Blood poisoning, medically known as sepsis, is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding what blood poisoning looks like and recognizing its early warning signs can make the difference between life and death. This comprehensive guide will help you identify the signs of blood poisoning and know when to seek emergency care.
Understanding Blood Poisoning and Its Appearance
Blood poisoning occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream and trigger a dangerous inflammatory response throughout the body. While it often starts from a seemingly minor infection, it can quickly escalate into a medical emergency if left untreated.
Visual Signs of Blood Poisoning
Skin Changes and Visible Symptoms
The most noticeable external signs of blood poisoning include:
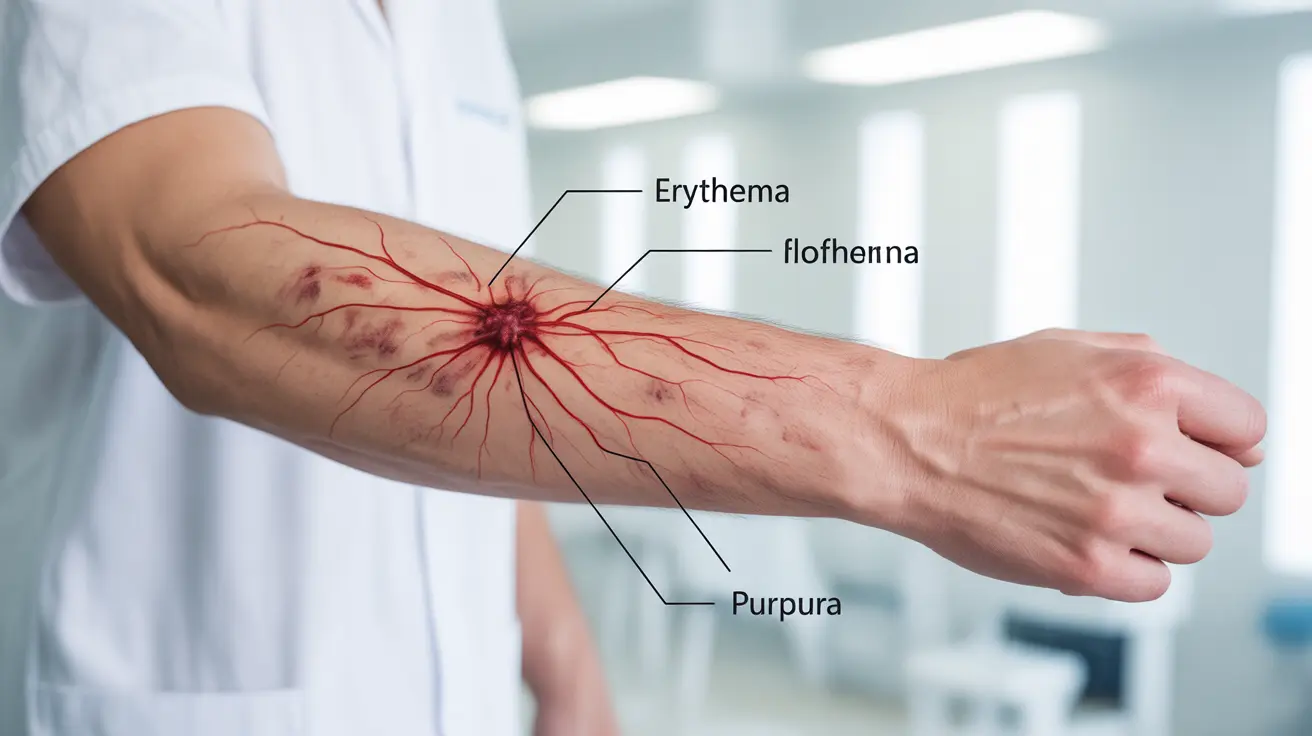
- Red streaks extending from the original infection site
- Skin discoloration, appearing mottled or blotchy
- Unusual paleness or grayish skin tone
- Widespread rash or tiny dark spots
- Significant swelling around wounds or infected areas
Other Physical Manifestations
Blood poisoning can present with several observable changes in the body:
- Excessive sweating
- Rapid breathing
- Visible shivering or trembling
- Extreme fatigue and weakness
- Decreased urination
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing early symptoms is crucial for prompt treatment. Key indicators include:
- Fever above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Rapid heart rate
- Confusion or disorientation
- Shortness of breath
- Extreme pain or discomfort
High-Risk Groups and Causes
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing blood poisoning:
- Elderly individuals
- People with weakened immune systems
- Those with chronic medical conditions
- Recent surgery patients
- Individuals with open wounds or infections
Emergency Care and Treatment
Blood poisoning requires immediate hospital treatment, which typically includes:
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Fluid replacement therapy
- Oxygen support when necessary
- Medication to maintain blood pressure
- Specialized care in severe cases
Prevention Strategies
Proper Wound Care
Preventing blood poisoning starts with proper wound care:
- Clean all cuts and scrapes thoroughly
- Use antiseptic solutions when appropriate
- Keep wounds covered with clean bandages
- Monitor for signs of infection
- Change dressings regularly
Preventive Healthcare
Additional preventive measures include:
- Staying up-to-date with vaccinations
- Managing chronic conditions effectively
- Practicing good hygiene
- Seeking prompt treatment for infections
- Regular health check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs and symptoms that blood poisoning (sepsis) looks like? Early signs include fever, rapid breathing and heart rate, confusion, and extreme fatigue. Skin may become mottled or show red streaks extending from an infection site.
How is blood poisoning diagnosed and treated in the hospital? Diagnosis involves blood tests, vital sign monitoring, and infection source identification. Treatment typically includes intravenous antibiotics, fluids, oxygen therapy, and close monitoring in a hospital setting.
What causes blood poisoning and who is at higher risk of getting it? Blood poisoning is caused by bacteria entering the bloodstream, usually from an infection. Higher-risk individuals include the elderly, those with weakened immune systems, chronic illness sufferers, and people with recent surgeries or wounds.
Can blood poisoning cause confusion or changes in skin color, and when should I seek emergency care? Yes, blood poisoning can cause mental confusion and skin color changes. Seek immediate emergency care if you notice these symptoms, especially when combined with fever, rapid breathing, or extreme fatigue.
How can I prevent blood poisoning through wound care and vaccinations? Prevent blood poisoning by practicing proper wound care, maintaining good hygiene, keeping vaccinations current, and seeking prompt medical attention for infections. Always clean and monitor wounds carefully.