heart Valve Defects
Heart valve defects typically fall into several main categories, each affecting heart function in different ways:
Valve Stenosis
This condition occurs when heart valves become stiff or narrow, restricting blood flow through the heart. The heart must work harder to pump blood through the narrowed opening, potentially leading to strain and complications.
Valve Regurgitation
Also known as valve insufficiency, this occurs when valves don't close properly, allowing blood to leak backward. This inefficient blood flow can lead to the heart working harder to maintain proper circulation.
Valve Prolapse
This condition happens when valve flaps don't close correctly, sometimes bulging backward. Mitral valve prolapse is the most common form of this defect.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Heart valve defects can present various symptoms, though some people may initially experience none. Key indicators include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Unusual fatigue or weakness
- Chest pain or pressure
- Irregular heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Swelling in ankles, feet, or abdomen
- Dizziness or fainting spells
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose heart valve defects:
- Physical examination and medical history review
- Echocardiogram (heart ultrasound)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Chest X-ray
- Cardiac MRI or CT scan
- Stress tests when needed
Treatment Approaches
Medical Management
Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the valve defect. Common approaches include:
- Blood thinners to prevent clots
- Beta-blockers to control heart rate
- Diuretics to reduce fluid buildup
- ACE inhibitors to help manage blood pressure
Surgical Options
When necessary, surgical interventions may include:
- Valve repair procedures
- Valve replacement surgery
- Minimally invasive catheter-based procedures
- Traditional open-heart surgery
Lifestyle Management
Several lifestyle modifications can help manage valve defects and support overall heart health:
- Regular moderate exercise as approved by your healthcare provider
- Heart-healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats
- Stress management techniques
- Regular medical check-ups
- Smoking cessation if applicable
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms of valve defects and how can I recognize them early?
Early symptoms include shortness of breath during activity, unusual fatigue, chest discomfort, and irregular heartbeat. Some people might also experience swelling in their legs or ankles. It's important to note that symptoms can develop gradually, so regular check-ups are essential for early detection.
- What causes different types of heart valve defects like stenosis, regurgitation, and prolapse?
Heart valve defects can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. Common causes include aging, infections like rheumatic fever, heart attacks, high blood pressure, and certain medical conditions affecting heart tissue. Some people may also develop valve problems due to genetic factors.
- How are valve defects diagnosed and what tests should I expect during evaluation?
Diagnosis typically begins with a physical exam and listening to heart sounds. Your doctor will likely order an echocardiogram, which uses ultrasound to visualize heart valve function. Additional tests may include ECG, chest X-ray, and sometimes cardiac catheterization for detailed evaluation.
- What treatment options are available for heart valve defects, including medications and surgical procedures?
Treatment options range from medication management to surgical intervention. Medications might include blood thinners, beta-blockers, or drugs to control blood pressure. Surgical options include valve repair or replacement, either through traditional surgery or minimally invasive procedures, depending on the specific condition.
- Can lifestyle changes help prevent worsening of valve defects or improve heart valve health?
Yes, lifestyle modifications can help manage valve defects. Regular exercise within prescribed limits, maintaining a heart-healthy diet, managing blood pressure, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to better outcomes. Regular medical monitoring and following your treatment plan are also crucial for preventing deterioration.