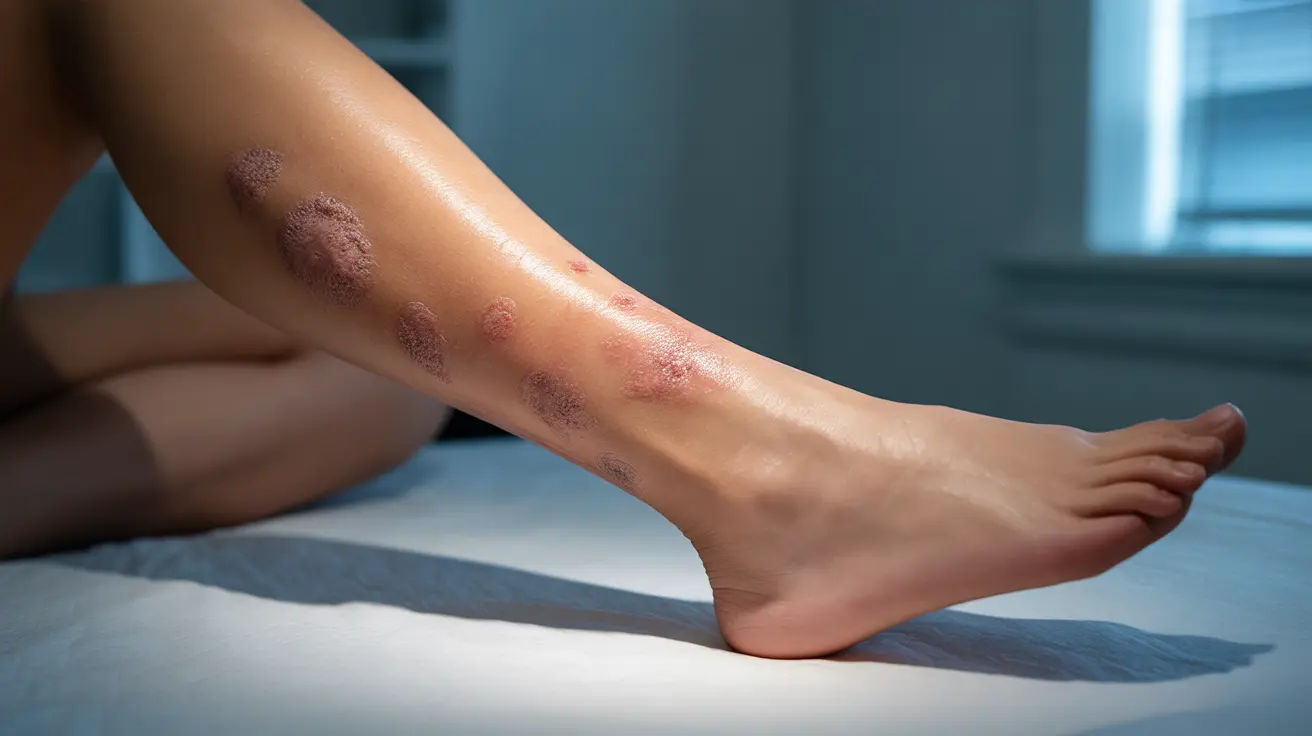
Varicose eczema is a chronic skin condition that commonly affects the lower legs, causing inflammation, itching, and changes in skin texture. This condition, also known as stasis dermatitis, typically develops in people who have underlying circulation problems or varicose veins. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
While varicose eczema can be concerning, the good news is that various treatment options and self-care measures can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about managing this condition effectively.
Signs and Symptoms of Varicose Eczema
Varicose eczema typically presents with several distinctive characteristics that affect the skin of the lower legs:
- Red, swollen, and scaly skin
- Intense itching and discomfort
- Dark brown discoloration of the skin
- Hardened, thickened skin patches
- Small white scars (atrophie blanche)
- Heavy, aching legs
- Ankle swelling that worsens throughout the day
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of varicose eczema is poor circulation in the lower legs, specifically related to problems with the veins. When veins don't function properly, fluid can build up in the legs, leading to increased pressure and inflammation of the skin.
Common Risk Factors Include:
- Age (more common in people over 50)
- Previous blood clots in the legs
- Varicose veins
- Obesity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Heart conditions
- High blood pressure
- Limited mobility
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically diagnose varicose eczema through a combination of physical examination and medical history review. During the examination, they will look for characteristic signs of the condition and assess overall circulation in the legs.
Diagnostic Tests May Include:
- Doppler ultrasound to check blood flow
- Patch testing to rule out other types of eczema
- Blood tests to check for underlying conditions
- Skin biopsy in certain cases
Treatment Approaches and Management
Treatment for varicose eczema focuses on improving circulation and managing skin symptoms. A comprehensive treatment plan often includes:
Medical Treatments:
- Topical corticosteroids for inflammation
- Emollients and moisturizers
- Compression therapy
- Antibiotics if infection is present
Self-Care Measures:
- Regular exercise to improve circulation
- Elevating legs when resting
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding scratching affected areas
- Wearing compression stockings as recommended
Preventing Complications
Without proper management, varicose eczema can lead to serious complications, including venous leg ulcers. Prevention strategies include:
- Consistent use of prescribed treatments
- Regular skin care routine
- Prompt treatment of any skin breaks
- Regular exercise and weight management
- Wearing appropriate compression garments
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of varicose eczema on the legs? The most common symptoms include red, itchy, and scaly skin on the legs, often accompanied by swelling, particularly around the ankles. The affected skin may become dark brown and feel hard or thickened over time.
What causes varicose eczema and which factors increase the risk of developing it? Varicose eczema is primarily caused by poor circulation in the legs, often related to varicose veins or blood flow issues. Risk factors include age over 50, obesity, previous blood clots, and conditions affecting circulation.
How is varicose eczema diagnosed by doctors and what tests might be needed? Doctors typically diagnose varicose eczema through physical examination and medical history review. They may perform additional tests like Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow and patch testing to rule out other conditions.
What are the most effective treatments and self-care measures for managing varicose eczema? Effective treatments include topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, compression therapy, and regular exercise. Self-care measures involve elevating legs, maintaining healthy weight, and consistent use of prescribed treatments.
Can varicose eczema lead to complications like leg ulcers, and how can these be prevented? Yes, varicose eczema can lead to leg ulcers if left untreated. Prevention involves consistent use of compression stockings, proper skin care, regular exercise, and prompt treatment of any skin breaks or infections.