Schwannoma tumors, while relatively rare, can be a source of concern for many individuals. These growths, which develop from the cells that form the protective covering of nerves, have intrigued medical professionals and patients alike. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the causes of schwannoma tumors, who may be at risk, and what you need to know about their development and impact on health.
Understanding schwannomas is crucial for early detection and proper management. Whether you're experiencing symptoms or simply seeking information, this article will provide valuable insights into these unique tumors and their implications for your health.
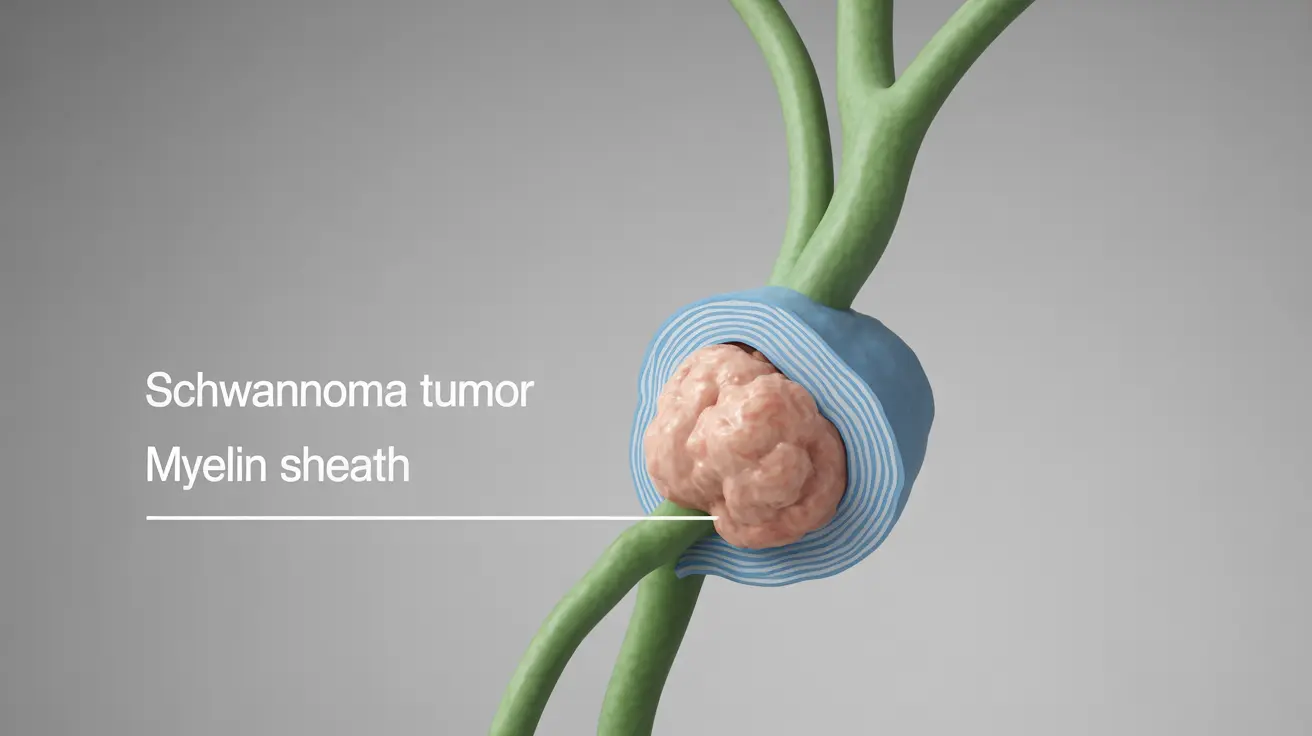
What is a Schwannoma Tumor?
A schwannoma is a type of tumor that originates in the Schwann cells, which are responsible for forming the myelin sheath around peripheral nerves. These tumors are typically benign (non-cancerous) and slow-growing, but they can cause various symptoms depending on their location and size.
Schwannomas can develop anywhere in the body where nerves are present, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Common locations include the vestibular nerve (acoustic neuroma), spinal nerves, and nerves in the arms and legs.
What Causes a Schwannoma Tumor?
The exact cause of schwannoma tumors is not fully understood, but several factors have been identified as potential contributors to their development:
Genetic Factors
Some schwannomas are associated with genetic conditions, particularly:
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2): A hereditary disorder characterized by the growth of noncancerous tumors in the nervous system.
