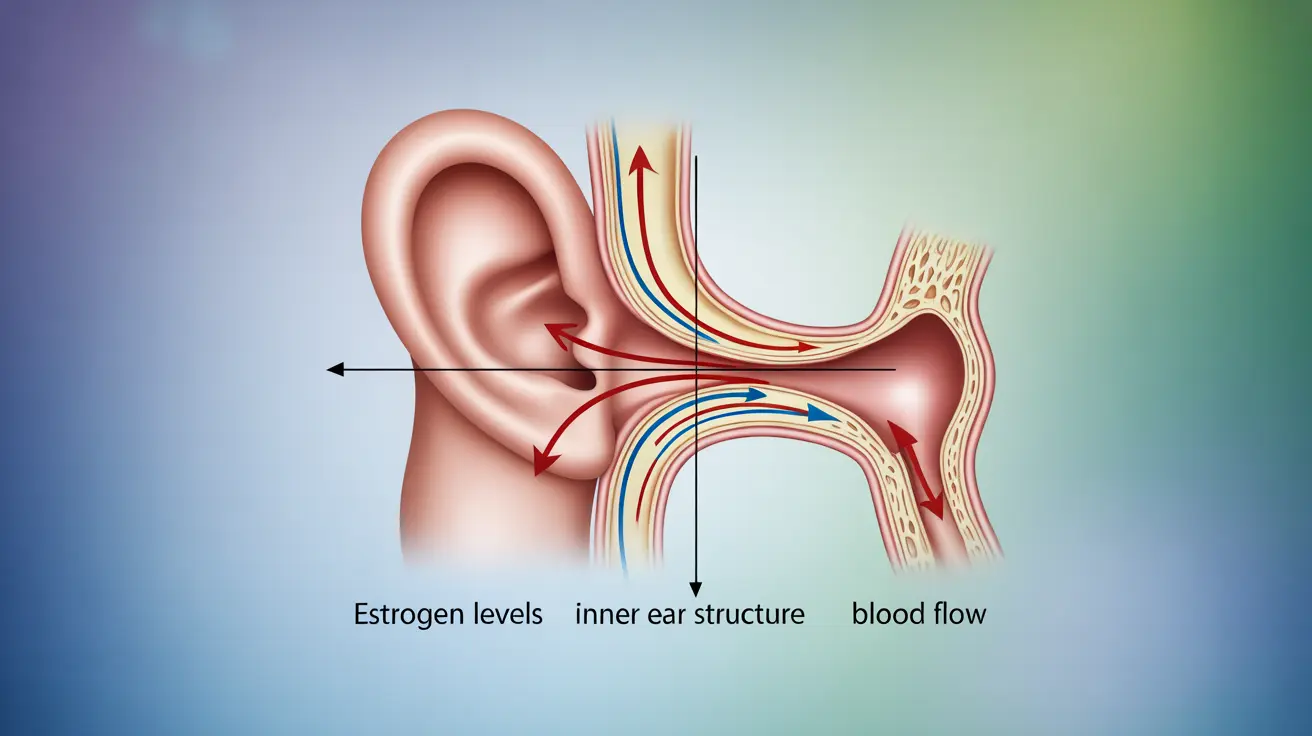
The connection between vertigo and menopause is a significant concern for many women experiencing this natural life transition. During menopause, hormonal fluctuations can affect various body systems, including those responsible for balance and spatial orientation. Understanding this relationship is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and maintaining quality of life during menopause.
This comprehensive guide explores the connection between menopause and vertigo, examining why these symptoms occur and what can be done to address them effectively.
The Hormonal Link Between Menopause and Vertigo
During menopause, estrogen levels fluctuate and eventually decline, which can impact multiple body systems. Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining inner ear health and blood flow, both of which are essential for balance and spatial orientation. When these hormonal changes occur, women may experience various forms of dizziness, including vertigo.
The vestibular system, responsible for balance and spatial orientation, can be particularly sensitive to hormonal fluctuations. This sensitivity may explain why many women experience new or worsening vertigo symptoms during menopause.
Common Types of Vertigo During Menopause
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
BPPV is characterized by brief episodes of spinning sensation triggered by specific head movements. Research suggests that menopausal women may be more susceptible to developing BPPV due to hormonal changes affecting calcium metabolism in the inner ear.
Hormonal Vertigo
This type of vertigo is directly related to fluctuating hormone levels during menopause. Symptoms may include:
- Spinning sensations
- Light-headedness
- Feeling off-balance
- Nausea
- Difficulty focusing
Treatment Options for Menopausal Vertigo
Medical Interventions
Several treatment approaches can help manage vertigo during menopause:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Vestibular rehabilitation exercises
- Anti-vertigo medications
- Balance therapy
- Canalith repositioning procedures for BPPV
Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve vertigo symptoms:
- Regular exercise focusing on balance
- Stress reduction techniques
- Adequate hydration
- Proper sleep hygiene
- Dietary modifications to reduce triggers
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps can help minimize vertigo episodes during menopause:
- Maintaining regular physical activity
- Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques
- Following a consistent sleep schedule
- Avoiding known triggers
- Regular medical check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes dizziness and vertigo during menopause?
Dizziness and vertigo during menopause are primarily caused by hormonal fluctuations, particularly changes in estrogen levels. These hormonal changes can affect the inner ear's function and blood flow, leading to balance problems and vertigo symptoms.
How are hormonal changes in menopause linked to balance problems and vertigo?
Estrogen affects the inner ear's fluid balance and blood flow. When levels fluctuate during menopause, it can disrupt the vestibular system's normal function, leading to balance issues and vertigo. Additionally, estrogen influences neurotransmitter function, which can affect balance and spatial orientation.
Can menopause increase the risk of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)?
Yes, menopause can increase the risk of BPPV. The hormonal changes during menopause can affect calcium metabolism and inner ear crystal formation, potentially leading to a higher incidence of BPPV in menopausal women.
What treatment options are available for managing vertigo related to menopause?
Treatment options include hormone replacement therapy, vestibular rehabilitation exercises, anti-vertigo medications, and specific treatments for BPPV such as the Epley maneuver. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
How can lifestyle changes help reduce dizziness symptoms during menopause?
Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress management, proper hydration, and maintaining good sleep habits can significantly help reduce dizziness symptoms. Additionally, identifying and avoiding personal triggers can help prevent vertigo episodes.