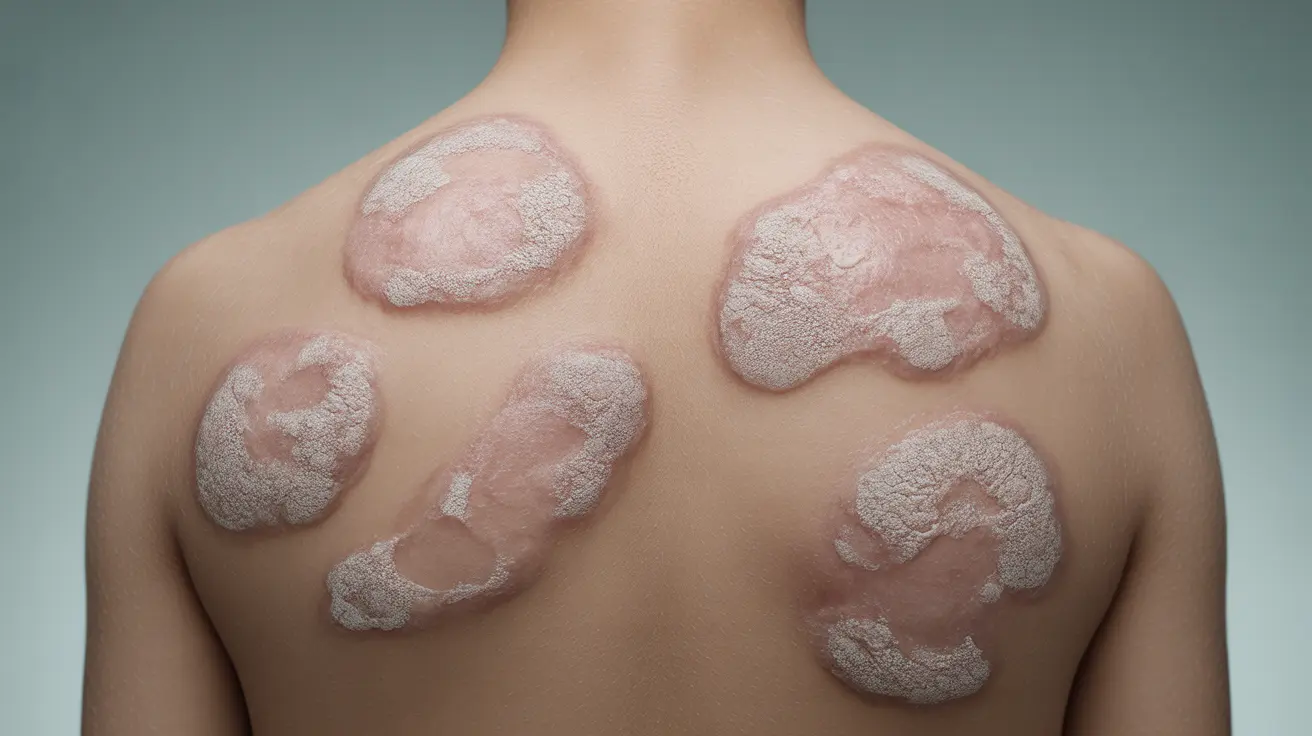
Psoriasis vulgaris, also known as plaque psoriasis, is the most common form of psoriasis affecting millions of people worldwide. This chronic autoimmune condition causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, scaly patches that can appear anywhere on the body. Understanding this condition is crucial for both diagnosis and effective management of symptoms.
While psoriasis vulgaris is a long-term condition, various treatment options and lifestyle modifications can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of psoriasis vulgaris, from its distinctive symptoms to the latest treatment approaches.
Recognizing Psoriasis Vulgaris Symptoms
The hallmark signs of psoriasis vulgaris include:
- Raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Thick, pitted nails
- Patches varying in size from small spots to large areas
These plaques commonly appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, though they can develop anywhere on the body. The severity can range from mild cases with a few small patches to severe cases covering large areas of the body.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers
Psoriasis vulgaris develops when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, accelerating the skin cell production process. While the exact cause isn't fully understood, several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetic predisposition
- Immune system dysfunction
- Environmental factors
- Stress
- Certain medications
Common triggers that can worsen psoriasis vulgaris include:
- Stress and anxiety
- Skin injuries or infections
- Cold, dry weather
- Certain medications
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
Treatment Approaches for Psoriasis Vulgaris
Treatment options typically follow a stepped approach, beginning with the least aggressive methods and progressing as needed:
Topical Treatments
First-line treatments often include:
- Corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogues
- Retinoids
- Coal tar preparations
Phototherapy
Light therapy can be effective when topical treatments aren't sufficient, using controlled exposure to natural or artificial UV light.
Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe cases, doctors may prescribe:
- Oral medications
- Biologics
- Immunosuppressants
Lifestyle Management Strategies
Several lifestyle modifications can help control psoriasis vulgaris:
- Maintaining good skin hygiene
- Using moisturizers regularly
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Following a balanced diet
- Avoiding known triggers
- Getting regular exercise
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Associated Health Risks
People with psoriasis vulgaris may have an increased risk of developing:
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Depression and anxiety
- Metabolic syndrome
- Type 2 diabetes
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms and physical signs of psoriasis vulgaris (plaque psoriasis)?
The main signs include raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales, dry and cracked skin, itching or burning sensations, and thick, pitted nails. These patches typically appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- What are the main treatment options available to manage psoriasis vulgaris?
Treatment options include topical medications (corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues), phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologics. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and individual response to therapy.
- What causes psoriasis vulgaris and what are common triggers that can worsen it?
Psoriasis vulgaris is caused by an overactive immune system and genetic factors. Common triggers include stress, skin injuries, infections, certain medications, cold weather, alcohol consumption, and smoking.
- How can lifestyle changes help control psoriasis vulgaris flare-ups?
Key lifestyle modifications include maintaining good skin hygiene, regular moisturizing, stress management, healthy diet, exercise, avoiding triggers, and limiting alcohol consumption. These changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
- What are the risks of developing psoriatic arthritis or other health conditions with psoriasis vulgaris?
People with psoriasis vulgaris have an increased risk of developing psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Regular medical monitoring is important for early detection and management of these associated conditions.