- Schwannomatosis: A rare condition that causes multiple schwannomas throughout the body.
In these cases, mutations in specific genes, such as the NF2 gene, can increase the likelihood of developing schwannomas.
Environmental Factors
While less clearly defined, some environmental factors may play a role in schwannoma development:
- Radiation exposure: High doses of radiation, particularly to the head and neck area, may increase the risk of certain types of schwannomas.
- Occupational exposures: Some studies suggest a potential link between certain occupational exposures and an increased risk of schwannomas, though more research is needed to confirm these associations.
Spontaneous Development
In many cases, schwannomas appear to develop spontaneously without a clear underlying cause. This spontaneous occurrence is more common in sporadic (non-inherited) cases of schwannoma.
Who is Most at Risk for Developing Schwannomas?
While schwannomas can affect anyone, certain factors may increase an individual's risk:
- Age: Schwannomas are most commonly diagnosed in adults between 20 and 50 years old.
- Genetic predisposition: Individuals with NF2 or schwannomatosis have a significantly higher risk.
- Family history: Those with a family history of schwannomas or related conditions may have an increased risk.
- Previous radiation exposure: Individuals who have undergone radiation therapy, especially to the head or neck, may be at higher risk for certain types of schwannomas.
Symptoms and Development of Schwannomas
The symptoms of a schwannoma can vary greatly depending on its location and size. Some common signs include:
- Numbness or tingling in the affected area
- Weakness in the muscles controlled by the affected nerve
- Pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (in the case of vestibular schwannomas)
- Balance problems
- Facial numbness or weakness (for facial nerve schwannomas)
Schwannomas typically grow slowly over time. In some cases, they may remain small and asymptomatic for years. However, as they enlarge, they can put pressure on surrounding nerves and tissues, leading to more noticeable symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a schwannoma tumor and who is most at risk?
Schwannoma tumors are primarily caused by genetic factors, particularly mutations in genes like NF2. Environmental factors such as radiation exposure may also play a role. Those most at risk include adults aged 20-50, individuals with genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis type 2 or schwannomatosis, and those with a family history of these tumors. People who have undergone radiation therapy, especially to the head or neck, may also have an increased risk.
What are the typical symptoms of a schwannoma and how do they develop over time?
Typical symptoms of schwannomas include numbness, tingling, weakness in affected areas, pain, and sometimes hearing loss or balance problems for vestibular schwannomas. These symptoms usually develop gradually as the tumor grows slowly over time. Initially, schwannomas may be asymptomatic, but as they enlarge and press on surrounding nerves and tissues, symptoms become more noticeable and may progress in severity.
Is a schwannoma always cancerous and can it turn into cancer?
Schwannomas are typically benign (non-cancerous) tumors. In very rare cases, they can become malignant, but this is extremely uncommon. The vast majority of schwannomas remain benign throughout their existence. However, even benign schwannomas can cause significant problems depending on their location and size, which is why proper monitoring and treatment are important.
How is a schwannoma diagnosed and what tests are needed for confirmation?
Diagnosing a schwannoma usually involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is the primary diagnostic tool, providing detailed images of the tumor and surrounding tissues. CT scans may also be used. In some cases, a biopsy might be necessary for definitive diagnosis, especially to rule out other types of tumors. Genetic testing may be recommended if a hereditary condition is suspected.
What are the treatment options for a schwannoma and is surgery always necessary?
Treatment options for schwannomas depend on the tumor's size, location, and symptoms. They include:
- Observation: For small, asymptomatic tumors, regular monitoring may be recommended.
- Surgery: Often the primary treatment, especially for larger or symptomatic tumors.
- Radiation therapy: May be used for tumors in difficult-to-reach locations or for patients who can't undergo surgery.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: A precise form of radiation therapy, useful for certain types of schwannomas.
Surgery is not always necessary, particularly for small, slow-growing tumors that don't cause symptoms. The decision for treatment is made on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient's overall health, tumor characteristics, and potential risks and benefits of intervention.
Understanding the causes, risks, and management of schwannoma tumors is crucial for anyone affected by this condition. While these tumors can be concerning, advances in medical science continue to improve diagnosis and treatment options, offering hope and better outcomes for patients.