Pregnancy brings many changes to a woman's body, and for some expectant mothers, managing atrial fibrillation (AF) becomes an important health consideration. AF is a heart rhythm disorder that requires careful attention during pregnancy to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
This comprehensive guide explores how AF affects pregnancy, what symptoms to watch for, and the best management strategies for this condition during the crucial nine months of gestation.
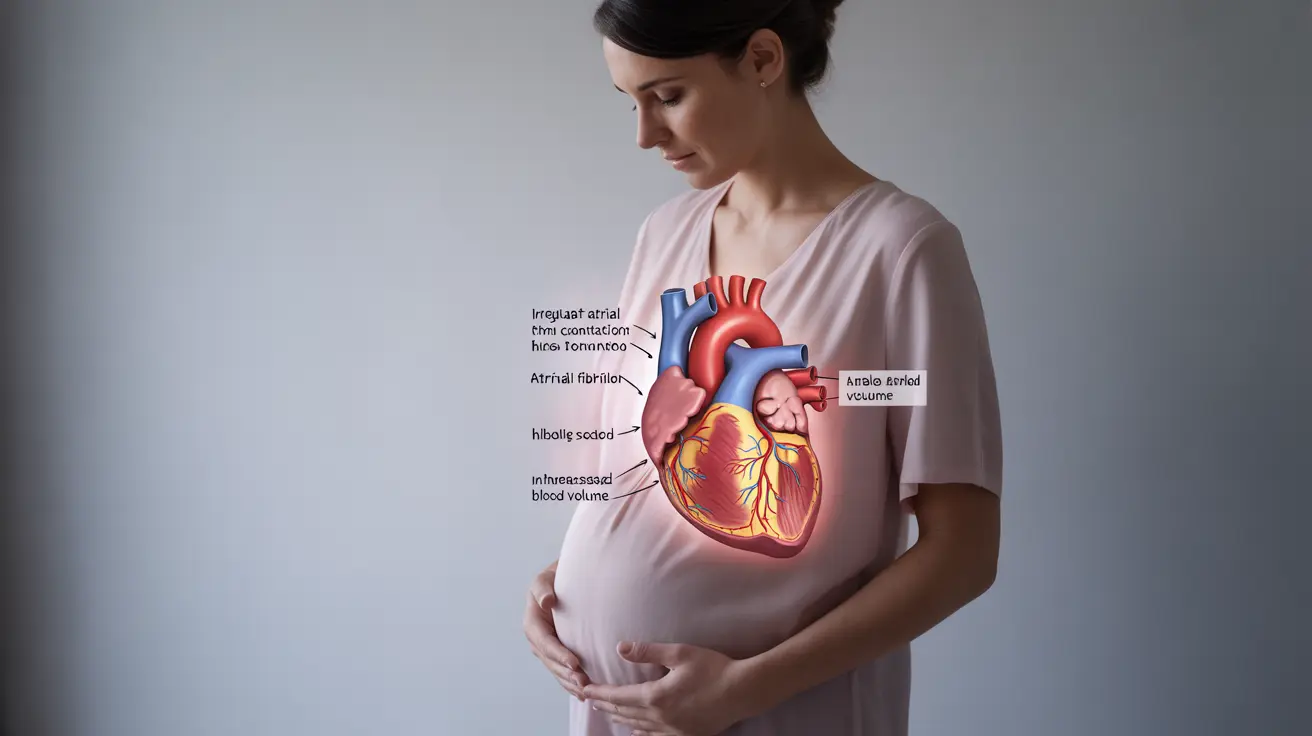
What is Atrial Fibrillation in Pregnancy?
Atrial fibrillation during pregnancy is a cardiac condition where the heart's upper chambers beat irregularly and often rapidly, disrupting normal blood flow. The cardiovascular changes that naturally occur during pregnancy, such as increased blood volume and heart rate, can sometimes trigger or worsen AF episodes.
During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant cardiovascular adaptations, including:
- Increased blood volume by 30-50%
- Higher cardiac output
- Elevated heart rate
- Changes in blood pressure
Recognizing AF Symptoms During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with AF may experience various symptoms that require immediate medical attention. These symptoms can sometimes be confused with normal pregnancy-related changes, making it crucial to know what to watch for:
Common AF Symptoms in Pregnancy
Key indicators include:
- Irregular heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath beyond normal pregnancy-related breathlessness
- Unusual fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain or discomfort
Managing AF Safely During Pregnancy
Treatment for AF during pregnancy requires a delicate balance between controlling the mother's symptoms and protecting the developing fetus. Healthcare providers typically develop individualized treatment plans based on several factors:
Monitoring and Medical Care
Regular monitoring is essential and may include:
- Frequent cardiac check-ups
- Regular fetal monitoring
- Blood pressure management
- Heart rate control
- Anticoagulation therapy when necessary
Lifestyle Modifications
Safe management strategies often include:
- Moderate activity as advised by healthcare providers
- Adequate rest and stress management
- Proper hydration
- Avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol
- Maintaining a heart-healthy diet
Medication Safety During Pregnancy
Not all AF medications are safe during pregnancy. Healthcare providers carefully select treatments that offer the best balance of effectiveness and safety for both mother and baby.
Generally Considered Safer Options
Some medications that may be used include:
- Selected beta-blockers
- Specific anticoagulants under careful monitoring
- Certain rate control medications
Medications to Avoid
Some AF medications that are typically avoided during pregnancy include:
- Certain antiarrhythmic drugs
- Some newer anticoagulants
- ACE inhibitors
Frequently Asked Questions
What is atrial fibrillation (AF) and how does it affect pregnancy?
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm condition affecting the heart's upper chambers. During pregnancy, it can impact both mother and baby by potentially affecting blood flow and oxygen delivery. The condition requires careful monitoring and management throughout pregnancy.
What symptoms should pregnant women watch for if they have AFib?
Pregnant women should watch for irregular heartbeat, unusual shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, dizziness, and chest discomfort. Any new or worsening symptoms should be reported to healthcare providers immediately.
How is atrial fibrillation managed safely during pregnancy without harming the fetus?
AF during pregnancy is managed through a combination of careful monitoring, safe medications, and lifestyle modifications. Treatment plans are individualized and may include specific heart rate control medications, anticoagulation when necessary, and regular cardiac and fetal monitoring.
Which medications for AF are considered safer or unsafe during pregnancy?
Certain beta-blockers and specific anticoagulants are generally considered safer during pregnancy. However, some medications like certain antiarrhythmic drugs and newer anticoagulants are typically avoided. All medication decisions should be made in consultation with healthcare providers.
Can atrial fibrillation during pregnancy increase risks for the baby or cause pregnancy complications?
Yes, AF during pregnancy can potentially increase risks for both mother and baby, including the risk of blood clots, reduced fetal growth, and pregnancy complications. However, with proper medical management and monitoring, many women with AF have successful pregnancies and healthy babies.